The Tigris and Euphrates: A Lifeline Through History
Related Articles: The Tigris and Euphrates: A Lifeline Through History
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Tigris and Euphrates: A Lifeline Through History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Tigris and Euphrates: A Lifeline Through History

The Tigris and Euphrates rivers, flowing through the fertile crescent of the Middle East, have shaped civilizations for millennia. Their importance transcends mere geography; they are the lifeblood of a region rich in history, culture, and innovation. This article delves into the significance of these rivers, exploring their geographical context, historical impact, and the challenges they face today.
A Geographical Tapestry
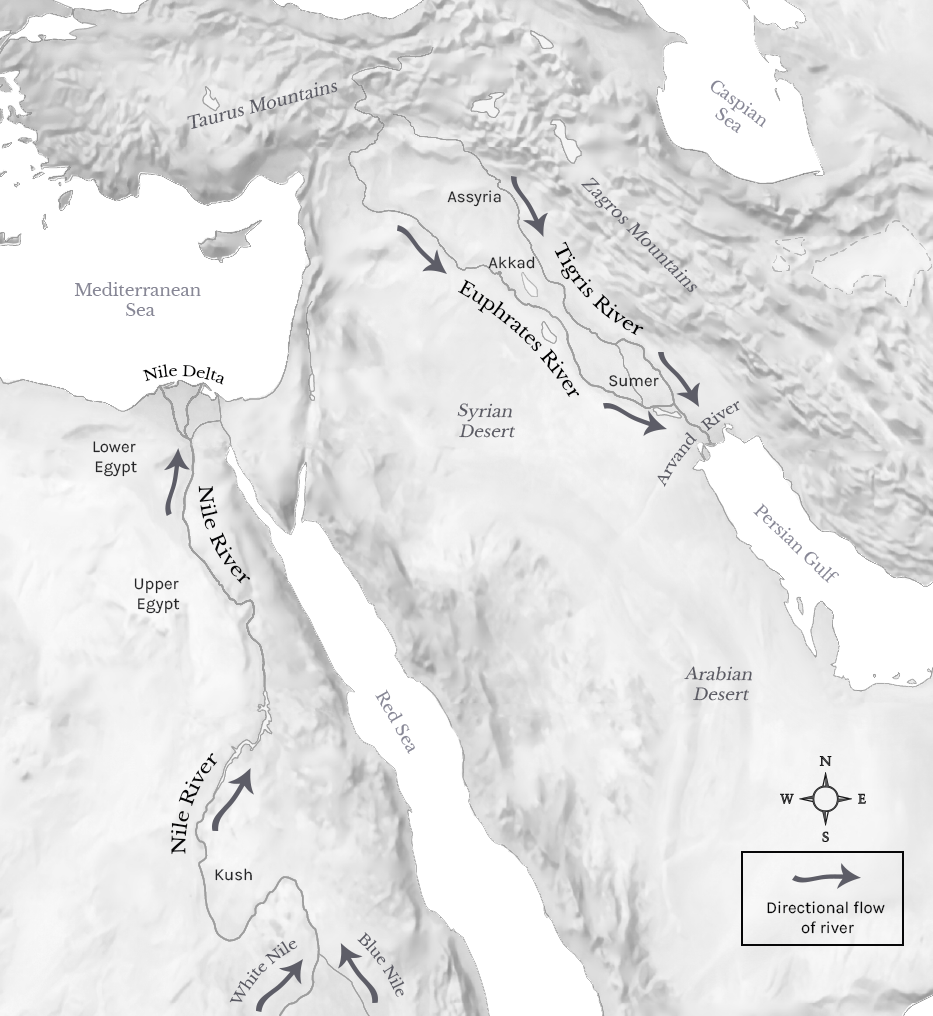
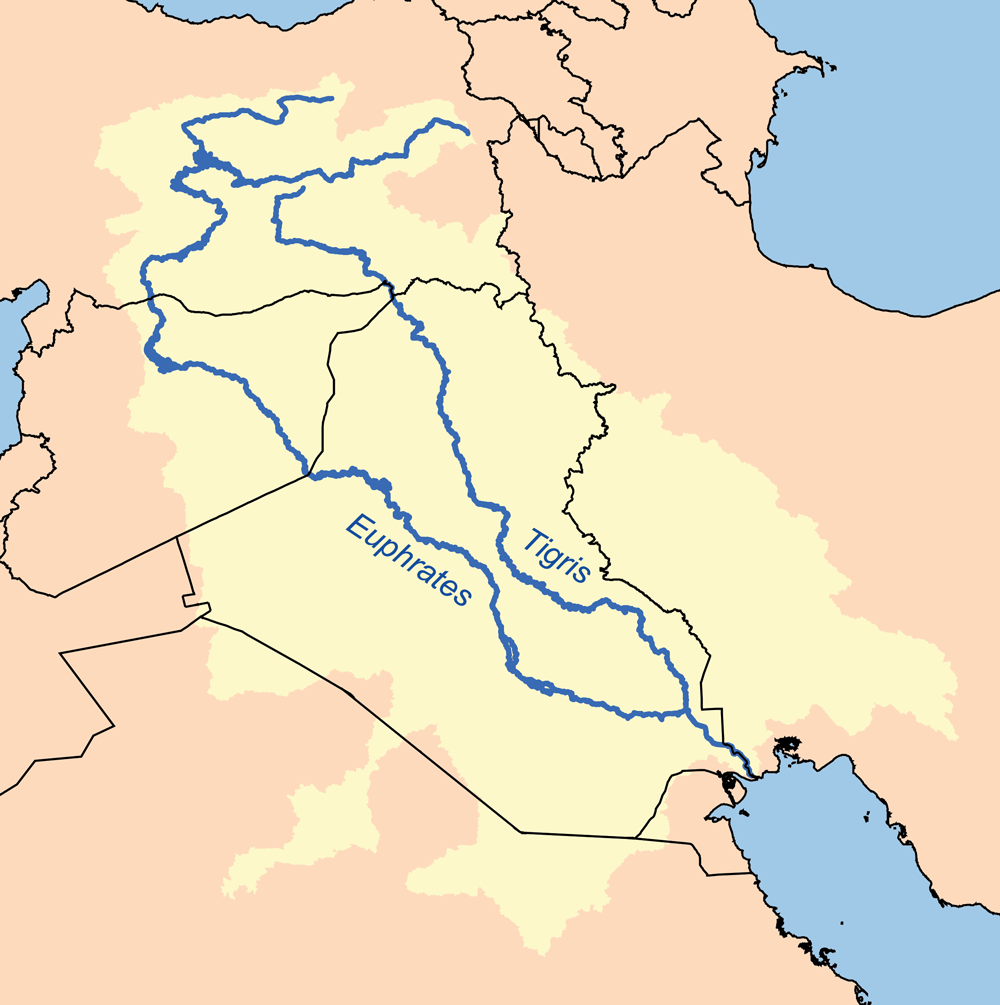
The Tigris and Euphrates originate in the Taurus Mountains of Turkey, flowing southeastwards through a landscape that transitions from mountainous terrain to vast plains. The Tigris, the shorter and more turbulent river, traverses a steeper course, while the Euphrates, meandering across a wider expanse, acts as a more gentle force. These rivers, converging in southern Iraq, form the Mesopotamian Marshlands, a unique ecosystem that once thrived as a cradle of civilization.
A Cradle of Civilization
The fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates, known as Mesopotamia, witnessed the rise of some of the world’s earliest civilizations. Sumerians, Babylonians, Assyrians, and Persians all flourished in this region, leaving behind a legacy of monumental architecture, sophisticated writing systems, and groundbreaking advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture. The rivers provided a reliable source of water for irrigation, enabling the development of agriculture, which in turn supported complex societies and the growth of cities.
The Rivers’ Influence on History
The Tigris and Euphrates played a crucial role in shaping the history of the region. Their waters facilitated trade and transportation, connecting disparate communities and empires. The rivers also served as natural barriers, providing strategic advantage to empires seeking to defend their territories.
- Sumerian Civilization: The Sumerians, one of the earliest known civilizations, emerged around 4000 BCE in Mesopotamia. They developed advanced irrigation systems, which allowed them to exploit the fertile land for agriculture. This agricultural surplus enabled the growth of cities, trade, and social complexity.
- Babylonian Empire: The Babylonians, known for their advanced legal system and astronomical observations, flourished under Hammurabi in the 18th century BCE. Their empire, stretching across Mesopotamia, relied heavily on the Tigris and Euphrates for irrigation, transportation, and trade.
- Assyrian Empire: The Assyrians, known for their military prowess, emerged as a dominant force in the region in the 9th century BCE. They built a vast empire, utilizing the Tigris and Euphrates for transportation and to support their military campaigns.
- Persian Empire: The Persians, under Cyrus the Great, conquered the Babylonian Empire in the 6th century BCE. They recognized the importance of the Tigris and Euphrates, integrating them into their vast network of roads and canals, facilitating trade and communication across their empire.
Beyond Ancient Empires: The Rivers’ Enduring Legacy
The Tigris and Euphrates continue to play a vital role in the modern world. Their waters support agriculture, provide drinking water for millions, and generate hydroelectric power. However, the rivers also face numerous challenges, including:
- Water Scarcity: Increasing population growth and the demands of modern agriculture have led to a depletion of water resources in the region. This has resulted in water shortages, conflicts between upstream and downstream users, and the degradation of wetlands.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities have polluted the rivers with chemicals, fertilizers, and sewage. This poses a threat to human health, wildlife, and the overall ecosystem.
- Climate Change: Climate change is exacerbating the challenges facing the Tigris and Euphrates. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns are leading to more frequent droughts, further straining water resources.
Navigating the Future: Challenges and Opportunities
The future of the Tigris and Euphrates depends on collaborative efforts to manage these vital resources sustainably. This requires:
- Regional Cooperation: The countries sharing these rivers (Turkey, Syria, Iraq, and Iran) must work together to develop a comprehensive water management plan that addresses the needs of all stakeholders.
- Sustainable Water Use: Promoting efficient irrigation techniques, reducing water waste in agriculture, and investing in water conservation measures are crucial steps towards sustainable water management.
- Environmental Protection: Stricter regulations and enforcement measures are needed to prevent pollution and protect the delicate ecosystem of the Tigris and Euphrates.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Investing in infrastructure to adapt to the effects of climate change, such as drought-resistant crops and water storage facilities, is essential to ensure the long-term sustainability of the region.
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers?
A: The Tigris and Euphrates rivers are vital for the Middle East, providing water for irrigation, drinking water for millions, and generating hydroelectric power. They also have a rich historical significance, having played a crucial role in the rise and fall of ancient civilizations.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the Tigris and Euphrates?
A: The rivers face challenges such as water scarcity, pollution, and the impacts of climate change. These challenges threaten the livelihoods of millions and the delicate ecosystem of the region.
Q: What can be done to address the challenges facing the Tigris and Euphrates?
A: Addressing these challenges requires regional cooperation, sustainable water use, environmental protection, and adaptation to climate change.
Tips
- Learn about the history and culture of the Tigris and Euphrates region. Understanding the region’s past can help appreciate the present challenges and the need for sustainable management.
- Support organizations working to protect the environment and promote sustainable water management in the region.
- Reduce your own water consumption and promote water conservation practices.
- Stay informed about the latest developments regarding the Tigris and Euphrates rivers and advocate for sustainable solutions.
Conclusion
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers, a lifeline for millennia, face a crossroads. While their historical importance remains undeniable, the challenges they face today require a concerted effort to ensure their future. Through regional cooperation, sustainable water management, environmental protection, and climate change adaptation, these rivers can continue to nourish the region and its people for generations to come.



.PNG)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Tigris and Euphrates: A Lifeline Through History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!