Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
Related Articles: Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at Lake Erie’s Bathymetry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
.jpg)
Lake Erie, the shallowest of the Great Lakes, holds a wealth of ecological and economic significance. Understanding its depths, or bathymetry, is crucial for managing its resources, navigating its waters, and safeguarding its delicate ecosystem. This article explores the intricacies of Lake Erie’s depth map, highlighting its importance in various fields and providing insights into its unique characteristics.
Mapping the Depths: A Window into Lake Erie’s Secrets
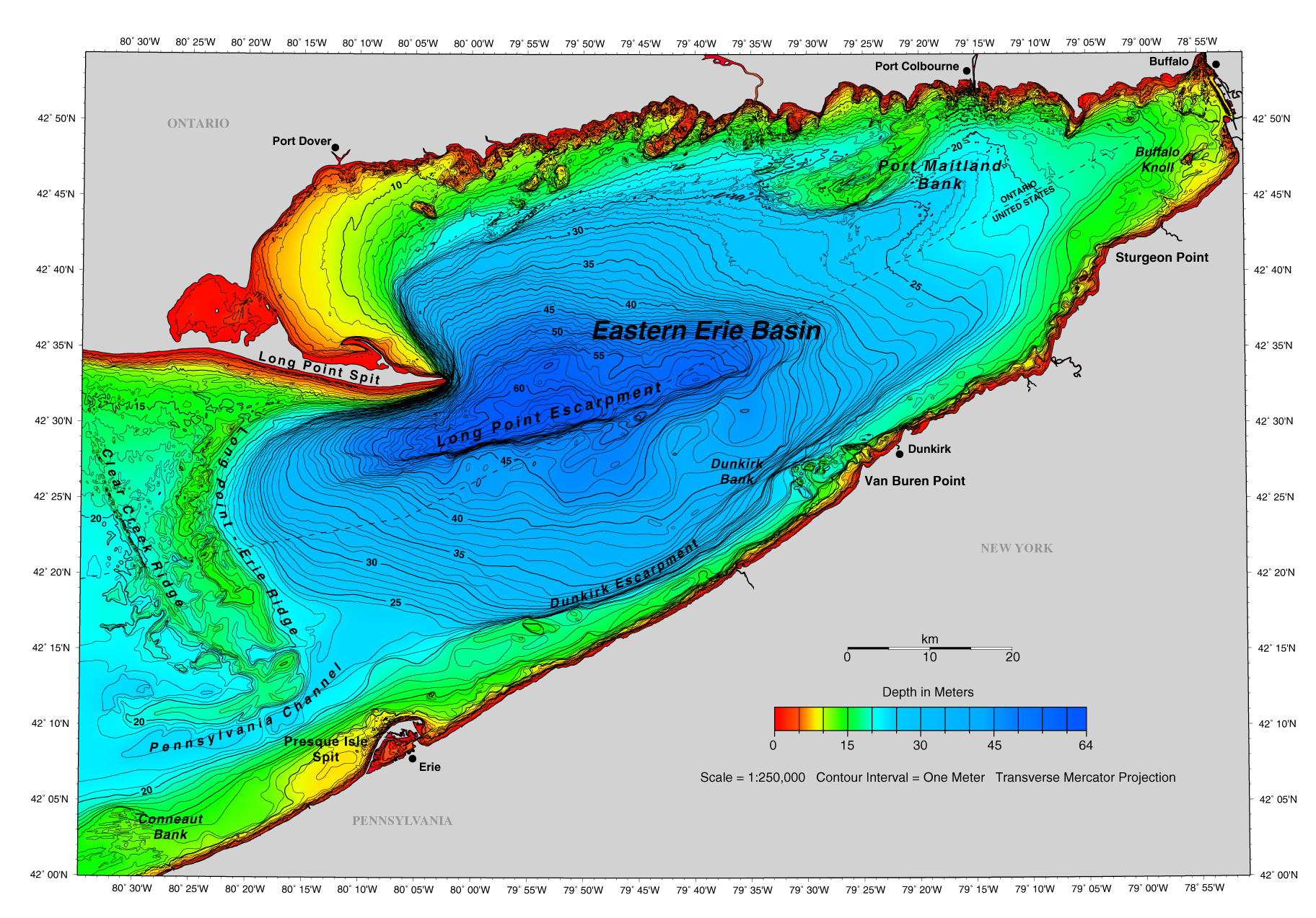
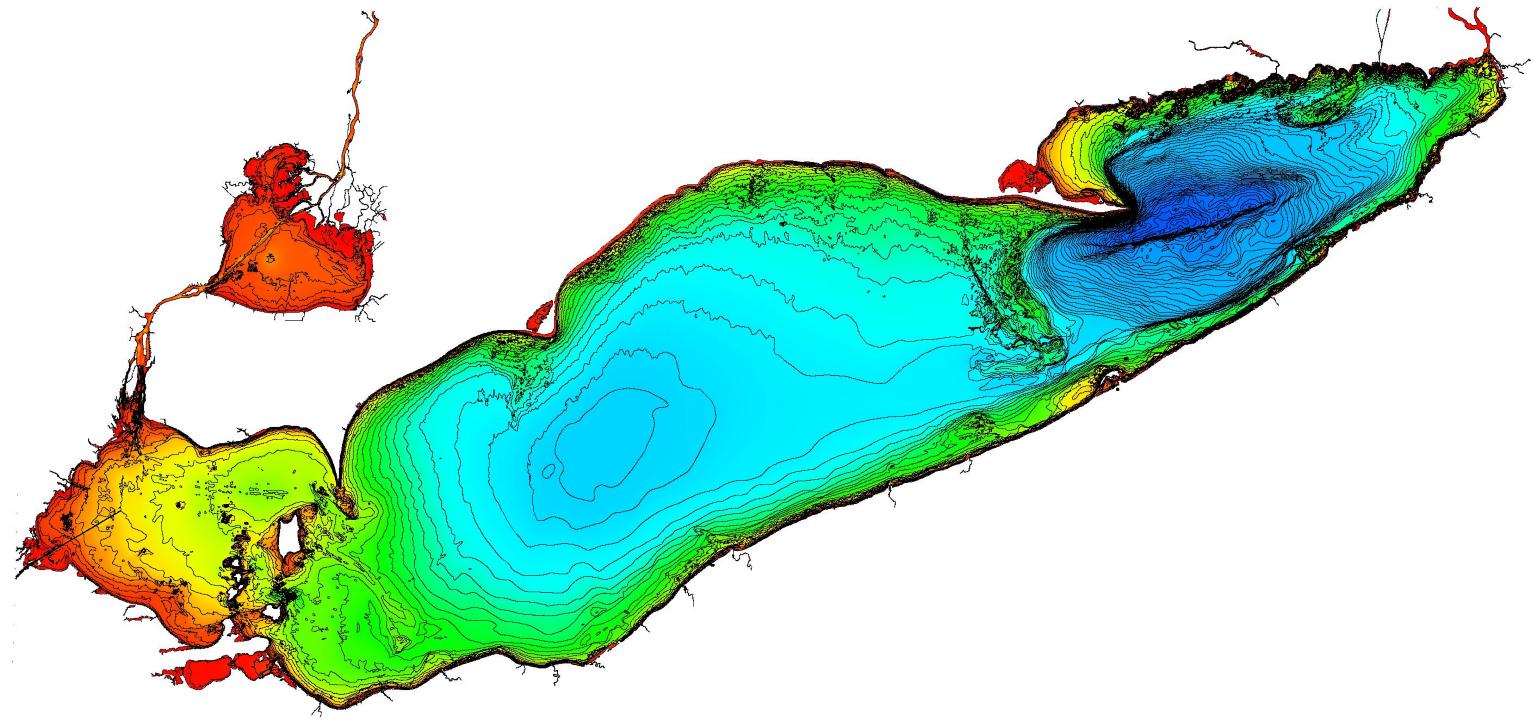
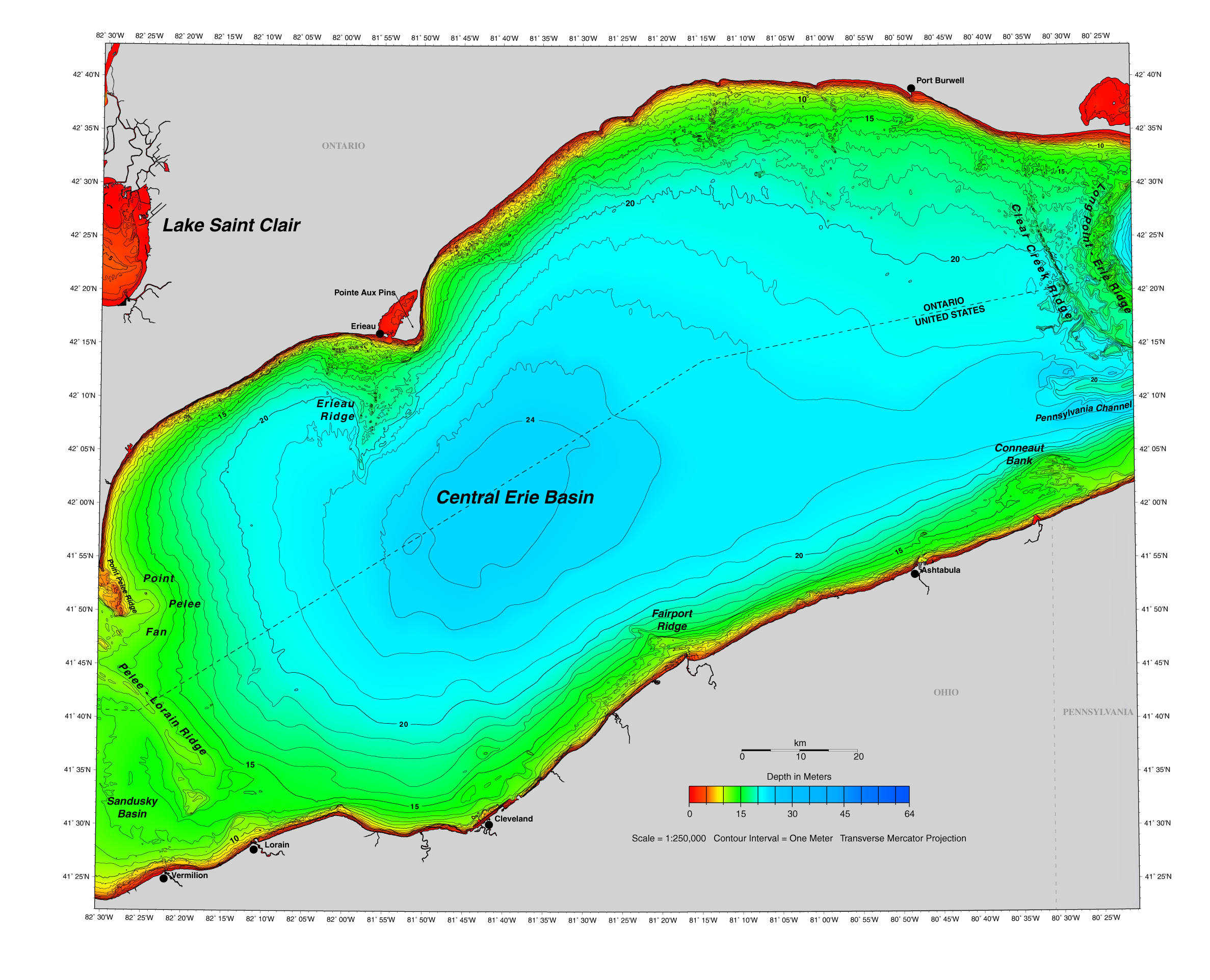
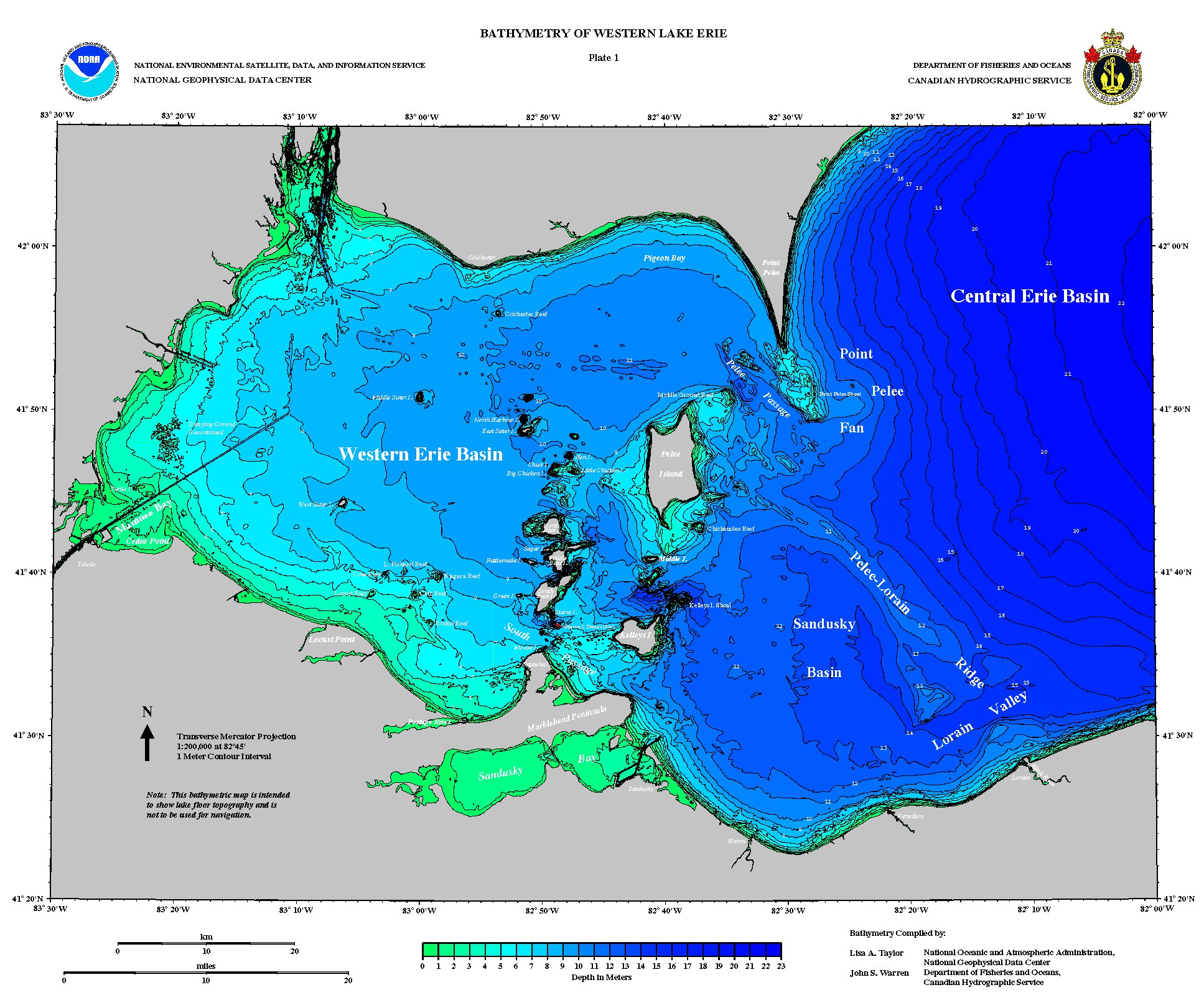
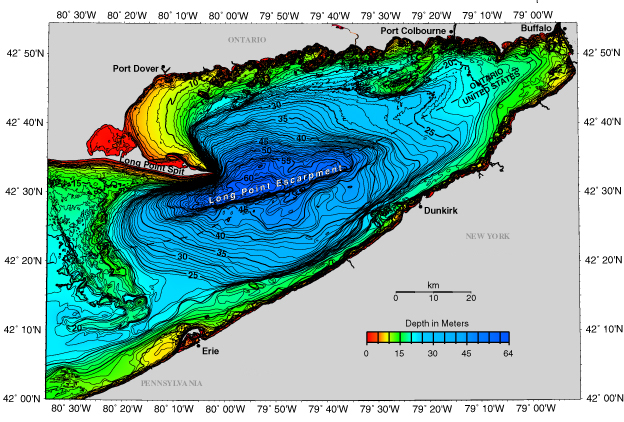
A depth map, also known as a bathymetric map, is a visual representation of the underwater topography of a body of water. For Lake Erie, this map reveals a landscape of varying depths, ranging from shallow, nearshore areas to deeper, central basins.
The central basin of Lake Erie, the deepest part, reaches approximately 64 meters (210 feet) in depth. In contrast, the western basin, the shallowest, averages only 6 meters (20 feet) deep. This significant difference in depth profoundly influences the physical, chemical, and biological processes within the lake.
The Importance of Depth: A Multifaceted Perspective
Understanding Lake Erie’s bathymetry is essential for a wide range of applications, including:
-
Navigation and Safety: Depth maps provide crucial information for safe navigation, particularly for large vessels and recreational boaters. They help identify potential hazards like shallow areas, submerged rocks, and shipwrecks, enabling mariners to plan routes and avoid potential collisions.
-
Resource Management: Lake Erie’s depths are vital for understanding the distribution and availability of valuable resources. Fisheries management relies heavily on bathymetric data to assess fish populations and determine sustainable fishing quotas. The distribution of benthic organisms, which form the base of the food web, is also influenced by depth, making this data crucial for ecological assessments.
-
Water Quality Monitoring: Depth plays a significant role in water circulation and mixing patterns within the lake. This affects the distribution of nutrients, pollutants, and oxygen levels. Understanding the depths allows researchers to model water flow and predict the spread of harmful algal blooms, a major environmental concern for Lake Erie.
-
Climate Change Impacts: Climate change is altering water temperatures and precipitation patterns, impacting Lake Erie’s depth and water levels. Bathymetric data is crucial for understanding these changes and predicting their impact on the lake’s ecosystem and resources.
-
Coastal Erosion and Shoreline Management: The depth map provides insights into the dynamics of waves and currents near the shoreline, which are crucial for understanding coastal erosion patterns. This information is essential for developing effective coastal protection strategies and managing shoreline development.
-
Hydrological Modeling: Bathymetric data is a fundamental input for hydrological models that simulate water flow, nutrient transport, and other processes within the lake. These models are essential for understanding the lake’s overall health and predicting the impact of various human activities.
Unique Features of Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
Lake Erie’s bathymetry exhibits several unique features that contribute to its distinct character:
-
Shallow Western Basin: The western basin’s shallowness makes it susceptible to rapid warming and nutrient enrichment, contributing to the frequent occurrences of harmful algal blooms.
-
Central Basin Depressions: The central basin features several depressions, including the Erie Basin and the Long Point Basin, which act as sinks for sediment and pollutants.
-
Submerged Shoals and Islands: The lake contains numerous submerged shoals and islands, which provide habitat for fish and other aquatic life. These features also influence water currents and wave patterns.
-
Historical Impacts: Human activities, such as dredging and land reclamation, have significantly altered Lake Erie’s bathymetry over time. This has impacted the lake’s ecosystem and resource availability.
FAQs about Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
Q: How is Lake Erie’s bathymetry measured?
A: Bathymetric data is collected through various methods, including:
- Multibeam Sonar: This technology emits sound waves that bounce off the lakebed, allowing researchers to create detailed maps of the underwater terrain.
- Single-beam Sonar: This traditional method uses a single sound wave to measure depth, but it provides less detailed information compared to multibeam sonar.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser beams to measure depth, providing accurate and high-resolution data.
Q: How often is Lake Erie’s bathymetry updated?
A: The frequency of bathymetric surveys varies depending on the purpose and available resources. However, regular updates are essential to account for changes in the lake’s depth due to natural processes and human activities.
Q: What are the challenges in mapping Lake Erie’s bathymetry?
A: Mapping Lake Erie’s bathymetry presents several challenges, including:
- Large Size: The lake’s vast size requires significant time and resources for comprehensive mapping.
- Variable Water Clarity: Turbidity caused by suspended sediments can interfere with sonar readings, making it difficult to obtain accurate depth measurements.
- Weather Conditions: Strong winds and waves can disrupt survey operations, making it challenging to collect reliable data.
Q: How does Lake Erie’s bathymetry compare to other Great Lakes?
A: Lake Erie is the shallowest of the Great Lakes, with an average depth of 19 meters (62 feet). This shallowness distinguishes it from the deeper lakes like Superior and Huron, which have average depths exceeding 140 meters (460 feet).
Tips for Understanding Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
- Visualize the Depths: Use online maps and interactive tools to explore Lake Erie’s bathymetry and gain a better understanding of its underwater topography.
- Explore Bathymetric Data: Access available bathymetric data from government agencies and research institutions to gain insights into specific areas of interest.
- Connect Bathymetry to Other Factors: Understand how depth influences other factors, such as water temperature, nutrient levels, and fish populations.
- Stay Informed about Updates: Keep abreast of new bathymetric surveys and research findings to stay up-to-date on the latest information about Lake Erie’s depths.
Conclusion
Lake Erie’s bathymetry is a critical component of its complex ecosystem. Understanding its depths is crucial for navigating its waters, managing its resources, and protecting its delicate environment. By utilizing advanced technologies and ongoing research, scientists and resource managers can continue to unravel the secrets of Lake Erie’s bathymetry, contributing to the sustainable management and preservation of this vital natural resource.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at Lake Erie’s Bathymetry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!