Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps of New York State
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps of New York State
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps of New York State. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps of New York State
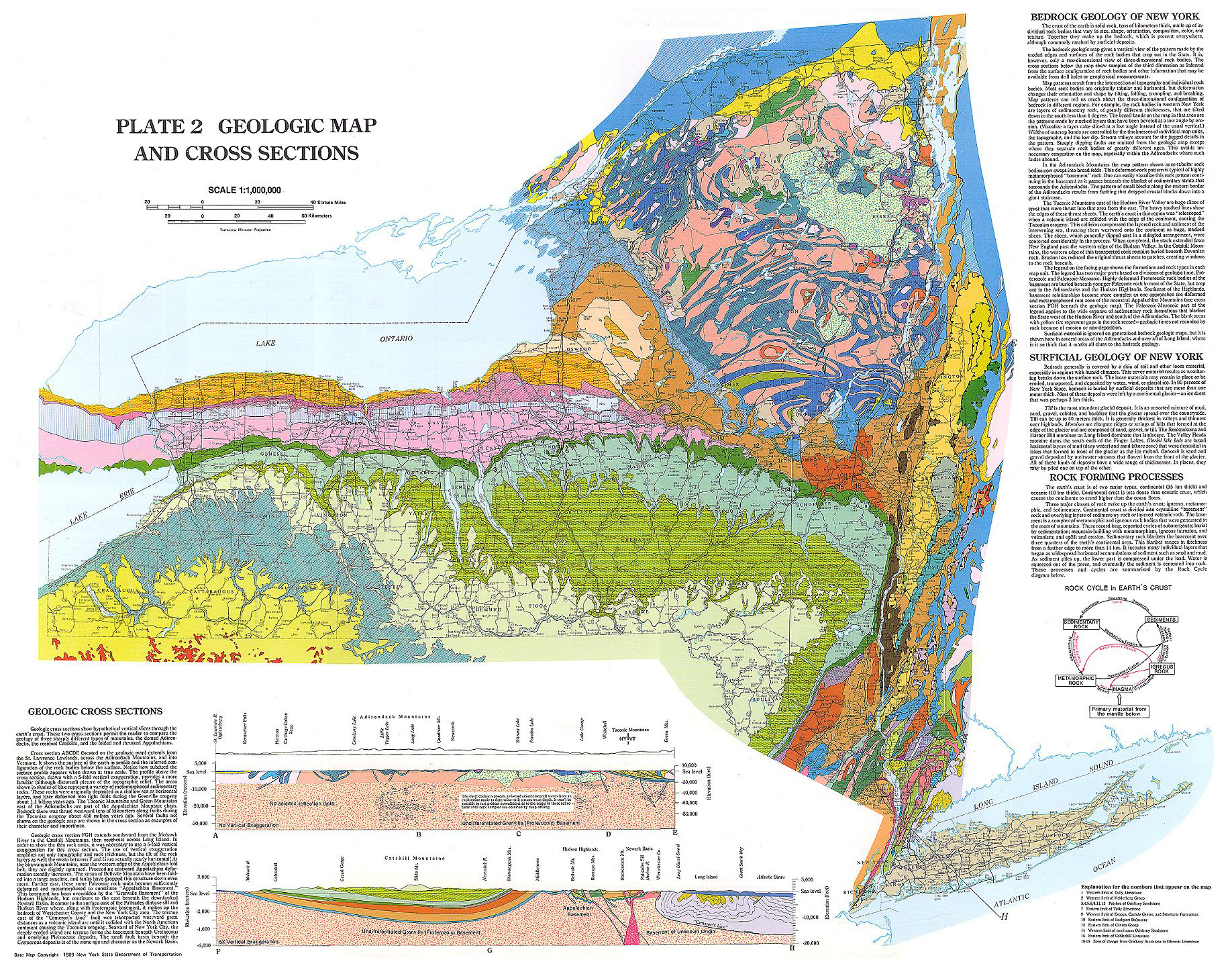
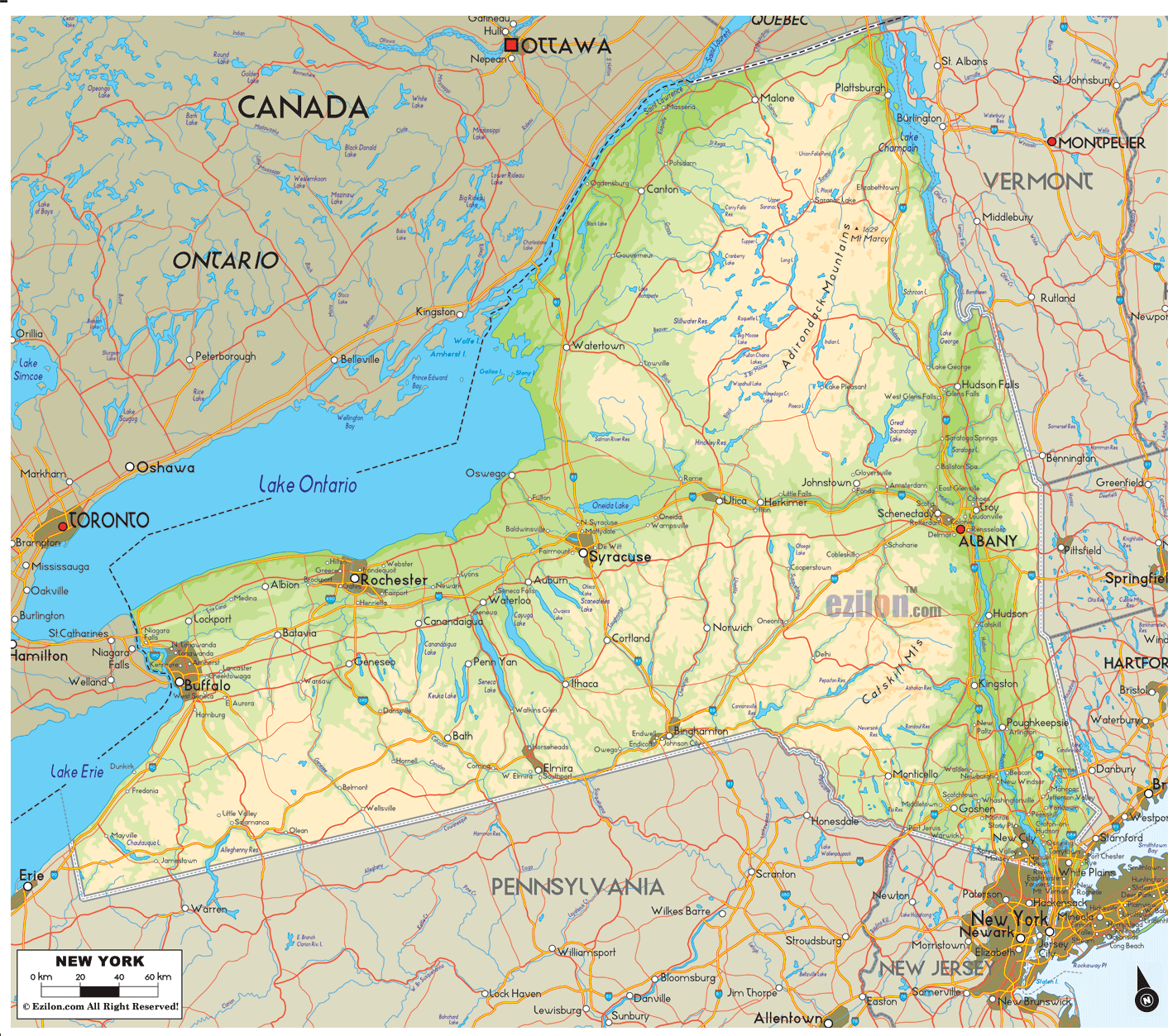
New York State, a tapestry of diverse landscapes, from the towering Adirondack Mountains to the gentle rolling hills of the Hudson Valley, presents a captivating canvas for exploration. Understanding the intricate details of this terrain is crucial for a myriad of purposes, from outdoor recreation and resource management to urban planning and infrastructure development. This is where topographic maps, with their unique ability to represent elevation and landforms, come into play, offering a powerful tool for navigating, analyzing, and appreciating the state’s diverse geography.
Understanding Topographic Maps: A Visual Language of Elevation
Topographic maps, unlike standard road maps, transcend the simple depiction of roads and towns. They utilize a system of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation, to portray the three-dimensional shape of the land. These lines, like the rings of a tree trunk, reveal the rise and fall of the terrain, providing a visual representation of hills, valleys, plateaus, and other landforms.
The Importance of Topographic Maps for New York State
Topographic maps of New York State hold immense value for various stakeholders, including:
- Outdoor Enthusiasts: Hikers, campers, and outdoor adventurers rely on topographic maps to navigate trails, identify potential hazards like steep slopes and cliffs, and plan routes based on elevation gain and terrain difficulty.
- Land Management Agencies: Agencies like the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) utilize topographic maps for resource management, habitat conservation, and wildfire prevention. The maps help in understanding the distribution of natural resources, identifying areas prone to erosion or flooding, and planning for sustainable land use.
- Civil Engineers and Planners: Topographic maps are essential for infrastructure development projects, such as road construction, dam building, and pipeline installation. They provide crucial information on terrain gradients, slope stability, and potential environmental impacts.
- Researchers and Scientists: Geographers, geologists, and environmental scientists use topographic maps to study landform evolution, analyze soil patterns, and understand the relationship between topography and ecological processes.
- Emergency Response Teams: During natural disasters like floods, landslides, and wildfires, topographic maps assist emergency responders in assessing the extent of damage, identifying evacuation routes, and coordinating rescue efforts.
Deciphering the Language of Contour Lines: A Guide to Reading Topographic Maps
Reading a topographic map requires understanding the conventions and symbols used to represent different features:
- Contour Lines: The most prominent feature on a topographic map, contour lines connect points of equal elevation. The closer the lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the slope.
- Index Contours: Every fifth contour line is typically labeled with its elevation, serving as a reference point for determining the elevation of other points on the map.
- Spot Elevations: Specific points on the map, often peaks or significant features, are marked with their exact elevation.
- Symbols: Topographic maps employ a standardized set of symbols to represent various features, such as roads, rivers, buildings, forests, and wetlands.
Navigating the Landscape: Using Topographic Maps for Outdoor Adventures
For outdoor enthusiasts, topographic maps are invaluable tools for safe and enjoyable adventures:
- Trail Planning: Identifying trails and their elevation profiles allows hikers to choose routes based on their experience and fitness level.
- Hazard Recognition: Topographic maps highlight potential hazards like steep slopes, cliffs, and areas prone to rockfall or landslides.
- Finding Water Sources: Identifying rivers, streams, and lakes on the map can help hikers locate water sources for drinking and camping.
- Estimating Travel Time: Understanding the terrain and elevation changes allows for more accurate estimates of travel time, ensuring adequate preparation and resources.
Beyond the Map: Utilizing Technology for Enhanced Exploration
While traditional topographic maps remain essential, technology has enhanced their use in several ways:
- Digital Topographic Maps: These maps, often available online or through mobile apps, provide interactive features like zoom capabilities, elevation profiles, and route planning tools.
- GPS Devices: Global Positioning System (GPS) devices utilize satellite signals to determine location and elevation, allowing users to navigate trails and track their progress.
- Smartphone Apps: Numerous smartphone apps integrate topographic maps with GPS functionality, providing real-time navigation, elevation data, and other useful features for outdoor adventures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Topographic Maps of New York State
Q: Where can I find topographic maps of New York State?
A: Topographic maps are available from various sources, including:
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS offers a wide range of topographic maps, both in print and digital formats, for New York State. Their website provides access to their map collection and tools for downloading and printing maps.
- New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC): The DEC provides topographic maps for specific areas within the state, focusing on parks, forests, and other natural areas.
- Outdoor Recreation Retailers: Many outdoor recreation stores, such as REI and L.L.Bean, carry topographic maps of New York State.
- Online Retailers: Websites like Amazon and REI.com offer a wide selection of topographic maps for different regions of New York State.
Q: What is the scale of a topographic map?
A: The scale of a topographic map refers to the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. Common scales for topographic maps of New York State include:
- 1:24,000: This scale represents one inch on the map as 24,000 inches (2,000 feet) on the ground.
- 1:62,500: This scale represents one inch on the map as 62,500 inches (5,208 feet) on the ground.
- 1:100,000: This scale represents one inch on the map as 100,000 inches (8,333 feet) on the ground.
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a road map?
A: While both maps provide information about locations, they differ in their focus:
- Topographic Map: Focuses on elevation, terrain, and natural features, using contour lines to represent the land’s three-dimensional shape.
- Road Map: Focuses on roads, towns, and other man-made features, providing information for driving and navigation.
Q: How can I learn to read a topographic map?
A: Learning to read a topographic map is a valuable skill. Here are some resources:
- USGS Website: The USGS website offers tutorials and resources on reading topographic maps.
- Online Tutorials: Numerous online resources provide step-by-step guides and videos on interpreting contour lines and map symbols.
- Outdoor Education Programs: Many organizations offer outdoor education programs that include instruction on map reading and navigation.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps of New York State
- Choose the Right Scale: Select a map with a scale appropriate for your intended activity and the area you’re exploring.
- Familiarize Yourself with Symbols: Understand the symbols used to represent different features on the map, including roads, rivers, forests, and elevation.
- Plan Your Route: Use the map to plan your route, considering elevation gain, terrain difficulty, and potential hazards.
- Mark Key Features: Use a pencil to mark important features on the map, such as trail intersections, water sources, and camping areas.
- Carry a Compass and GPS: A compass and GPS device can be helpful for navigating and staying on track.
Conclusion
Topographic maps of New York State serve as invaluable tools for understanding, navigating, and appreciating the state’s diverse landscape. From outdoor recreation to resource management and infrastructure development, these maps provide a visual language that unlocks the secrets of the terrain. By understanding the principles of contour lines and map symbols, individuals can enhance their outdoor adventures, plan for sustainable land use, and make informed decisions about the state’s natural resources. As technology continues to evolve, topographic maps are becoming increasingly accessible and user-friendly, empowering individuals to explore, analyze, and protect the unique landscapes of New York State.

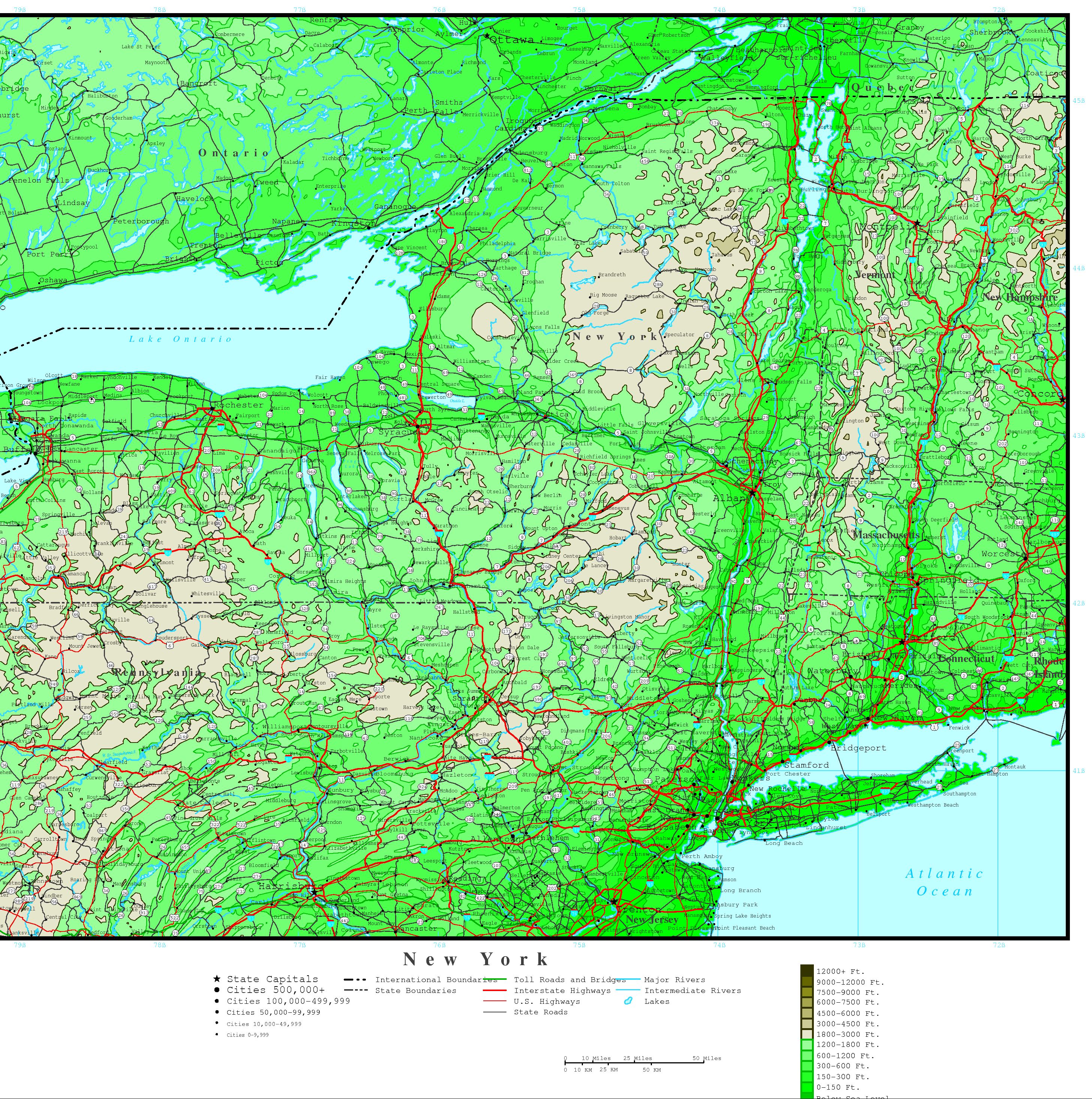
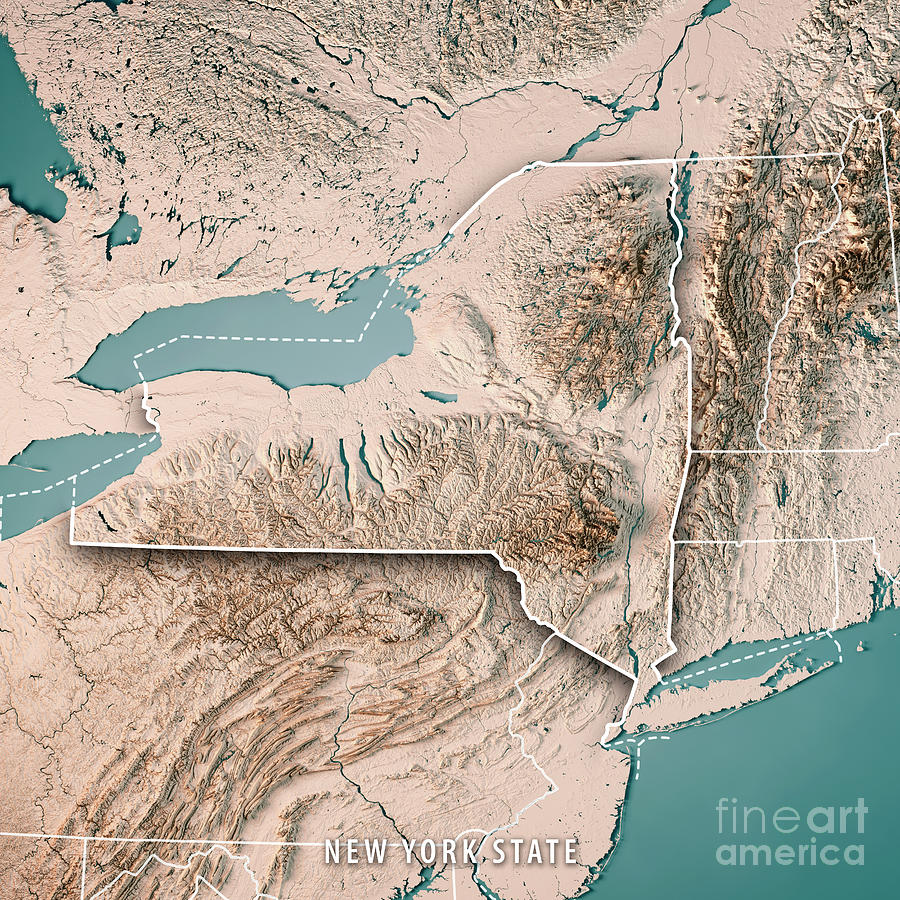

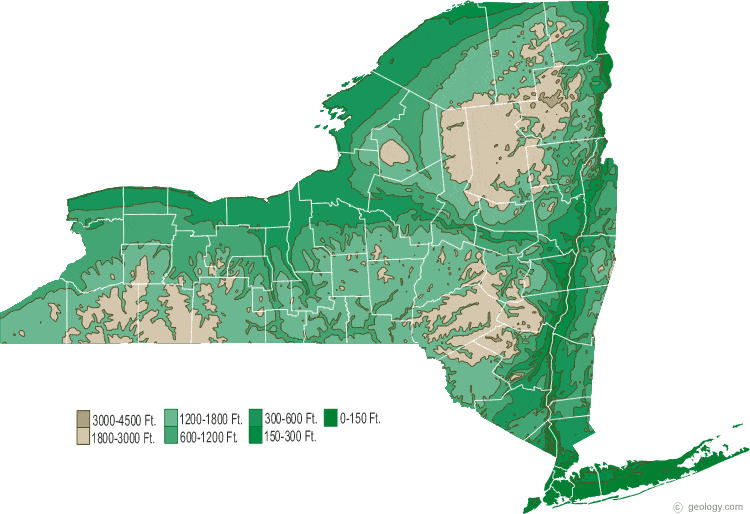

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps of New York State. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!