Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
- 3.1 Depicting the Earth’s Form: The Essence of Topographic Maps
- 3.2 Unlocking the Potential: Applications of Topographic Maps
- 3.3 The Power of Detail: Understanding Topographic Map Symbols
- 3.4 Navigating the Terrain: Using Topographic Maps for Orientation and Navigation
- 3.5 The Evolution of Topographic Maps: Embracing Technology for Enhanced Accuracy and Accessibility
- 3.6 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Topographic Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Using Topographic Maps Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Topographic Maps
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps

Topographic maps are more than just intricate lines and numbers on a piece of paper. They are powerful tools that capture the Earth’s surface in a way that reveals its three-dimensional form, providing invaluable insights for a wide range of applications. These maps serve as visual representations of the landscape, encompassing its elevation, terrain features, and natural and man-made structures.
Depicting the Earth’s Form: The Essence of Topographic Maps
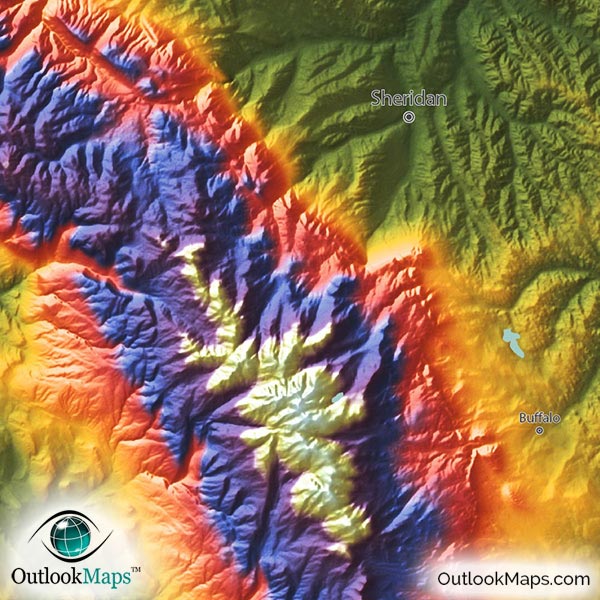
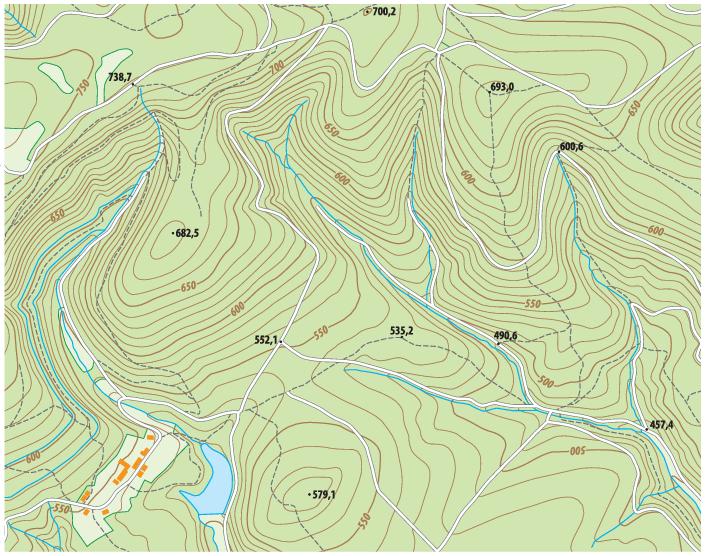
The primary function of a topographic map is to depict the shape of the Earth’s surface. This is achieved through the use of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. These lines, resembling a series of interconnected loops, provide a visual representation of the terrain’s undulations, from gentle slopes to steep cliffs. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the terrain, while wider spacing indicates a gentler incline.
Beyond elevation, topographic maps also incorporate a wealth of information, including:
- Hydrography: Rivers, lakes, streams, and other water bodies are meticulously mapped, capturing their courses, sizes, and depths.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, and other vegetation types are depicted, offering insights into the ecological characteristics of the area.
- Cultural Features: Roads, railroads, buildings, and other man-made structures are included, providing context to the natural landscape.
- Elevation Points: Specific points of known elevation are marked, offering precise measurements for height calculations.
- Geographic Coordinates: Latitude and longitude lines are incorporated, enabling accurate location identification and navigation.
This comprehensive representation of the landscape makes topographic maps indispensable for various disciplines and activities, ranging from scientific research to engineering projects and everyday navigation.
Unlocking the Potential: Applications of Topographic Maps
The diverse applications of topographic maps stem from their ability to provide accurate and detailed information about the Earth’s surface. They serve as vital tools in the following fields:
1. Surveying and Engineering:
- Site Planning and Development: Topographic maps are essential for planning and designing infrastructure projects, ensuring that buildings, roads, and other structures are built on stable and suitable terrain.
- Civil Engineering: Topographic maps are crucial for road construction, bridge design, and dam building, providing critical data on elevation changes, soil conditions, and water flow.
- Land Management: Topographic maps assist in land use planning, conservation efforts, and resource management, providing insights into terrain features and potential environmental impacts.
- Construction: Topographic maps guide excavation, foundation design, and grading processes, ensuring proper construction and minimizing potential hazards.
2. Environmental Science and Management:
- Habitat Mapping: Topographic maps are used to delineate and analyze different habitats, providing insights into species distribution and ecosystem dynamics.
- Flood Risk Assessment: Topographic maps are used to assess flood risks, identifying areas prone to flooding and informing mitigation strategies.
- Erosion Control: Topographic maps help identify areas susceptible to erosion, guiding the development of erosion control measures.
- Water Resource Management: Topographic maps are used to analyze watershed boundaries, surface water flow, and groundwater resources, facilitating sustainable water management.
3. Navigation and Recreation:
- Hiking and Backpacking: Topographic maps are indispensable for navigating trails, identifying elevation changes, and planning routes for hiking and backpacking expeditions.
- Camping and Outdoor Activities: Topographic maps help locate campsites, water sources, and access points for outdoor recreation, ensuring safe and enjoyable experiences.
- Search and Rescue: Topographic maps are used by search and rescue teams to locate missing individuals, providing crucial information on terrain features and potential hazards.
- Emergency Response: Topographic maps are valuable tools for emergency responders, enabling them to navigate challenging terrain and access areas affected by natural disasters.
4. Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
- Data Integration and Analysis: Topographic maps serve as a foundation for GIS databases, providing essential data for spatial analysis, modeling, and visualization.
- Land Use Planning: Topographic maps are integrated into GIS systems to analyze land use patterns, identify potential development areas, and evaluate environmental impacts.
- Urban Planning: Topographic maps are used in urban planning to assess terrain features, infrastructure needs, and development constraints.
- Resource Management: Topographic maps are integrated into GIS systems to track and manage natural resources, ensuring sustainable use and conservation.
5. Military and Defense:
- Military Operations: Topographic maps are crucial for military planning, providing detailed information on terrain features, potential obstacles, and enemy positions.
- Intelligence Gathering: Topographic maps are used to analyze enemy terrain, identify strategic locations, and plan military maneuvers.
- Logistics and Transportation: Topographic maps guide the movement of troops and equipment, ensuring efficient transportation and supply lines.
- Target Identification: Topographic maps are used to locate targets, assess their vulnerability, and plan effective attacks.
The Power of Detail: Understanding Topographic Map Symbols
The effectiveness of topographic maps lies not only in their ability to depict the landscape but also in their use of standardized symbols that convey a wealth of information. These symbols are crucial for understanding the map’s content and interpreting its data.
- Contour Lines: As previously mentioned, contour lines are the most prominent feature of topographic maps. They represent points of equal elevation, with thicker lines indicating major elevation changes.
- Spot Elevations: Specific points of known elevation are marked with numbers, providing precise measurements for height calculations.
- Water Features: Rivers, lakes, streams, and other water bodies are depicted using blue lines, with varying widths indicating the size of the water body.
- Vegetation: Different vegetation types are represented by specific symbols, such as trees, shrubs, and grasslands.
- Cultural Features: Roads, railroads, buildings, and other man-made structures are depicted using symbols that represent their type and size.
- Relief Shading: Some topographic maps use relief shading, a technique that creates a three-dimensional effect by shading areas based on their elevation.
Understanding these symbols is essential for interpreting topographic maps and extracting valuable information from them.
Navigating the Terrain: Using Topographic Maps for Orientation and Navigation
Topographic maps are invaluable for navigating complex terrain, providing information that is vital for planning routes, identifying landmarks, and avoiding potential hazards.
- Route Planning: Topographic maps allow users to plan routes that minimize elevation changes, identify potential obstacles, and optimize travel time.
- Landmark Identification: Topographic maps depict landmarks, such as mountains, rivers, and buildings, providing visual cues for navigation.
- Hazard Recognition: Topographic maps highlight potential hazards, such as steep slopes, cliffs, and dense vegetation, enabling users to avoid dangerous areas.
- Elevation Determination: Contour lines and spot elevations provide information about elevation changes, allowing users to estimate the difficulty of a route and plan accordingly.
- Compass and GPS Integration: Topographic maps can be used in conjunction with compasses and GPS devices for accurate navigation, providing a comprehensive understanding of the surrounding terrain.
The Evolution of Topographic Maps: Embracing Technology for Enhanced Accuracy and Accessibility
Topographic maps have evolved significantly over time, embracing technological advancements to enhance their accuracy, accessibility, and usability.
- Digital Topographic Maps: Digital topographic maps are created using advanced surveying techniques and GIS software, providing highly accurate and detailed representations of the landscape.
- Online Mapping Services: Online mapping services, such as Google Maps and OpenStreetMap, integrate topographic data, providing interactive and user-friendly access to topographic information.
- Mobile Mapping Apps: Mobile mapping apps, such as Gaia GPS and AllTrails, offer offline topographic maps, making them accessible even in areas with limited internet connectivity.
- 3D Topographic Models: Advanced technologies, such as LiDAR scanning, enable the creation of three-dimensional topographic models, offering immersive and realistic representations of the landscape.
These advancements have made topographic maps more accessible, user-friendly, and powerful than ever before, expanding their applications and impact across various disciplines.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Topographic Maps
1. What are the different types of topographic maps?
Topographic maps can be categorized based on their scale, purpose, and geographic coverage. Some common types include:
- Large-Scale Maps: Large-scale maps depict small areas in detail, typically used for engineering projects, site planning, and urban planning.
- Medium-Scale Maps: Medium-scale maps cover larger areas with less detail, suitable for regional planning, recreational activities, and general navigation.
- Small-Scale Maps: Small-scale maps cover vast areas with minimal detail, used for global planning, thematic analysis, and educational purposes.
2. How are topographic maps created?
Topographic maps are created using a combination of surveying techniques, including:
- Traditional Surveying: This involves using instruments like theodolites, levels, and total stations to measure distances, angles, and elevations.
- Aerial Photography: Aerial photographs are taken from aircraft or drones, providing images that are used to create topographic maps.
- LiDAR Scanning: LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) uses lasers to measure distances and create highly accurate three-dimensional models of the terrain.
3. What are the advantages of using topographic maps?
Topographic maps offer several advantages over other types of maps:
- Detailed Information: Topographic maps provide comprehensive information about the landscape, including elevation, terrain features, and cultural features.
- Accurate Representation: Topographic maps are highly accurate, providing reliable data for planning, navigation, and decision-making.
- Standardized Symbols: The use of standardized symbols ensures consistent interpretation and understanding of the map’s content.
- Versatile Applications: Topographic maps are applicable to a wide range of disciplines and activities, from scientific research to engineering projects and everyday navigation.
4. What are the limitations of topographic maps?
While topographic maps are powerful tools, they also have some limitations:
- Scale and Detail: The scale of a topographic map determines its level of detail, limiting its usefulness for specific applications.
- Outdated Information: Topographic maps can become outdated as the landscape changes, requiring periodic updates.
- Limited 3D Visualization: While contour lines provide a representation of elevation, they do not offer a fully immersive 3D experience.
5. How can I learn to read and interpret topographic maps?
There are various resources available to learn how to read and interpret topographic maps:
- Online Tutorials: Numerous online tutorials and videos provide step-by-step guidance on understanding map symbols, interpreting contour lines, and navigating using topographic maps.
- Books and Manuals: Specialized books and manuals on topographic mapping offer in-depth explanations and practical exercises.
- Workshops and Courses: Workshops and courses offered by organizations like the Boy Scouts of America and the American Hiking Society provide hands-on training in topographic map reading and navigation.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps Effectively
- Choose the Right Scale: Select a topographic map with a scale appropriate for your needs and the area you are exploring.
- Understand the Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the standardized symbols used on topographic maps to interpret their content accurately.
- Identify Your Location: Use landmarks, compass bearings, and GPS coordinates to locate yourself on the map.
- Plan Your Route: Use the map to plan your route, considering elevation changes, potential obstacles, and hazards.
- Check for Updates: Ensure that the map you are using is up-to-date, as the landscape can change over time.
- Practice and Experience: The more you use topographic maps, the more proficient you will become in interpreting their information and navigating using them.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps have played a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the Earth’s surface and guiding our interactions with it. From scientific exploration to engineering projects and everyday navigation, these maps continue to provide invaluable insights, enabling us to plan, design, and navigate the world around us. As technology advances, topographic maps are evolving, becoming more accurate, accessible, and powerful, ensuring their continued relevance in the years to come.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/topomap2-56a364da5f9b58b7d0d1b406.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!