Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Charts
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Charts
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Charts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Charts
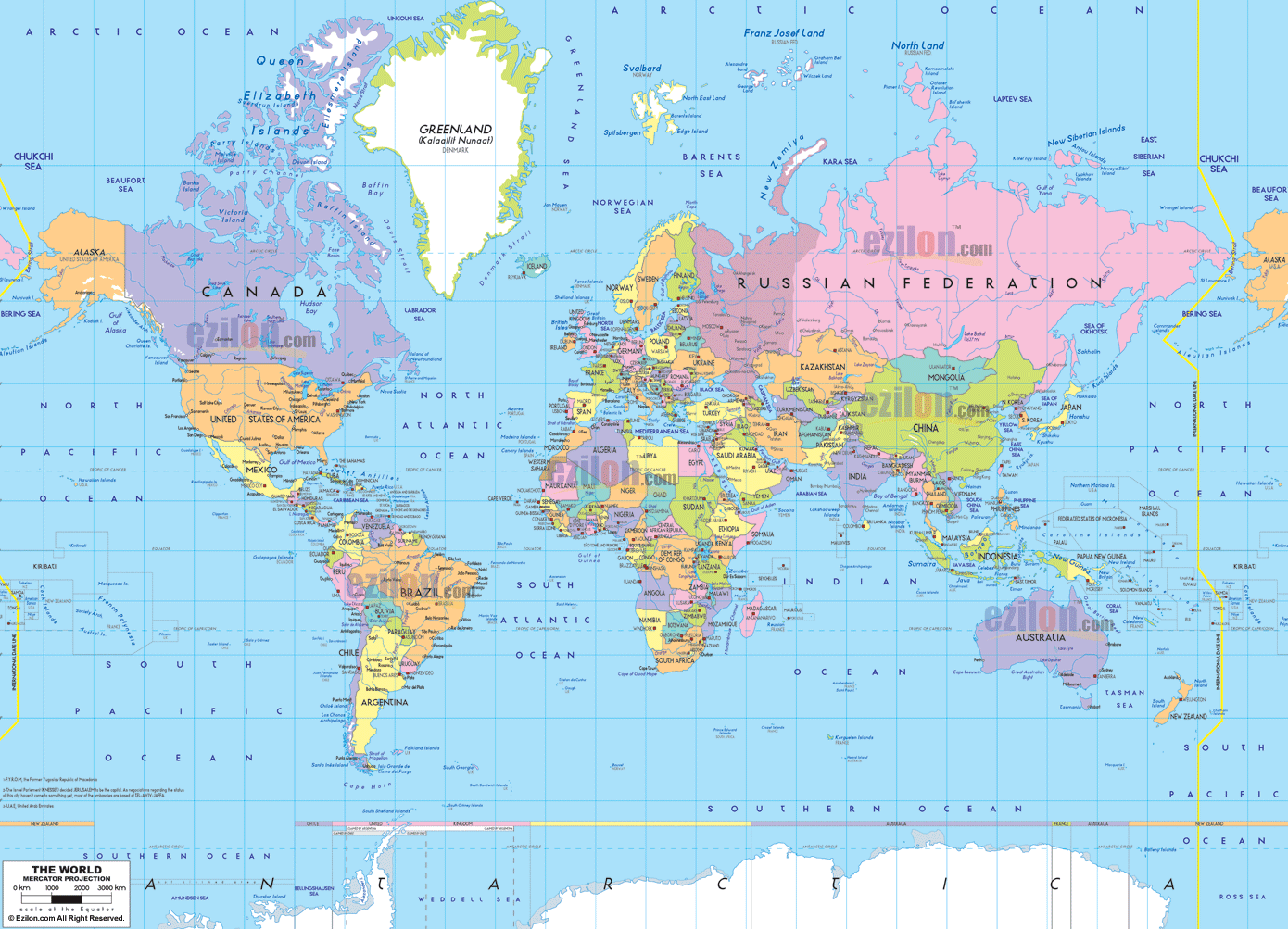
The world map, a timeless and indispensable tool, transcends its simple appearance as a mere depiction of Earth’s surface. It serves as a foundation for understanding global connections, visualizing complex data, and fostering critical thinking about our planet. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted nature of world map charts, exploring their construction, applications, and significance in various fields.
The Foundation: Constructing a World Map Chart
A world map chart is a visual representation of the Earth’s geography, employing a variety of projections to translate the three-dimensional sphere onto a two-dimensional surface. This process inevitably involves distortion, as a flat map cannot accurately represent all aspects of a curved surface. Different projections prioritize specific aspects, such as preserving area, shape, or distance, leading to diverse visual representations of the world.
Common Projections and Their Impact
- Mercator Projection: Popular for navigation, this projection preserves angles and shapes, making it useful for seafaring. However, it distorts areas, exaggerating the size of landmasses near the poles.
- Robinson Projection: This projection balances area and shape distortion, offering a visually appealing representation of the globe. It is widely used for general maps, but it does not preserve any specific property accurately.
- Gall-Peters Projection: This projection preserves area, accurately depicting the relative sizes of continents. However, it distorts shapes, making it less suitable for navigational purposes.
- Azimuthal Equidistant Projection: This projection preserves distances from a central point, making it useful for mapping specific locations. However, it distorts shapes and areas further away from the central point.
The choice of projection significantly impacts the visual representation of the world, influencing our perception of relative sizes, distances, and shapes. Recognizing the limitations of each projection is crucial for interpreting data and avoiding misinterpretations.
Beyond Geography: The Power of Data Visualization
World map charts transcend their role as mere geographical representations. They serve as powerful tools for visualizing and analyzing complex data, revealing patterns and trends across the globe. This application extends to diverse fields, including:
- Demographics: Population density, migration patterns, and demographic trends can be visualized on world map charts, highlighting global disparities and regional variations.
- Economics: Trade routes, economic activity, and resource distribution can be mapped, revealing global interconnectedness and economic power dynamics.
- Climate Change: Temperature anomalies, sea level rise, and deforestation can be visualized, highlighting the spatial impact of climate change and its consequences.
- Politics: Electoral maps, political alliances, and conflict zones can be visualized, providing insights into global political dynamics and regional tensions.
- Health: Disease outbreaks, vaccination coverage, and healthcare access can be mapped, aiding in disease surveillance and resource allocation.
By overlaying data on a world map, analysts gain a comprehensive understanding of global patterns and interrelationships, fostering informed decision-making and promoting awareness of global issues.
Benefits and Importance of World Map Charts
- Enhanced Understanding: World map charts provide a visual framework for understanding global connections, fostering a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our planet.
- Data Exploration and Analysis: Visualizing data on a world map allows for pattern recognition, trend identification, and the discovery of hidden relationships.
- Communication and Advocacy: World map charts serve as powerful tools for communication, effectively conveying complex data and raising awareness about global issues.
- Decision-Making Support: By providing a spatial context for data, world map charts inform decision-making in various fields, from resource allocation to policy development.
Frequently Asked Questions about World Map Charts
Q: What are the limitations of world map charts?
A: World map charts inherently involve distortion due to the projection process. This distortion can affect the accuracy of distances, areas, and shapes, depending on the chosen projection. It is crucial to consider the limitations of the projection used when interpreting data visualized on world map charts.
Q: How can I choose the right projection for my data?
A: The choice of projection depends on the specific data being visualized and the intended message. For example, if visualizing area-based data, such as population density, an equal-area projection is recommended. However, if focusing on shape and distance, a conformal projection might be more appropriate.
Q: What are some best practices for creating effective world map charts?
A: Effective world map charts prioritize clarity and visual impact. They utilize appropriate color schemes, consistent legends, and clear labeling. They also avoid clutter and excessive information overload, focusing on conveying the key message effectively.
Q: How can I use world map charts in my research or presentations?
A: World map charts can be used to visualize data, present findings, and communicate complex information effectively. They can be incorporated into research papers, presentations, and reports, adding a visual dimension to data analysis and enhancing audience understanding.
Tips for Utilizing World Map Charts
- Choose the Right Projection: Select a projection that aligns with the specific data being visualized and the intended message.
- Maintain Clarity and Simplicity: Avoid clutter and information overload, focusing on conveying the key message effectively.
- Utilize Color and Symbolism: Employ appropriate color schemes and symbols to highlight key features and trends.
- Provide Context and Explanations: Ensure that the map is accompanied by clear labels, legends, and explanatory text.
- Consider Audience Understanding: Tailor the complexity and detail of the map to the audience’s knowledge and understanding.
Conclusion
World map charts are invaluable tools for understanding our interconnected world, visualizing complex data, and fostering informed decision-making. By recognizing their capabilities and limitations, we can leverage their power to gain insights into global patterns, trends, and challenges. From exploring geographical features to analyzing data across diverse fields, world map charts serve as essential visual aids for navigating our increasingly complex and interconnected world.


![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Charts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!