Unraveling the Landscape of Ancient Sparta: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape of Ancient Sparta: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape of Ancient Sparta: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape of Ancient Sparta: A Geographical Exploration
The ancient city-state of Sparta, renowned for its military prowess and unique social structure, occupied a distinct geographical space in the Peloponnese region of Greece. Understanding the terrain and layout of Sparta is crucial for grasping the intricacies of its history, culture, and military strategies.
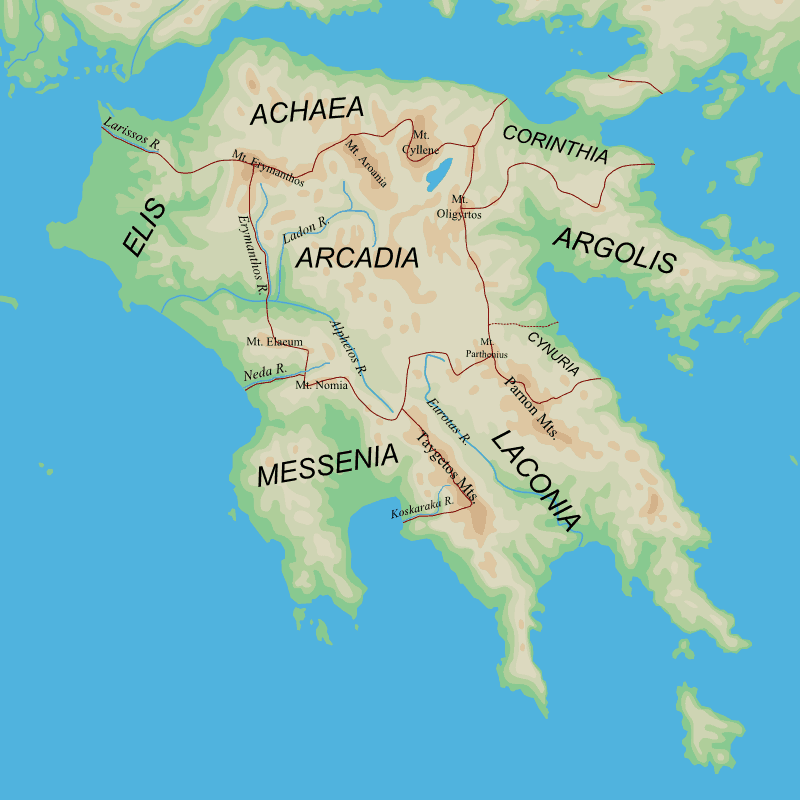
The Physical Landscape of Laconia:
Sparta’s territory, known as Laconia, encompassed a diverse landscape that played a significant role in shaping its development. The region was bordered by the Taygetus Mountains to the west, a rugged and imposing range that served as a natural barrier, and the fertile plains of the Eurotas River valley to the east. This valley, watered by the Eurotas River, provided fertile land for agriculture, supporting Sparta’s population and its military campaigns.
The City of Sparta:
The city of Sparta itself was located within the Eurotas Valley, strategically placed at the confluence of the Eurotas and the Krios rivers. This location offered strategic advantages, providing access to both the valley and the surrounding hills. The city was not fortified with walls, a testament to Sparta’s confidence in its military might and its ability to defend itself through the strength of its citizens.
The Strategic Significance of the Taygetus Mountains:
The Taygetus Mountains, towering over Sparta, served multiple strategic purposes. They provided a natural defense against potential invaders from the west, acting as a formidable barrier. The mountains also offered resources, including timber for construction and quarries for building materials. Moreover, the mountainous terrain facilitated the development of a unique Spartan military training system, which emphasized resilience and adaptability in challenging environments.
The Eurotas River Valley: A Lifeline for Sparta:
The Eurotas River Valley was the heart of Sparta’s economy and agricultural production. The fertile plains provided a reliable source of food, supporting the city’s population and enabling it to maintain a large army. The river itself was a vital resource, providing water for irrigation, transportation, and drinking.
The Perioeci and the Helots:
Beyond the city of Sparta, the Lacedaemonian territory was inhabited by two distinct groups: the Perioeci and the Helots. The Perioeci, free inhabitants of the region, served as artisans, merchants, and skilled laborers, contributing to the economic and social fabric of Laconia. The Helots, a subjugated population, were bound to the land and served as agricultural laborers. Their labor sustained Sparta’s economy and provided a source of manpower for the military.
The Importance of the Spartan Military:
The geographical features of Laconia played a crucial role in shaping Sparta’s military strategies. The rugged terrain and the presence of the Taygetus Mountains facilitated the development of a unique military training system that emphasized discipline, endurance, and the ability to operate in difficult conditions. This training, combined with the large pool of manpower provided by the Helots, made Sparta a formidable military power.
The Spartan Social Structure:
The geographical landscape of Laconia also influenced Sparta’s social structure. The city’s reliance on agriculture and its military prowess led to the development of a rigid social hierarchy, with a strong emphasis on discipline, obedience, and military service. The Spartan lifestyle was centered around the military, with education and training starting at a young age.
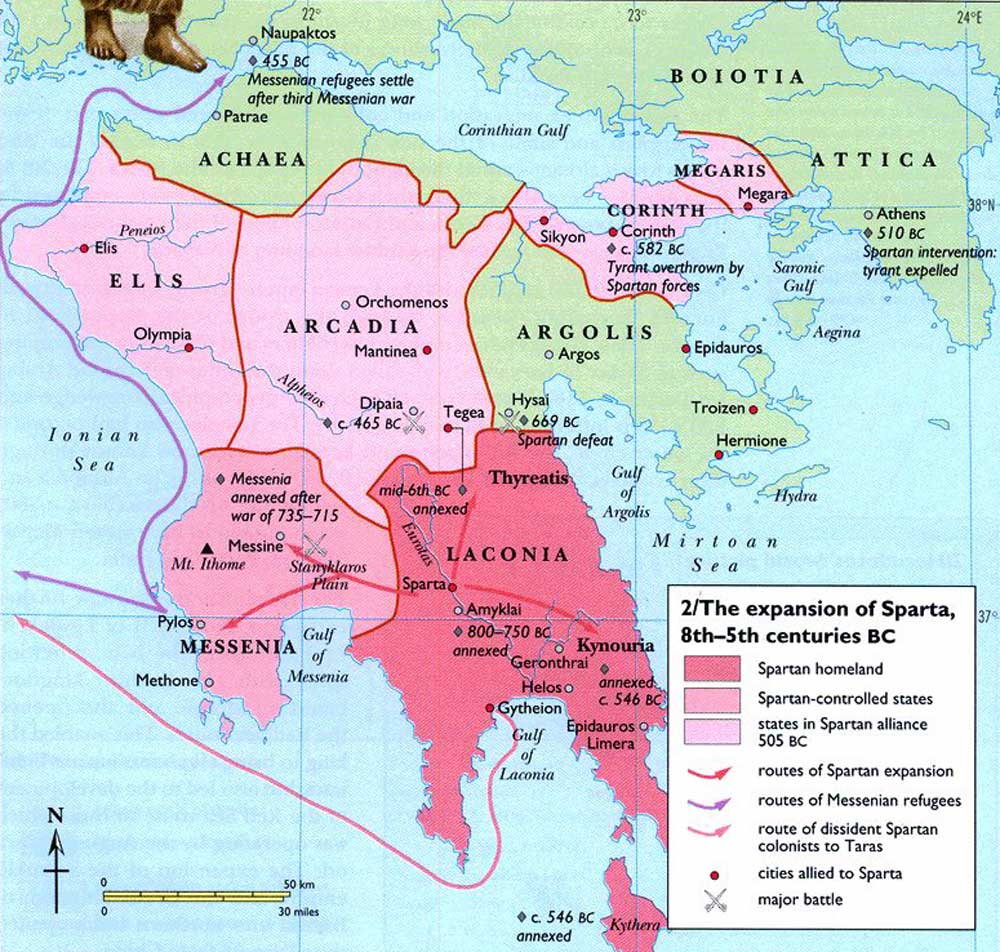
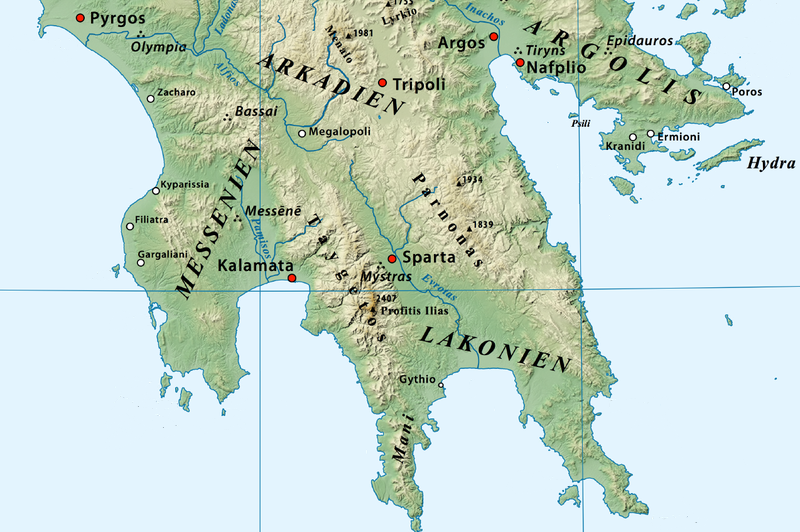
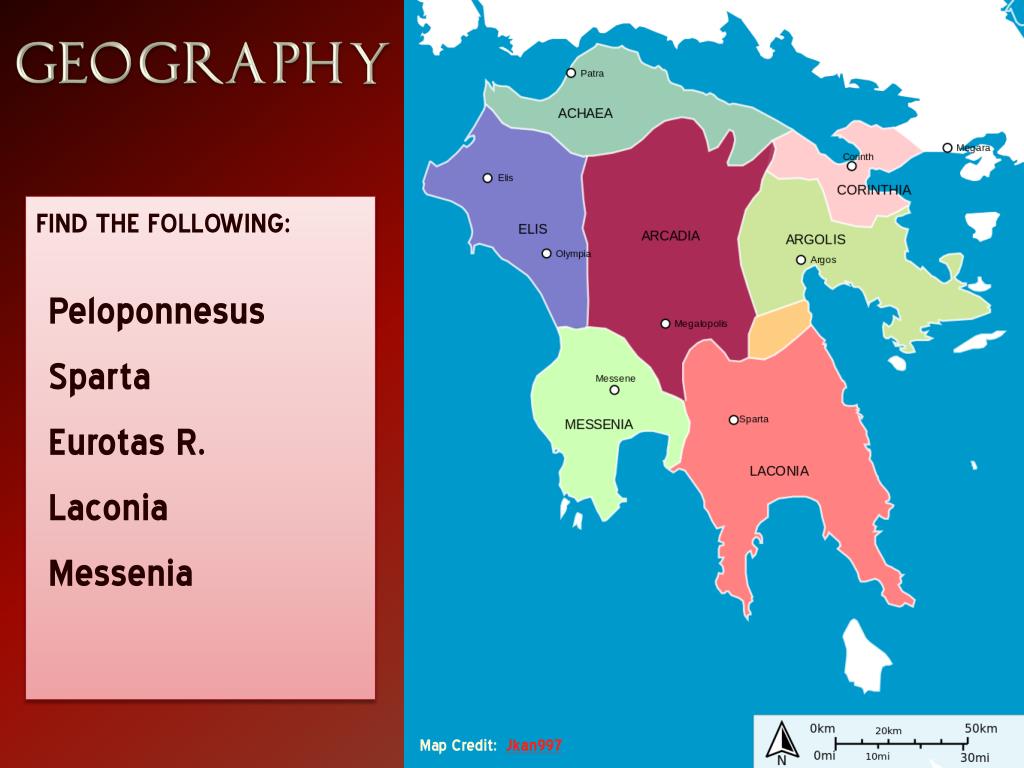
A Map of Ancient Sparta: Unveiling the Secrets of the City-State:
A detailed map of ancient Sparta reveals the intricate connections between its physical landscape, social structure, and military strategies. The map illustrates the strategic location of the city within the Eurotas Valley, the imposing presence of the Taygetus Mountains, and the fertile plains that sustained its population. It highlights the key routes of communication and trade, connecting Sparta to its neighboring regions.
Examining the Map: FAQs about Ancient Sparta
Q: What were the main geographical features of ancient Sparta?
A: The main geographical features of ancient Sparta were the Taygetus Mountains, the Eurotas River Valley, and the city of Sparta itself.
Q: How did the Taygetus Mountains influence Spartan life?
A: The Taygetus Mountains provided a natural defense against invaders, offered resources like timber and stone, and influenced the Spartan military training system.
Q: What was the significance of the Eurotas River Valley?
A: The Eurotas River Valley was the heart of Sparta’s agriculture, providing fertile land for farming and water for irrigation, transportation, and drinking.
Q: What were the Perioeci and the Helots?
A: The Perioeci were free inhabitants of Laconia who served as artisans, merchants, and skilled laborers. The Helots were a subjugated population who worked the land and provided manpower for the military.
Q: How did geography influence Spartan military strategies?
A: The rugged terrain of Laconia and the Taygetus Mountains contributed to the development of a unique military training system that emphasized discipline, endurance, and adaptability.
Q: What was the relationship between Sparta’s geography and its social structure?
A: Sparta’s reliance on agriculture and its military prowess led to a rigid social hierarchy with a strong emphasis on discipline, obedience, and military service.
Tips for Understanding Ancient Sparta through its Map:
- Identify key geographical features: Pay attention to the Taygetus Mountains, the Eurotas River Valley, and the location of the city of Sparta.
- Consider the strategic implications: Analyze how the terrain influenced Spartan military strategies and defense.
- Explore the economic and social aspects: Understand how the geographical features supported Sparta’s agriculture and its social structure.
- Compare Sparta to other ancient Greek cities: Examine how Sparta’s geography differed from that of Athens or other city-states.
Conclusion:
The geographical landscape of ancient Sparta played a pivotal role in shaping its history, culture, and military strategies. The city’s location within the Eurotas River Valley, its proximity to the Taygetus Mountains, and the presence of fertile plains and resources all contributed to its development as a powerful and influential city-state. By studying a map of ancient Sparta, we gain valuable insights into the unique characteristics of this ancient civilization and its lasting impact on the course of history.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape of Ancient Sparta: A Geographical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!