The Physical Geography of the Middle East: A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes
Related Articles: The Physical Geography of the Middle East: A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Physical Geography of the Middle East: A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Physical Geography of the Middle East: A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes

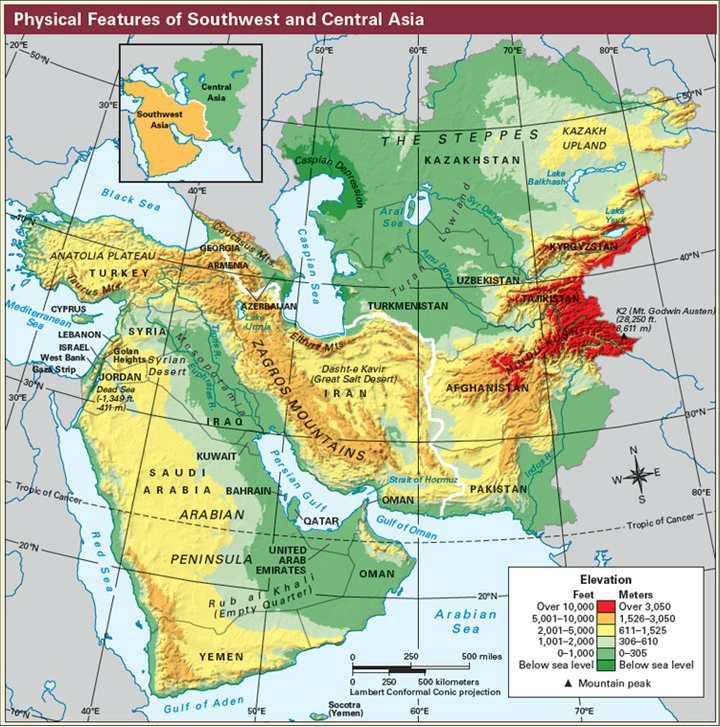
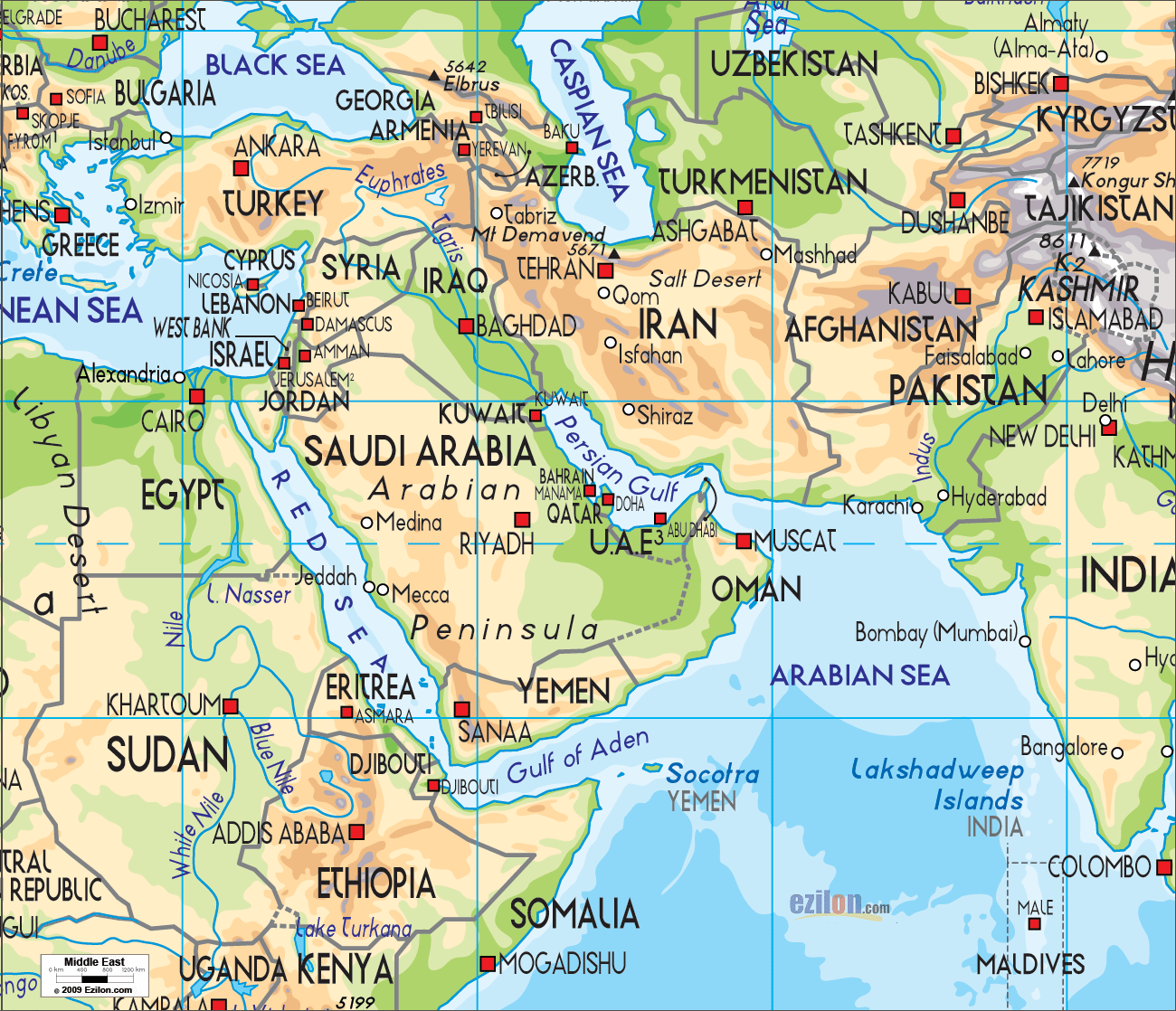
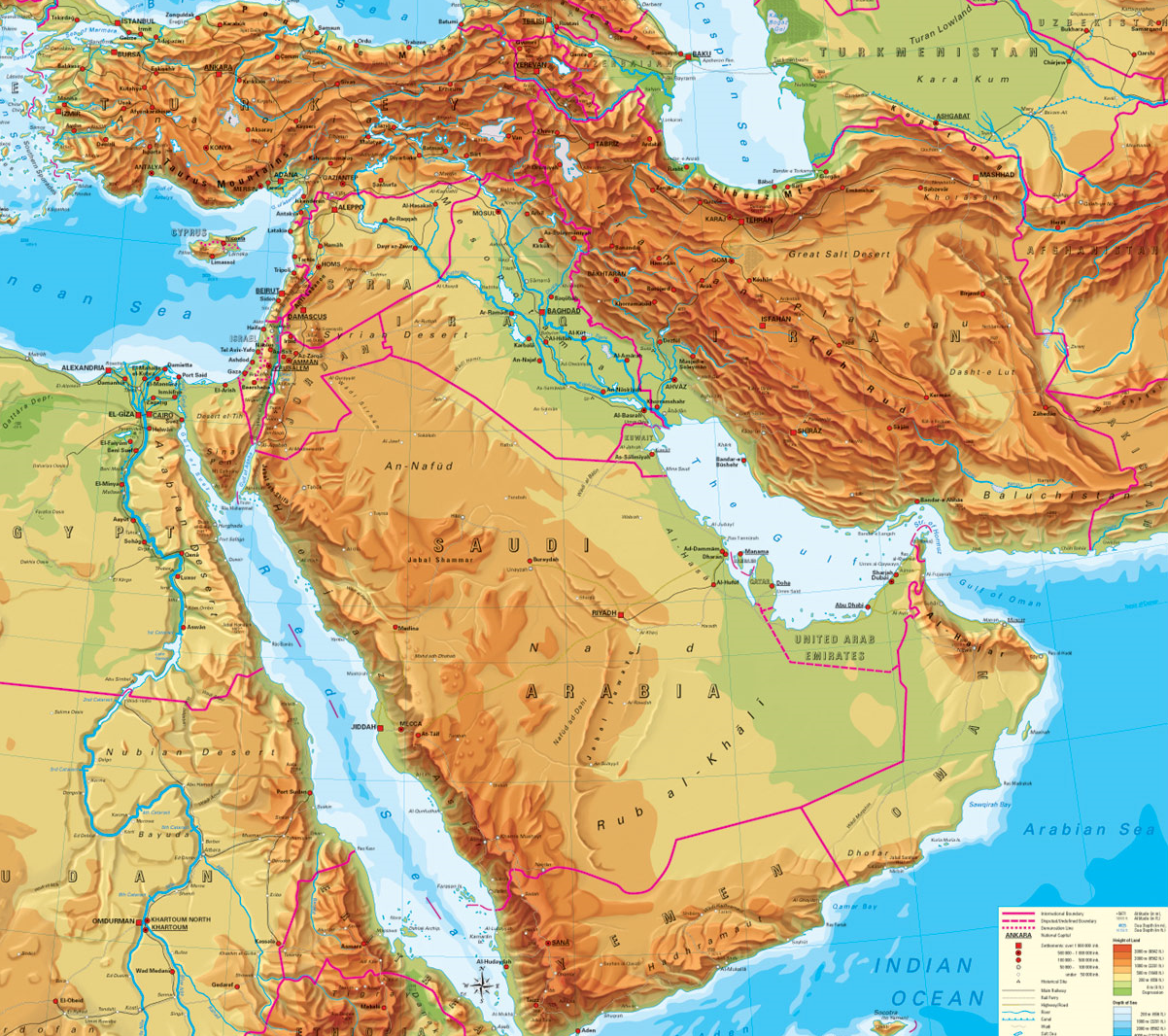
The Middle East, a region encompassing a vast expanse of land stretching from North Africa to Central Asia, is characterized by a remarkable diversity of physical features. This intricate mosaic of landscapes, from towering mountains to scorching deserts, has profoundly shaped the region’s history, culture, and way of life. Understanding these geographical features is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the Middle East and appreciating its unique significance in the global context.
Mountains: A Backbone of Resilience
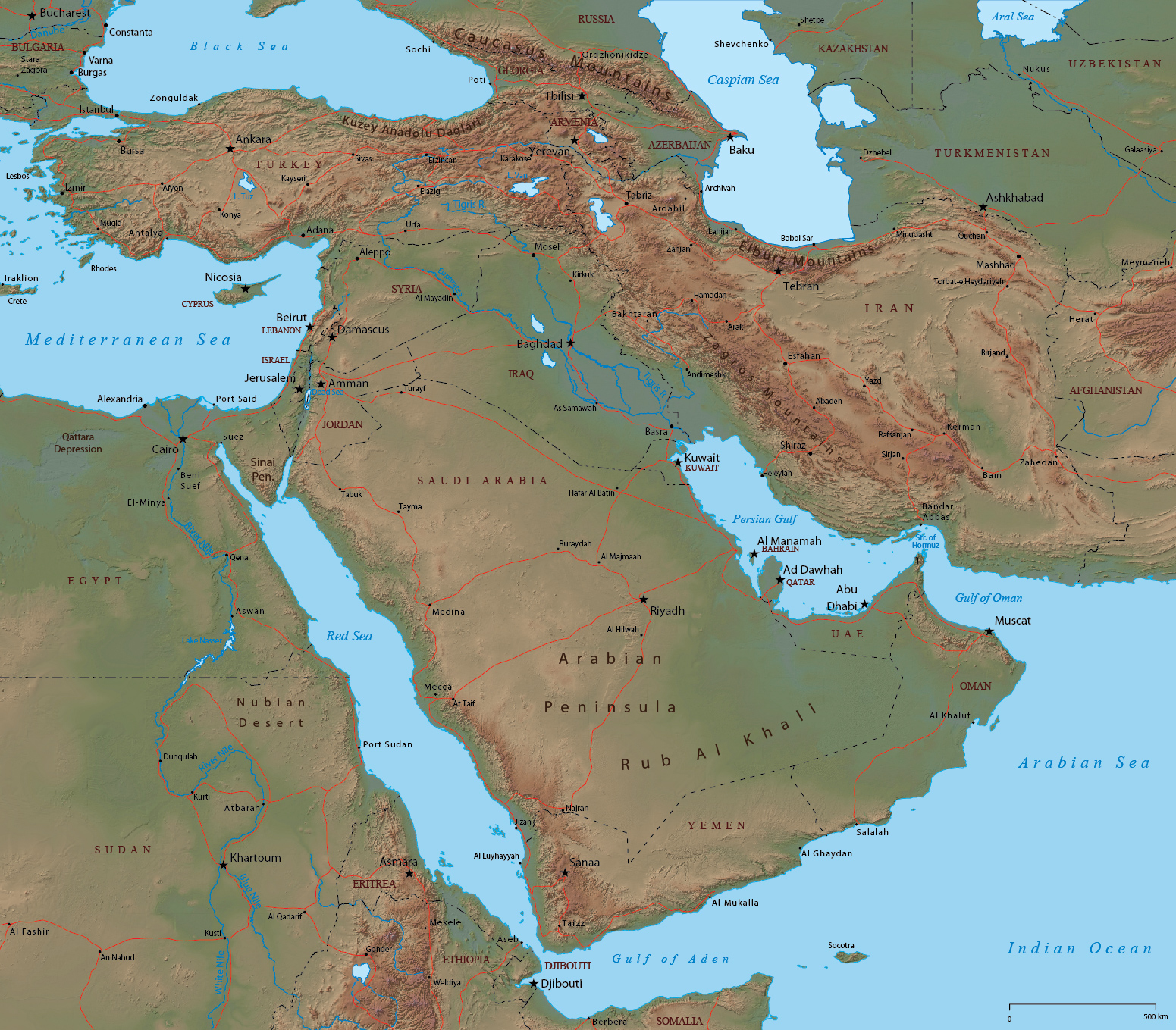
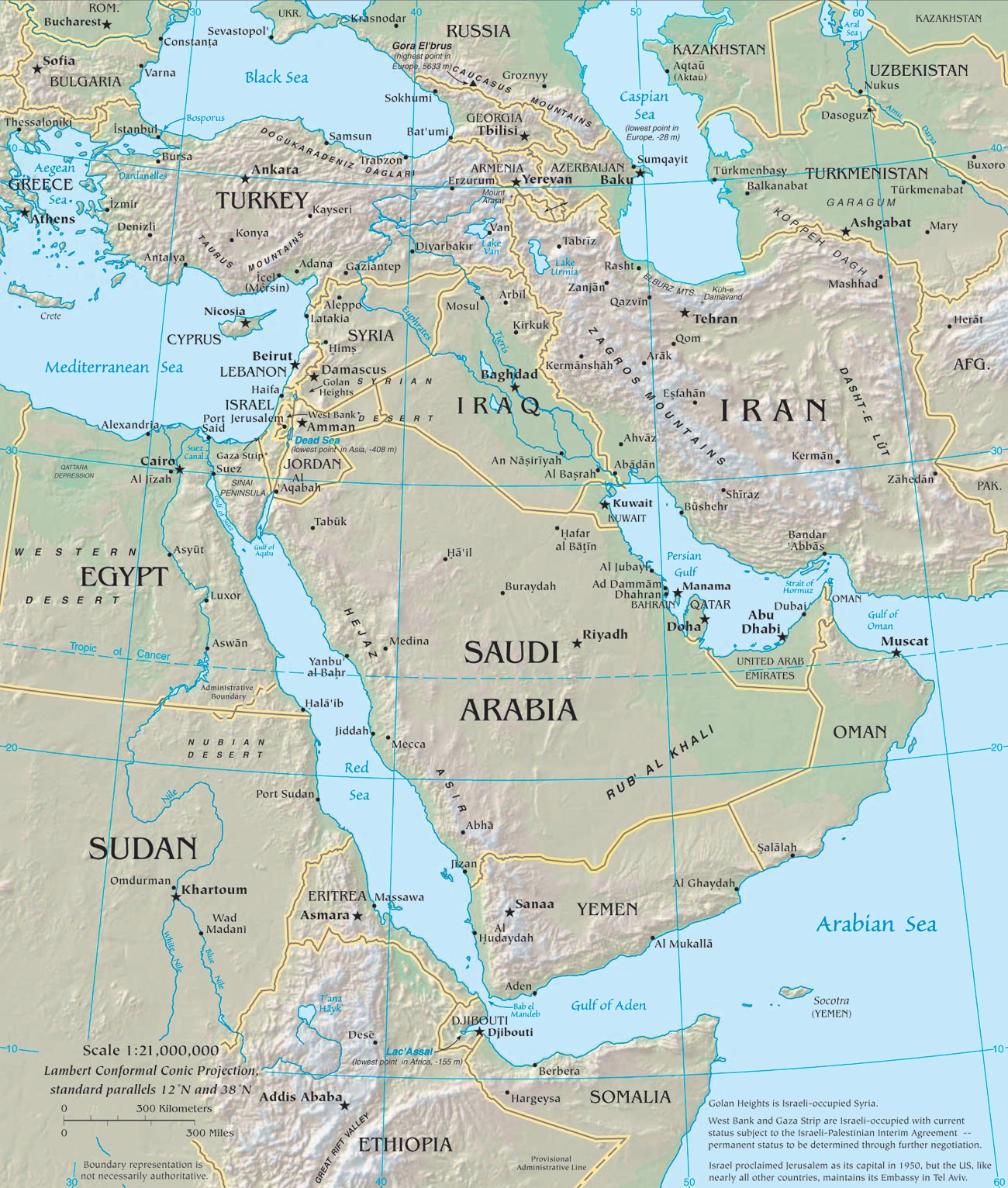
The Middle East is home to several prominent mountain ranges, forming a backbone across the region. The Zagros Mountains, stretching from Turkey through Iraq and Iran, are a formidable barrier, separating the Iranian Plateau from the Mesopotamian Plain. These mountains, formed by the collision of the Arabian and Eurasian tectonic plates, are a source of valuable mineral resources and provide a refuge for diverse flora and fauna.
The Taurus Mountains, located in southern Turkey, are another significant range, marking the southern boundary of the Anatolian Plateau. These mountains are known for their rugged terrain, abundant forests, and historic significance, hosting numerous ancient ruins and settlements.
The Lebanon Mountains, rising along the Mediterranean coast, are a prominent feature of Lebanon, known for their majestic peaks and fertile slopes, which have been cultivated for centuries. The Anti-Lebanon Mountains, paralleling the Lebanon Mountains to the east, are characterized by their dry, rocky landscape, offering a stark contrast to the lushness of their western counterparts.
Deserts: A Harsh Yet Inspiring Realm
Deserts dominate a significant portion of the Middle East, covering vast expanses of land with their distinctive aridity and harsh conditions. The Arabian Desert, the largest in the region, stretches across the Arabian Peninsula, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes, from rolling sand dunes to rocky plateaus.
The Syrian Desert, situated in the eastern part of the Levant, is known for its arid climate and sparse vegetation, offering a challenging environment for human settlement. The Negev Desert, located in southern Israel, is a rugged and desolate landscape, home to ancient archaeological sites and a unique ecosystem adapted to the harsh conditions.
Plateaus and Plains: Land of Contrasts
The Middle East also features extensive plateaus and plains, each with its own unique characteristics. The Iranian Plateau, a vast elevated region in Iran, is characterized by its arid climate, high altitudes, and mineral resources. The Anatolian Plateau, located in Turkey, is a fertile region known for its agriculture, with numerous rivers flowing through its valleys.
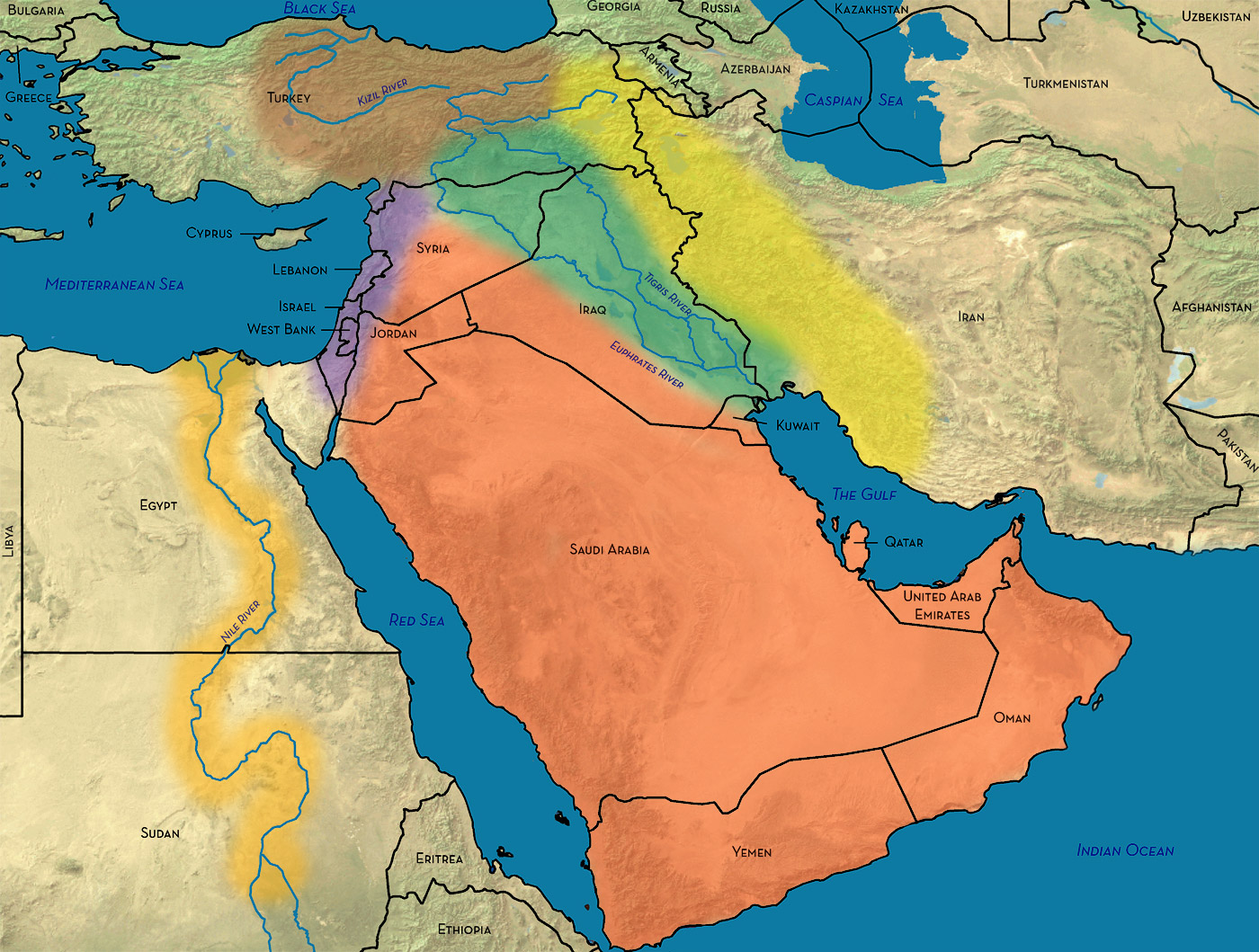
The Mesopotamian Plain, situated between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, is a historic region known for its fertile soil and its role as the birthplace of ancient civilizations. The Jordan Valley, a narrow depression running along the Jordan River, is a fertile corridor, providing a vital water source for the region.
Water Bodies: Lifeline of the Middle East
The Middle East is home to several important water bodies, playing a crucial role in sustaining life and shaping the region’s history. The Mediterranean Sea, bordering the region to the west, has been a vital trade route and a source of sustenance for centuries.
The Red Sea, separating the Arabian Peninsula from Africa, is a rich marine environment, renowned for its diverse coral reefs and marine life. The Persian Gulf, located between the Arabian Peninsula and Iran, is a major source of oil and gas, playing a significant role in the global energy market.
The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, flowing through Iraq, are essential water sources for agriculture and human settlements, playing a crucial role in the development of ancient Mesopotamia. The Jordan River, flowing through Lebanon, Syria, Israel, and Jordan, is a vital resource for water supply and irrigation, but also a source of conflict due to its limited resources.
Volcanoes: A Remnant of the Earth’s Fire
While not as prevalent as in other parts of the world, the Middle East features several volcanic features, offering a glimpse into the Earth’s dynamic geological processes. The Mount Ararat, located in eastern Turkey, is a dormant volcano, known for its biblical significance and its majestic peak.
The Mount Damavand, located in Iran, is the highest peak in the Middle East and a dormant volcano, with its snow-capped summit offering stunning views of the surrounding landscape. The Mount Sabalan, also located in Iran, is another dormant volcano, known for its hot springs and its unique ecosystem.
The Importance of Physical Features
The diverse physical features of the Middle East have profoundly influenced the region’s history, culture, and way of life. The mountains have provided protection and strategic advantage, shaping the course of conflicts and empires. The deserts have tested the resilience of human settlement, fostering adaptation and innovation. The plateaus and plains have been the cradle of civilizations, offering fertile land for agriculture and trade.
The water bodies have been lifelines for communities, providing sustenance, transportation, and trade routes. The volcanoes, though dormant, serve as a reminder of the Earth’s dynamic nature, shaping the landscape and influencing the region’s geological history.
FAQs about the Physical Features of the Middle East
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in the Middle East?
A: The major mountain ranges in the Middle East include the Zagros Mountains, Taurus Mountains, Lebanon Mountains, Anti-Lebanon Mountains, and the Atlas Mountains (in North Africa, which is often considered part of the Middle East).
Q: What are the main deserts in the Middle East?
A: The main deserts in the Middle East include the Arabian Desert, Syrian Desert, Negev Desert, and the Sahara Desert (in North Africa, which is often considered part of the Middle East).
Q: What are the major plateaus and plains in the Middle East?
A: The major plateaus and plains in the Middle East include the Iranian Plateau, Anatolian Plateau, Mesopotamian Plain, and the Jordan Valley.
Q: What are the major water bodies in the Middle East?
A: The major water bodies in the Middle East include the Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, Persian Gulf, Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, Jordan River, Nile River (in North Africa, which is often considered part of the Middle East), and the Dead Sea.
Q: What are the major volcanoes in the Middle East?
A: The major volcanoes in the Middle East include Mount Ararat, Mount Damavand, and Mount Sabalan.
Tips for Studying the Physical Features of the Middle East
- Utilize maps: Explore detailed maps of the Middle East to visualize the location and extent of its various physical features.
- Research individual features: Conduct in-depth research on specific mountains, deserts, plateaus, plains, water bodies, and volcanoes to gain a comprehensive understanding of their unique characteristics.
- Explore satellite imagery: Use online tools like Google Earth to view satellite imagery of the region, providing a visual perspective on the landscape and its features.
- Read historical accounts: Examine historical texts and accounts to understand how the physical features of the Middle East have shaped the region’s history and culture.
Conclusion
The physical features of the Middle East are a testament to the region’s unique geological history and diverse landscape. From towering mountains to scorching deserts, from fertile plains to vast plateaus, the region presents a fascinating tapestry of contrasts, shaping the lives of its people and influencing the course of history. Understanding these physical features is essential for comprehending the complexities of the Middle East and appreciating its significance in the global context.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Physical Geography of the Middle East: A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!