The Wall: A Map of the World’s Largest Defense Structure
Related Articles: The Wall: A Map of the World’s Largest Defense Structure
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Wall: A Map of the World’s Largest Defense Structure. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Wall: A Map of the World’s Largest Defense Structure
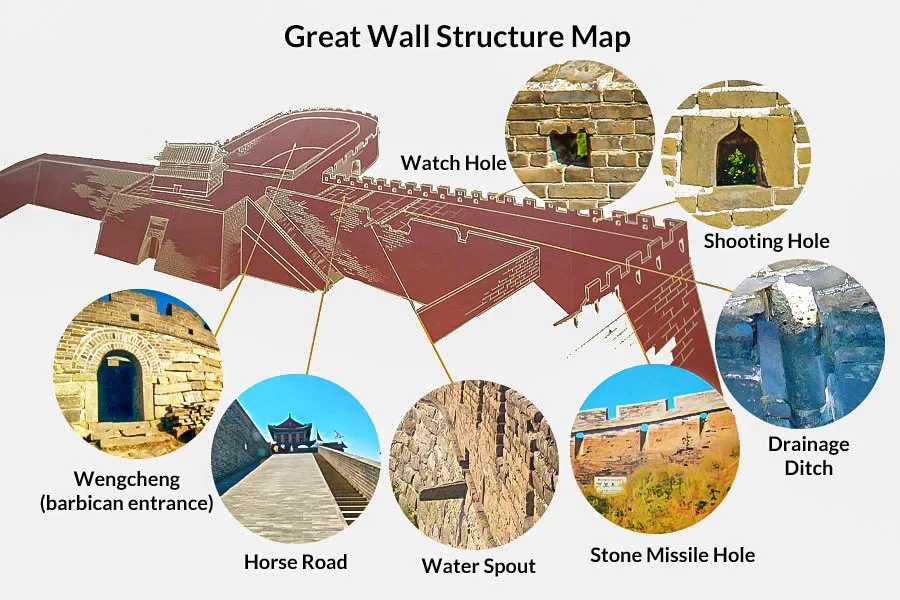
The Great Wall of China, a colossal feat of engineering and a testament to human ambition, stands as one of the most iconic structures in the world. Its history spans centuries, its purpose evolving with the changing tides of power. Yet, understanding the Wall’s significance requires more than just appreciating its physical grandeur. It necessitates understanding its intricate layout, its strategic purpose, and its impact on the landscape and culture of China.
Mapping the Wall: A Complex Tapestry of History and Geography
The "Wall" is not a single monolithic structure, but rather a complex network of fortifications that evolved over time. Its construction began in the 7th century BC, during the Warring States period, with individual states building walls to defend their territories. The Qin Dynasty (221-206 BC) unified these disparate structures, creating the first continuous wall stretching across northern China.
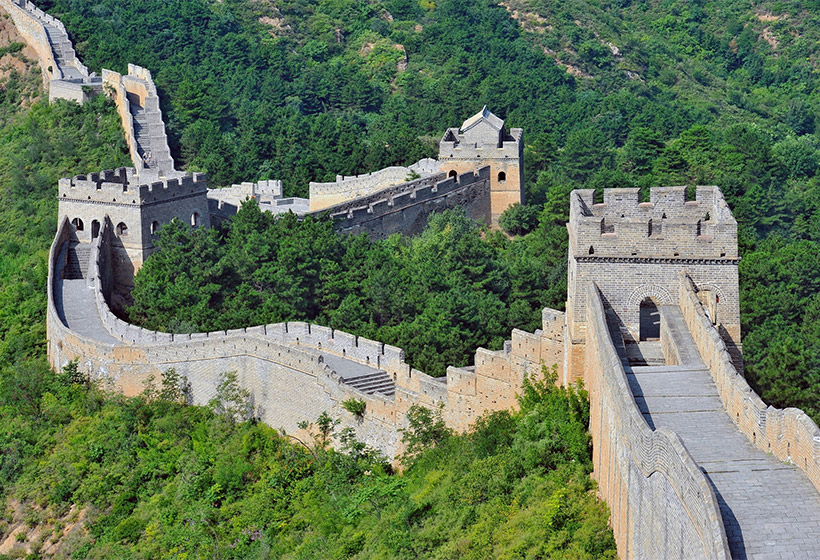
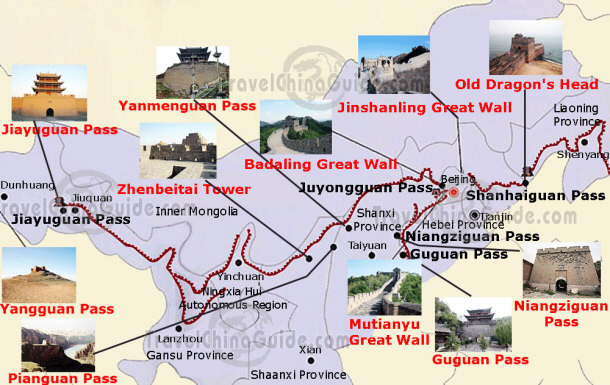
Later dynasties, including the Han, Sui, and Ming, continued to expand and strengthen the Wall. The Ming Dynasty (1368-1644) is credited with constructing the most recognizable section of the Wall, featuring iconic watchtowers and fortified gates. This section, often referred to as the "Ming Wall," is the one most frequently depicted in images and visited by tourists.
Mapping the Wall reveals a remarkable story of adaptation and innovation. Its layout reflects the changing threats faced by China, from nomadic tribes to foreign invaders. The Wall’s path was influenced by natural barriers such as mountains and rivers, as well as strategic considerations like access to trade routes and agricultural land.
Beyond the Physical Structure: The Wall’s Strategic Significance
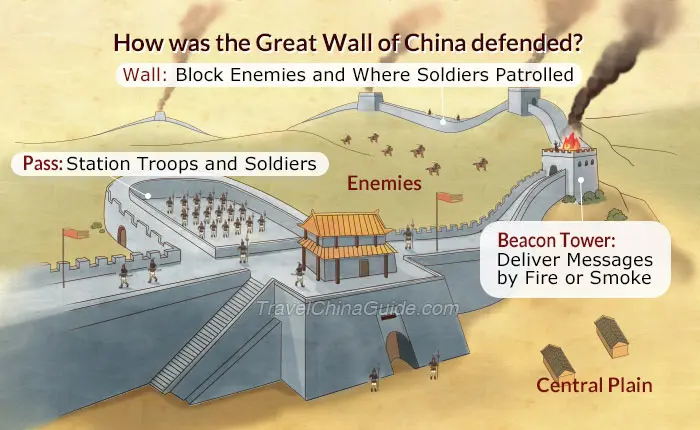
The Wall’s primary function was defense. It served as a barrier against nomadic tribes from the north, preventing raids and invasions. The Wall’s design incorporated innovative features to enhance its defensive capabilities:
- Watchtowers: Strategically placed towers allowed defenders to observe the surrounding area and signal approaching threats.
- Gates: Fortified gates controlled access to the Wall, allowing for controlled entry and exit.
- Defensive Structures: Moats, trenches, and other obstacles were integrated into the Wall’s design to impede attackers.
The Wall’s impact extended beyond its physical presence. It fostered the development of a unique military culture, with specialized units trained in defending the Wall and maintaining its infrastructure. The Wall also played a crucial role in shaping the identity of the Chinese people, symbolizing their resilience and determination in the face of adversity.
Mapping the Wall’s Legacy: From Defense to Tourism
Today, the Great Wall stands as a symbol of China’s rich history and cultural heritage. While no longer serving its original defensive purpose, it has become a major tourist destination, drawing millions of visitors each year.
Mapping the Wall helps us understand its enduring legacy:
- Preservation and Restoration: Mapping the Wall’s different sections and their historical significance informs conservation efforts.
- Cultural Heritage: The Wall’s inclusion on the UNESCO World Heritage List underscores its global importance.
- Economic Impact: Tourism generated by the Wall contributes significantly to the local economy.
FAQs about the Great Wall of China
1. How long is the Great Wall of China?
The Great Wall’s length is a subject of debate. Some estimates suggest it stretches over 21,196 kilometers (13,170 miles), while others place it closer to 8,850 kilometers (5,500 miles). The discrepancy arises from the inclusion of different sections built by various dynasties.
2. What materials were used to build the Great Wall?
The Wall was constructed primarily using rammed earth, brick, stone, and wood. The specific materials varied depending on the location and the time period.
3. How many people died building the Great Wall?
The number of deaths during the Wall’s construction is uncertain. Historical accounts suggest that millions of laborers, including convicts and conscripted soldiers, were involved, and many perished due to harsh working conditions and disease.
4. Can you walk the entire length of the Great Wall?
While the Wall is not continuous throughout its entire length, several sections are accessible to hikers. Walking the entire length is challenging due to the Wall’s condition and the presence of private land.
5. What is the best time to visit the Great Wall?
The best time to visit the Great Wall depends on individual preferences. Spring and autumn offer pleasant weather and fewer crowds, while winter can be cold but offers stunning snow-covered landscapes.
Tips for Visiting the Great Wall of China
- Choose a section: Research the different sections of the Wall and select one that aligns with your interests.
- Plan your transportation: Consider the distance and accessibility of the chosen section when planning transportation.
- Wear comfortable shoes: The Wall can be challenging to walk on, especially during winter.
- Pack water and snacks: There are limited food and drink options at many Wall sections.
- Respect the environment: Leave no trace and avoid touching or damaging the Wall.
Conclusion
The Great Wall of China, a masterpiece of human ingenuity and a testament to the resilience of the Chinese people, continues to fascinate and inspire. Mapping its intricate layout, understanding its strategic purpose, and appreciating its enduring legacy helps us comprehend the profound impact it has had on Chinese history and culture. As a symbol of human ambition and a reminder of the past, the Wall stands as a testament to the power of collective effort and the enduring spirit of humanity.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Wall: A Map of the World’s Largest Defense Structure. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!