Unveiling the Power Grid: An Exploration of Electricity Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power Grid: An Exploration of Electricity Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power Grid: An Exploration of Electricity Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power Grid: An Exploration of Electricity Maps
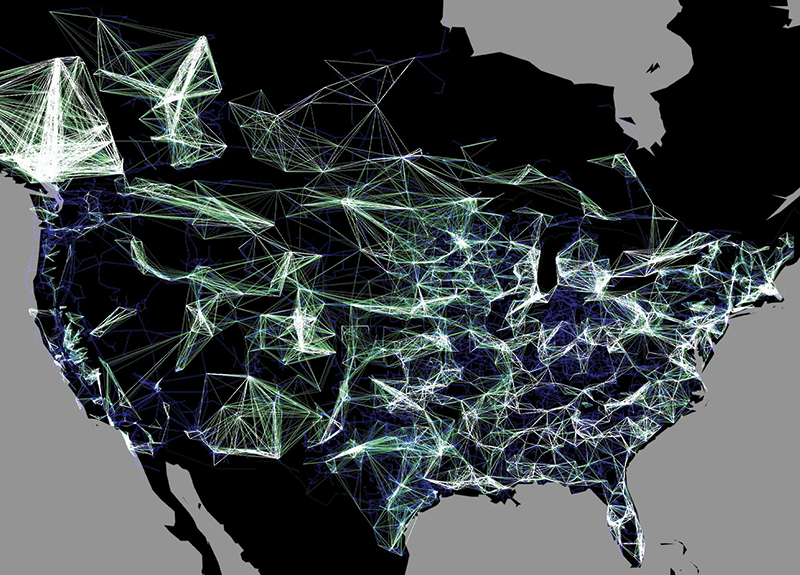
Electricity, the lifeblood of modern civilization, flows through an intricate network of power lines, transformers, and generators, spanning continents and connecting millions of consumers. Visualizing this complex system is crucial for understanding its operation, identifying potential vulnerabilities, and optimizing its performance. Enter the electricity map, a powerful tool that provides a clear and comprehensive representation of the global energy landscape.
A Visual Representation of the Power Grid:
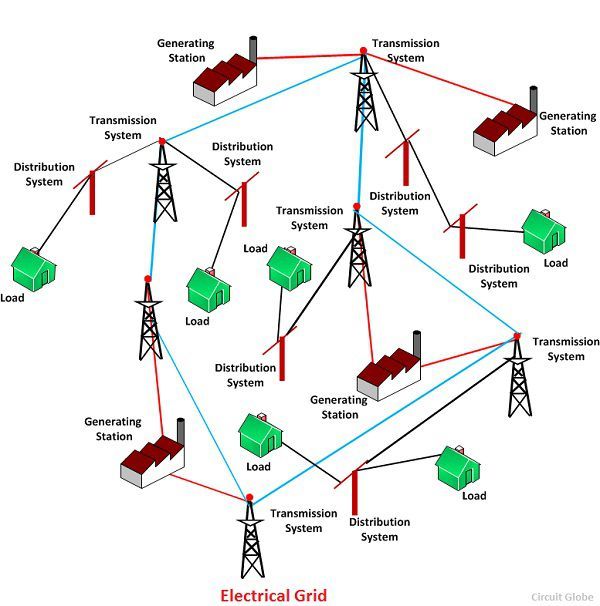
Electricity maps are graphical representations of the electrical grid, showcasing the interconnectedness of power generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure. They provide a visual overview of:
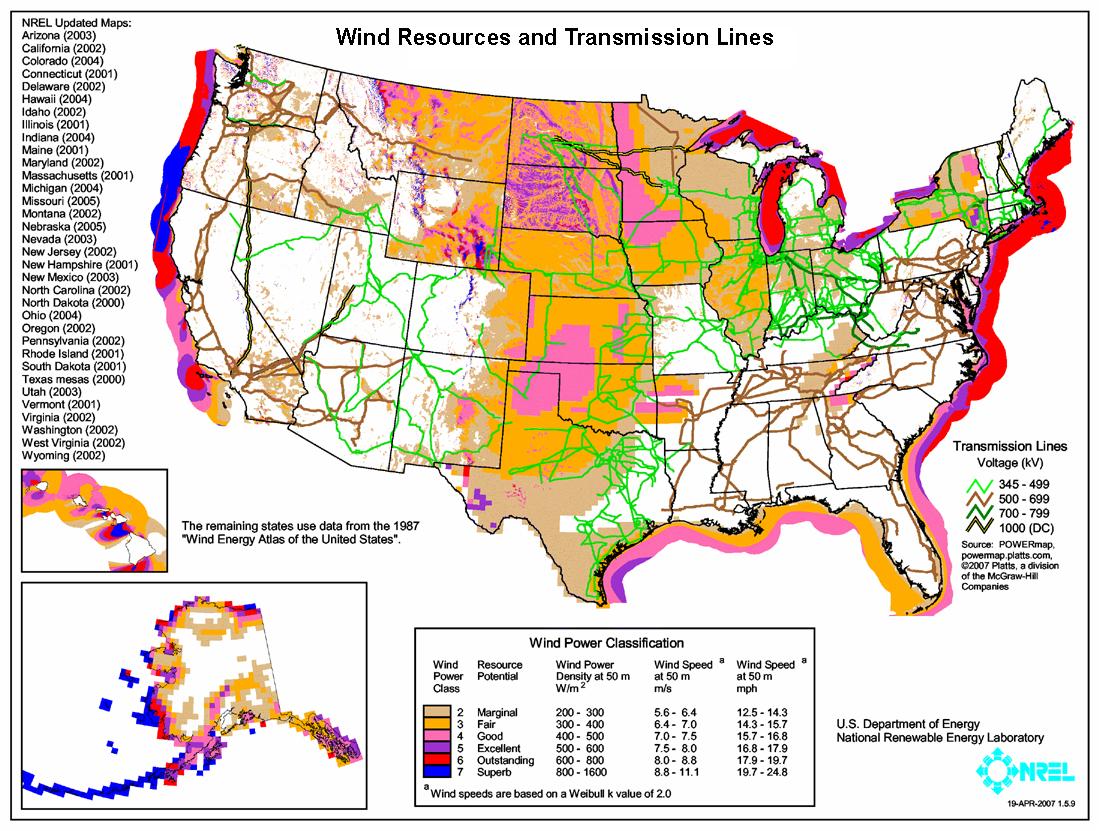
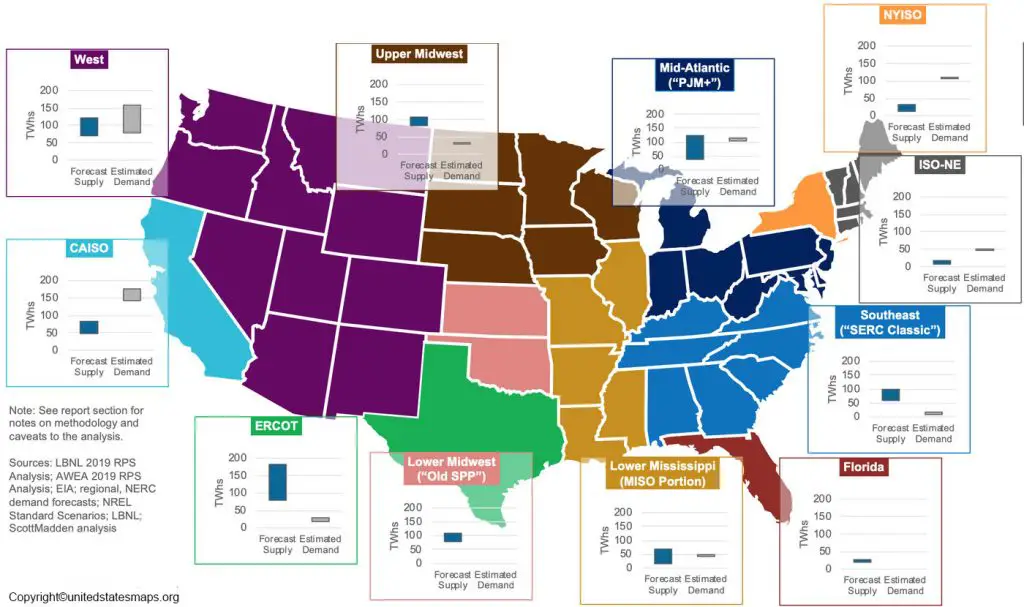
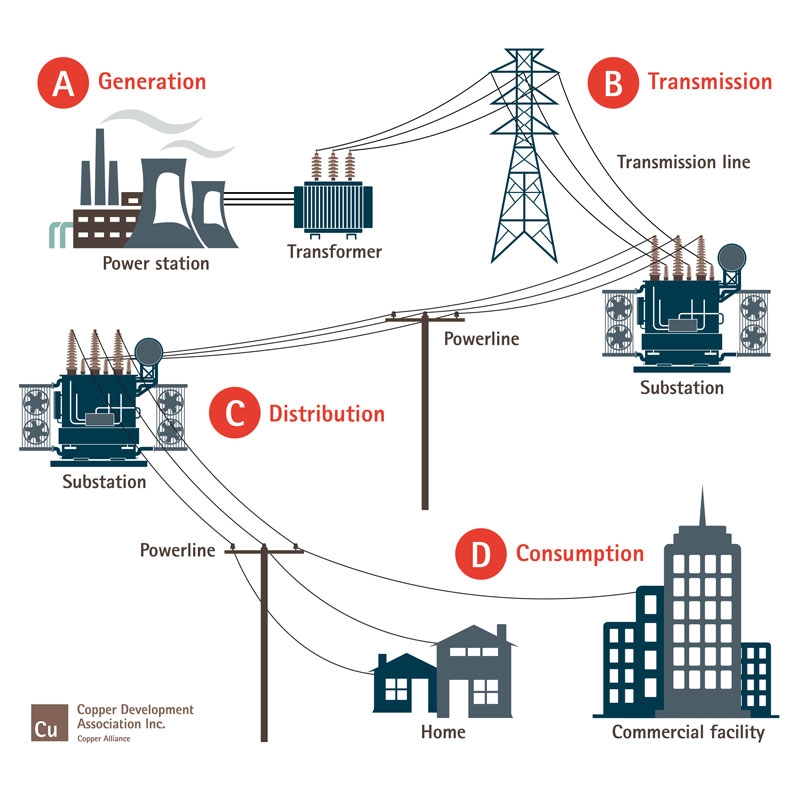
- Power Plants: These are the sources of electricity generation, ranging from traditional fossil fuel plants to renewable sources like solar and wind farms. The map depicts their location, type, and capacity, offering insights into the energy mix of a region.
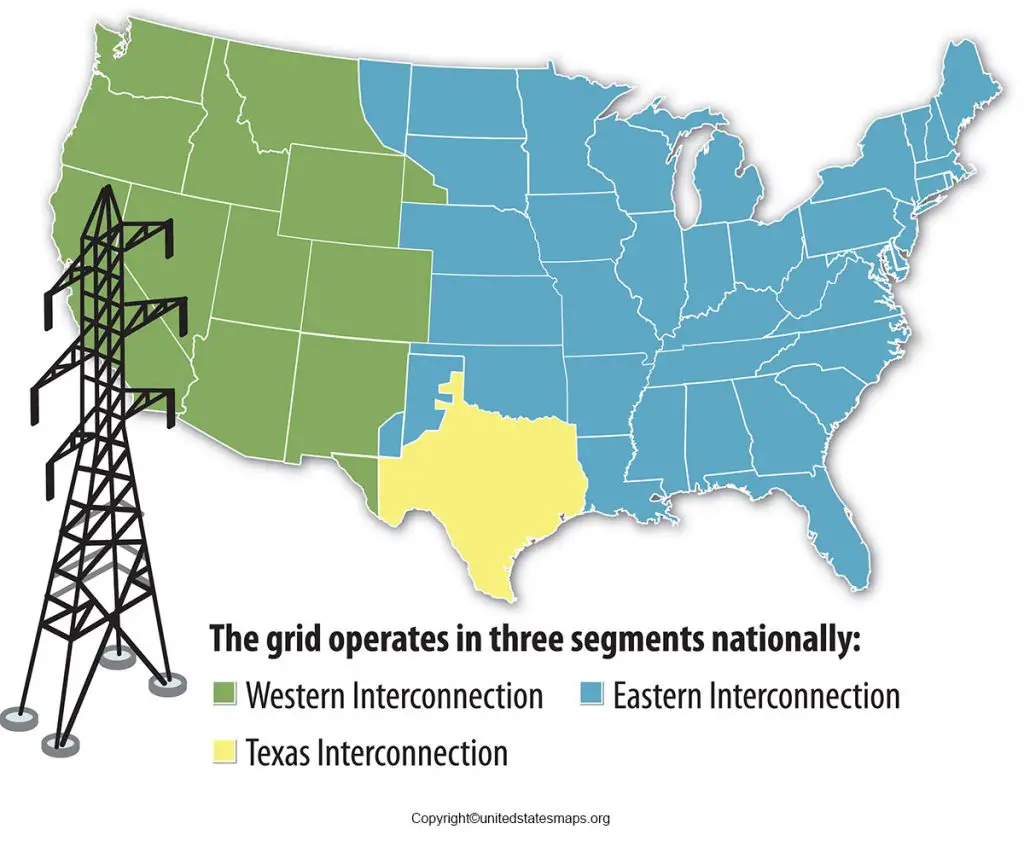
- Transmission Lines: High-voltage power lines transport electricity over long distances, connecting power plants to major load centers. The map displays the network of transmission lines, highlighting key corridors and interconnections.
- Substations: These facilities transform high-voltage electricity to lower voltages suitable for distribution within local areas. The map shows the locations of substations and their role in the power grid.
- Distribution Networks: The final stage of electricity delivery involves distributing power to individual consumers through a network of low-voltage lines and transformers. The map illustrates the distribution network, showcasing the density of power lines and the reach of electricity service.
Beyond a Static Snapshot:
Modern electricity maps are not merely static representations of the grid. They are dynamic, interactive tools that offer real-time data and analysis capabilities. These features include:
- Real-time Data Visualization: The map can display live data on electricity generation, consumption, and transmission flows. This allows users to track energy production and consumption patterns in real-time, providing insights into grid performance and demand fluctuations.
- Interactive Exploration: Users can zoom in and out of specific areas, explore individual power plants or transmission lines, and analyze data related to specific points on the grid. This interactive nature enhances the understanding of the power grid’s complexities.
- Scenario Modeling: Electricity maps can be used to simulate various scenarios, such as the impact of a power plant outage or a sudden surge in demand. This helps in planning for contingencies and optimizing grid operations.
- Data Integration: Electricity maps often integrate data from various sources, including weather forecasts, energy market data, and consumer usage patterns. This allows for a more holistic view of the grid and its interactions with external factors.
The Importance of Electricity Maps:
Electricity maps serve as invaluable tools for a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Energy Utilities: They provide a comprehensive view of the grid, facilitating efficient operation, maintenance, and planning. This includes identifying potential bottlenecks, optimizing power flow, and coordinating grid upgrades.
- Policymakers: Electricity maps provide crucial insights into the energy landscape, helping policymakers understand regional energy dependence, track the adoption of renewable energy sources, and develop effective energy policies.
- Researchers: These maps serve as a platform for studying energy trends, analyzing grid performance, and developing new technologies for improving grid efficiency and reliability.
- Consumers: Electricity maps can empower consumers by providing information about electricity sources, pricing, and consumption patterns, helping them make informed energy choices.
FAQs about Electricity Maps:
1. How are electricity maps created?
Electricity maps are typically created using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, which combines spatial data with attribute information. Data sources include:
- Grid Infrastructure Data: This includes the location and specifications of power plants, transmission lines, substations, and distribution networks.
- Energy Consumption Data: This data reflects the electricity demand at various locations and times.
- Renewable Energy Data: This includes information on the location and capacity of solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources.
2. What are the benefits of using an electricity map?
Electricity maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Grid Visibility: They provide a comprehensive overview of the power grid, enabling better understanding and analysis.
- Improved Grid Management: They facilitate efficient operation, maintenance, and planning of the power grid.
- Optimized Energy Use: They help in identifying areas for energy efficiency and optimizing energy consumption.
- Strategic Planning: They support informed decision-making for grid expansion, renewable energy integration, and energy policy development.
3. Are electricity maps accurate?
The accuracy of electricity maps depends on the quality and availability of data. While some maps may rely on publicly available information, others use proprietary data from energy utilities. The accuracy can be influenced by factors such as:
- Data Source Reliability: The reliability of data sources significantly impacts the accuracy of the map.
- Data Update Frequency: Real-time data provides a more accurate representation of the grid than static data.
- Data Granularity: The level of detail in the data influences the map’s accuracy and resolution.
4. What are the limitations of electricity maps?
While powerful tools, electricity maps have certain limitations:
- Data Availability: The availability of comprehensive and accurate data is crucial for creating reliable maps.
- Data Security: Sharing sensitive grid data poses security risks and requires appropriate safeguards.
- Visualization Complexity: Visualizing a complex system like the power grid can be challenging, requiring clear and intuitive representations.
- Dynamic Nature of the Grid: The power grid is constantly evolving, making it difficult to keep maps updated in real-time.
Tips for Utilizing Electricity Maps:
- Choose a Reliable Source: Select maps from reputable organizations with access to accurate and up-to-date data.
- Understand the Data: Familiarize yourself with the data sources, data update frequency, and limitations of the map.
- Explore Interactively: Utilize the interactive features to zoom in, explore specific areas, and analyze data related to individual components of the grid.
- Consider the Context: Interpret the data within the context of regional energy policies, market dynamics, and environmental factors.
Conclusion:
Electricity maps are essential tools for visualizing and understanding the complex and dynamic nature of the power grid. They provide a comprehensive overview of the energy landscape, facilitating efficient grid management, informed policy decisions, and innovative solutions for a sustainable energy future. By leveraging the power of visualization, electricity maps empower stakeholders to navigate the intricacies of the power grid, ensuring a reliable and resilient energy system for generations to come.

![GIS for Electric Utilities [The Ultimate Guide] GIS Cloud](https://www.giscloud.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GIS-for-Electric-Utilities-electric-utility-asset-management-software.png?x94370)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power Grid: An Exploration of Electricity Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!