Unraveling the World’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Köppen Climate Classification System
Related Articles: Unraveling the World’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Köppen Climate Classification System
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the World’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Köppen Climate Classification System. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the World’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Köppen Climate Classification System

The Earth’s climate is a complex and dynamic system, influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these intricate interactions is crucial for a variety of purposes, from predicting weather patterns to comprehending the impact of climate change. To navigate this complexity, scientists have developed various classification systems, with the Köppen climate classification system standing out as a widely used and influential tool.
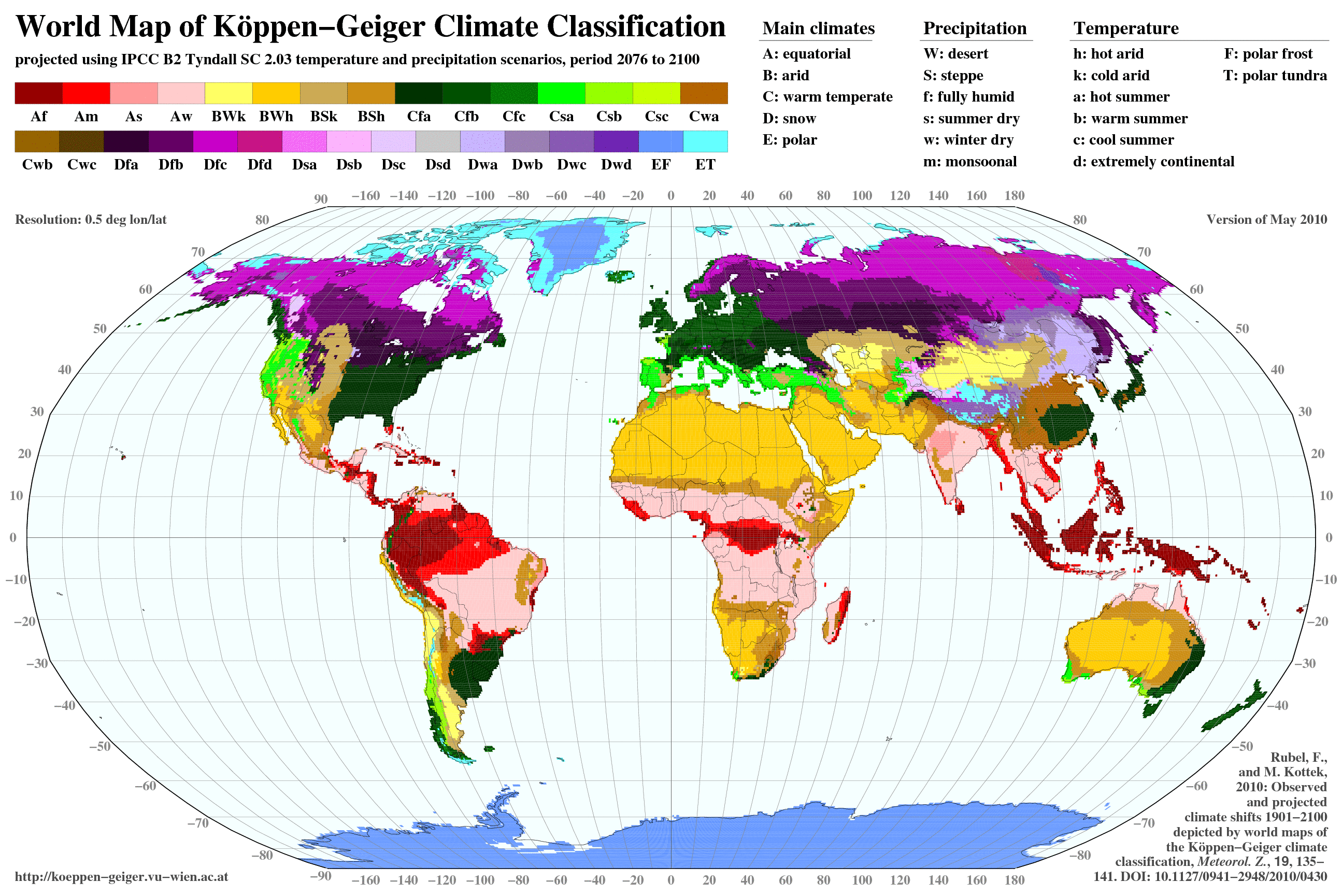
Developed by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen in the early 20th century, this system provides a framework for understanding the global distribution of climates based on temperature and precipitation patterns. The Köppen system categorizes the world’s climates into five primary groups, each further subdivided into numerous subtypes. This hierarchical structure allows for a nuanced understanding of climate variations across the globe.
Delving into the System’s Structure
The five primary groups in the Köppen climate classification system are:
-
A: Tropical Climates: Characterized by consistently warm temperatures throughout the year, with an average monthly temperature exceeding 18°C (64.4°F). These climates are further subdivided based on precipitation patterns:
- Af: Tropical Rainforest: Abundant rainfall throughout the year, typically exceeding 60mm (2.4 inches) per month.
- Am: Tropical Monsoon: Distinct wet and dry seasons, with heavy rainfall during the monsoon season.
- Aw: Tropical Savanna: A distinct dry season, typically during the winter months.
-
B: Dry Climates: Marked by arid conditions with low precipitation levels. These climates are further subdivided based on temperature:
- BW: Desert: Very low precipitation, typically less than 250mm (10 inches) per year.
- BS: Steppe: Semi-arid conditions with slightly higher precipitation than deserts, usually between 250mm (10 inches) and 500mm (20 inches) per year.
-
C: Temperate Climates: Experience moderate temperatures with distinct warm and cold seasons. These climates are further subdivided based on precipitation patterns and temperature:
- Cf: Temperate Oceanic: Mild winters and warm summers, with rainfall spread throughout the year.
- Cw: Temperate Subtropical: Mild winters and hot, humid summers, with a dry period in the winter.
- Cs: Temperate Mediterranean: Warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
-
D: Continental Climates: Characterized by significant temperature differences between seasons, with cold winters and warm summers. These climates are further subdivided based on precipitation patterns and temperature:
- Df: Humid Continental: Cold winters and warm, humid summers, with rainfall distributed throughout the year.
- Dw: Subarctic: Long, cold winters and short, cool summers, with significant snowfall.
-
E: Polar Climates: Dominated by freezing temperatures for most of the year, with limited precipitation. These climates are further subdivided based on temperature:
- ET: Tundra: Very cold temperatures with permafrost, supporting limited vegetation.
- EF: Ice Cap: Extremely cold temperatures with permanent ice and snow cover.
Mapping the World’s Climate Diversity
The Köppen climate classification system is often presented in the form of a map, visually depicting the distribution of different climate types across the globe. This map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the global climate system, revealing patterns and variations that might otherwise remain hidden. The map highlights how climate is influenced by geographical factors such as latitude, altitude, proximity to oceans, and mountain ranges.
Beyond Classification: Applications and Importance
The Köppen climate classification system has proven invaluable for a wide range of applications, including:
- Climate Change Research: By analyzing historical climate data and comparing it with current trends, scientists can identify shifts in climate zones and assess the impact of climate change on different regions.
- Agriculture and Resource Management: Understanding the climate of a particular region is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices, managing water resources, and planning land use.
- Urban Planning and Design: The Köppen system helps urban planners design cities that are resilient to extreme weather events and adapt to changing climate conditions.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Different climate zones support distinct ecosystems and biodiversity. By understanding climate patterns, conservation efforts can be tailored to specific regions and their unique ecological characteristics.
- Tourism and Recreation: The Köppen system helps identify areas with favorable climates for tourism and recreation, promoting sustainable tourism development.
FAQs about the Köppen Climate Classification System
-
What are the limitations of the Köppen system?
- The Köppen system is based solely on temperature and precipitation data, neglecting other important factors like humidity, wind patterns, and sunshine hours.
- It does not account for microclimates, which can vary significantly within a larger climate zone.
- The boundaries between climate zones can be somewhat arbitrary, leading to potential inconsistencies in classification.
-
How does the Köppen system relate to other climate classification systems?
- The Köppen system is one of many climate classification systems, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Other notable systems include the Thornthwaite system, which focuses on potential evapotranspiration, and the Trewartha system, which incorporates more detailed temperature and precipitation criteria.
-
How has the Köppen system evolved over time?
- Since its initial development, the Köppen system has undergone several revisions and updates to reflect advancements in climate science and data availability. These updates have refined the classification criteria and incorporated new insights into climate dynamics.
Tips for Understanding and Using the Köppen Climate Classification System
- Explore interactive maps: Numerous online resources provide interactive maps that allow users to explore the Köppen climate classification system in detail. These maps often include detailed information about each climate type and its characteristics.
- Consult climate data sources: To gain a deeper understanding of a specific location’s climate, consult climate data sources such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) or the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- Consider the context: When analyzing climate data using the Köppen system, it’s important to consider the broader context of the region, including its geography, elevation, and proximity to water bodies.
- Stay informed about updates: The Köppen climate classification system is constantly evolving as new data and research emerge. Stay informed about updates and revisions to ensure you are using the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Conclusion
The Köppen climate classification system stands as a testament to the power of scientific inquiry and its ability to unravel the complexities of the natural world. This system provides a framework for understanding the global distribution of climates, enabling scientists, policymakers, and citizens alike to make informed decisions about resource management, adaptation to climate change, and sustainable development. While the Köppen system has limitations, its enduring relevance highlights its value as a tool for exploring the intricacies of the Earth’s climate tapestry.


.svg.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the World’s Climate Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Köppen Climate Classification System. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!