The Ottoman Empire in World War I: A Map Unveils a Complex Story
Related Articles: The Ottoman Empire in World War I: A Map Unveils a Complex Story
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Ottoman Empire in World War I: A Map Unveils a Complex Story. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ottoman Empire in World War I: A Map Unveils a Complex Story
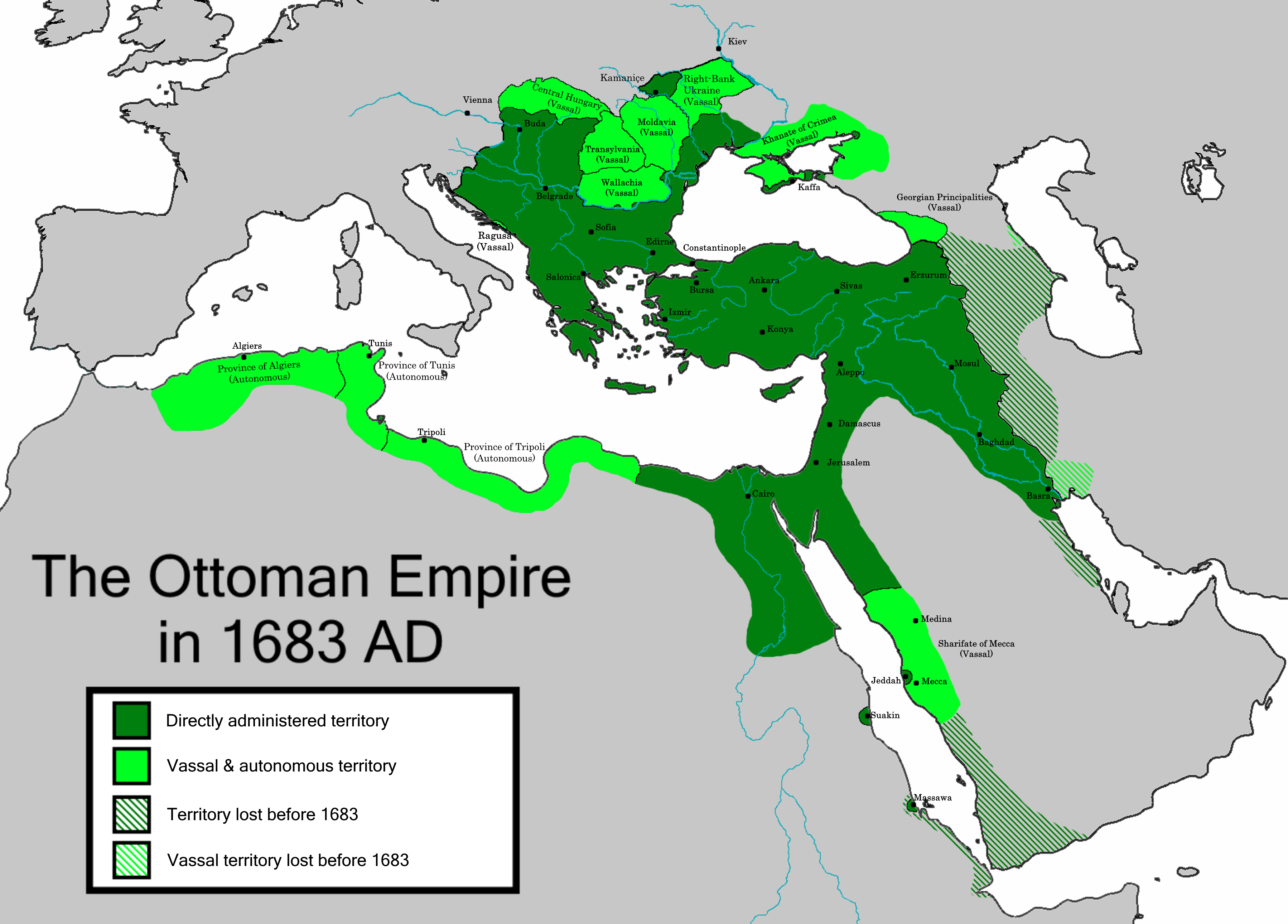
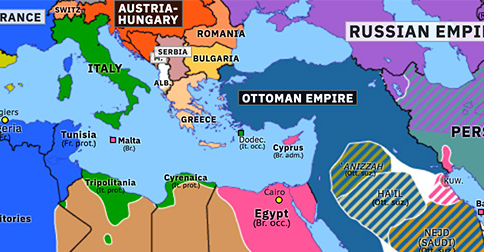
The Ottoman Empire, a sprawling multi-ethnic and multi-religious realm, found itself at the heart of a global conflict in 1914. Its involvement in World War I, driven by a complex web of political and economic motivations, had profound consequences for the empire’s future and the reshaping of the Middle East. Examining a map depicting the Ottoman Empire during World War I provides a crucial lens through which to understand the war’s impact on the region and the empire’s eventual demise.
A Vast and Diverse Empire:
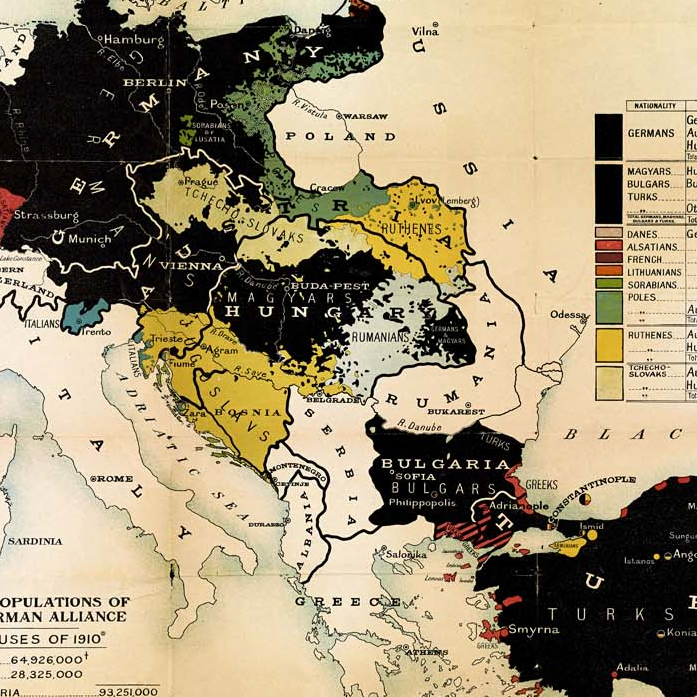
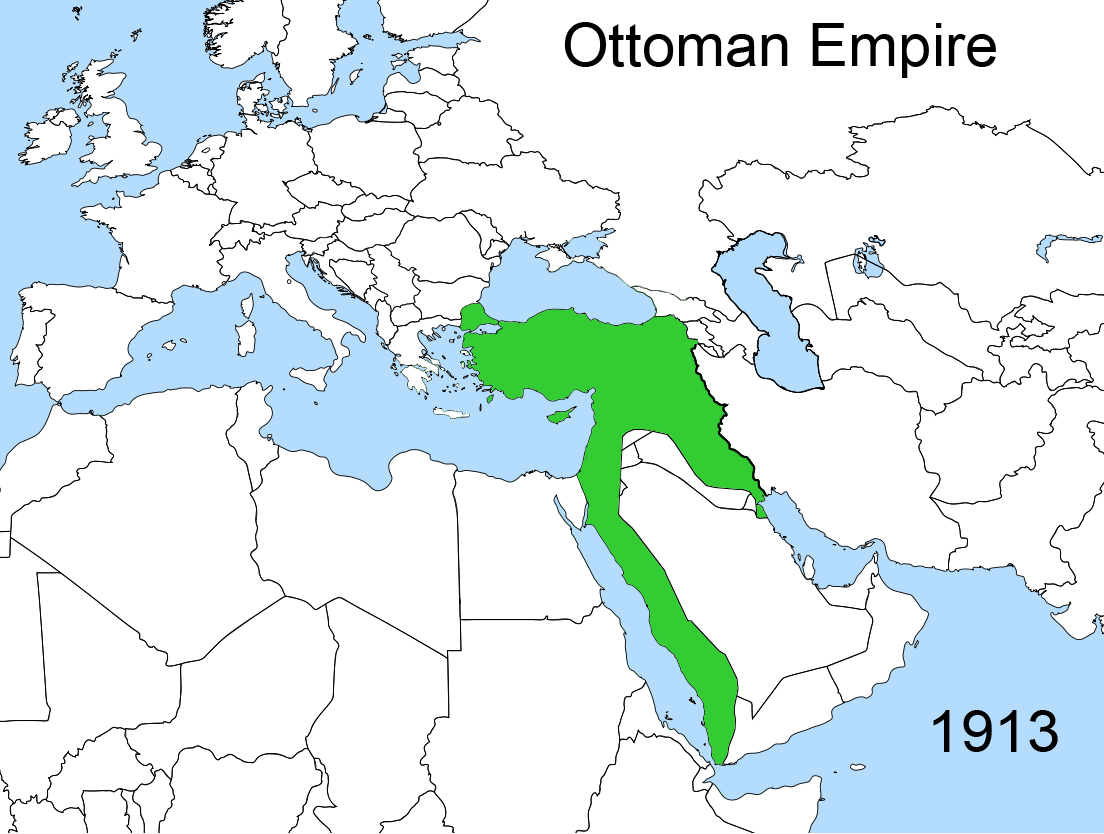
The Ottoman Empire in 1914 stretched across three continents, encompassing a vast territory from southeastern Europe to North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Its diverse population included Turks, Arabs, Greeks, Armenians, Kurds, and many other ethnicities, each with their own cultural and religious identities. This internal diversity was a source of both strength and weakness for the empire, as it faced challenges in maintaining unity and managing conflicting aspirations.
The Ottoman Empire’s Strategic Location:
The Ottoman Empire’s strategic location, controlling key land and sea routes between Europe, Asia, and Africa, made it a vital player in global affairs. This strategic importance was further amplified during World War I, as the empire’s vast territory became a battleground for the Allied and Central Powers. The Ottoman Empire’s control over the Dardanelles Strait, a vital waterway connecting the Black Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, was particularly crucial for the Allied Powers, who sought to secure supply routes to Russia.
The Ottoman Empire’s Entry into the War:
The Ottoman Empire’s entry into World War I on the side of the Central Powers in 1914 was a pivotal moment in the conflict. The empire’s decision was driven by a confluence of factors:
- The Rise of German Influence: Germany’s growing economic and military influence in the Ottoman Empire, particularly through the construction of the Baghdad Railway, had created a strong alliance between the two powers.
- The Ottoman Empire’s Desire for Expansion: The Ottoman Empire, seeking to regain lost territories in the Balkans and the Caucasus, saw an opportunity for territorial expansion through its alliance with Germany.
- The Ottoman Empire’s Fear of Russia: The Ottoman Empire harbored a deep-seated fear of Russia’s expansionist ambitions in the region, particularly in the Caucasus. Joining the Central Powers was seen as a means to counter Russian influence.
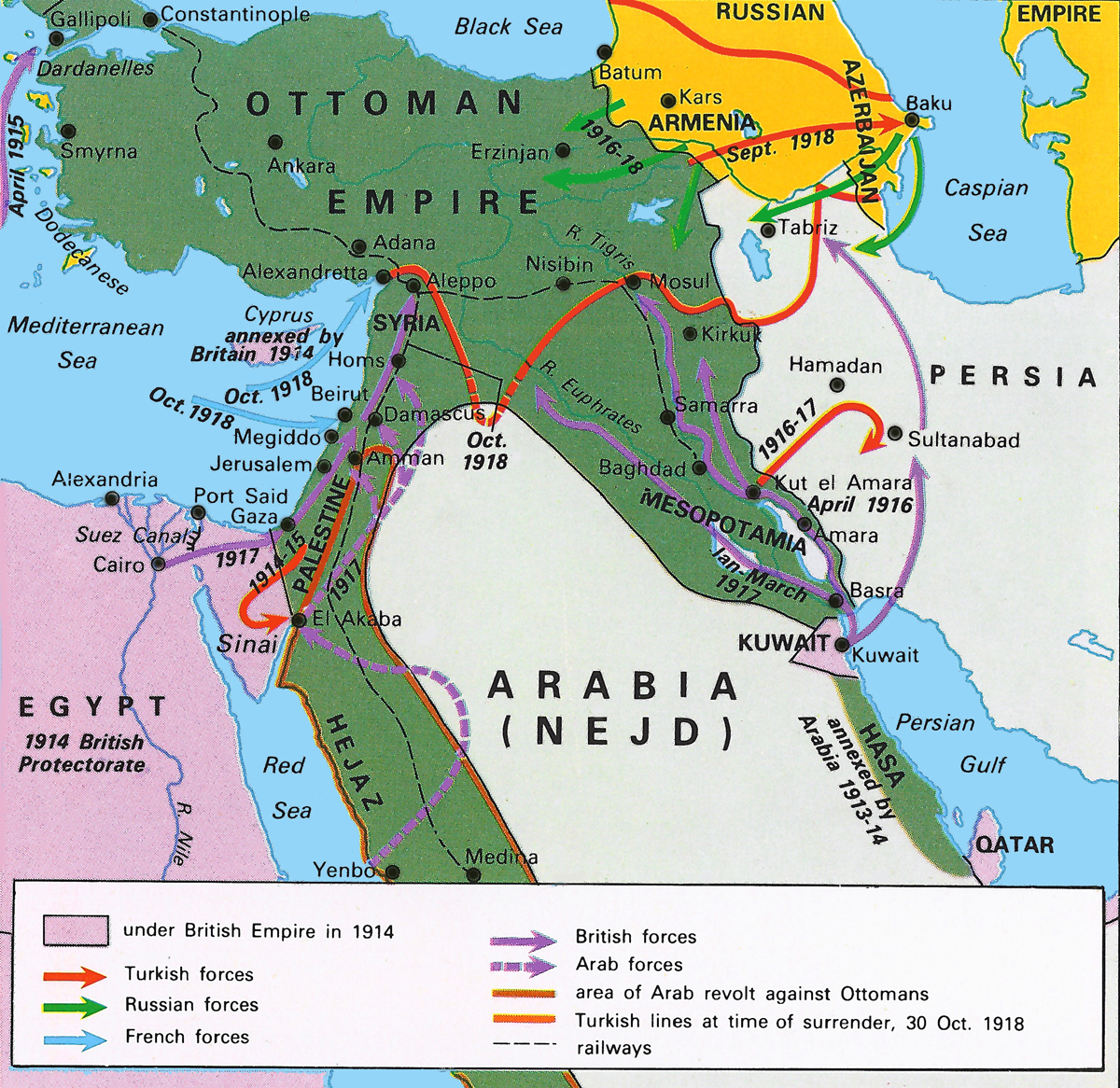
The Ottoman Empire’s War Front:
The Ottoman Empire’s war front was vast and multifaceted, encompassing multiple theaters of war:
- The Dardanelles Campaign: The Allied Powers’ attempt to capture the Dardanelles Strait in 1915, aiming to establish a supply route to Russia, resulted in a bloody stalemate and a significant Allied defeat.
- The Caucasus Campaign: The Ottoman Empire fought against Russia in the Caucasus, aiming to secure control of the region and prevent Russian expansion. This campaign was characterized by fierce battles and shifting control of territory.
- The Middle Eastern Front: The Ottoman Empire fought against the British Empire in the Middle East, particularly in Mesopotamia and Palestine. This front saw the rise of Arab nationalism and the eventual defeat of the Ottoman Empire.
The Ottoman Empire’s Internal Challenges:
The Ottoman Empire faced numerous internal challenges during the war:
- Ethnic Tensions: The war exacerbated ethnic tensions within the empire, particularly between Turks and Armenians. The Armenian Genocide, a systematic campaign of extermination of Armenians by the Ottoman government, occurred during this period.
- Economic Strain: The war placed immense strain on the Ottoman Empire’s economy, leading to shortages of food, supplies, and manpower.
- Political Instability: The war weakened the Ottoman government and led to a rise in dissent and opposition.
The Ottoman Empire’s Collapse:
The Ottoman Empire’s defeat in World War I marked the end of its long and complex history. The empire’s territories were divided among the victorious Allied Powers, leading to the creation of new nation-states in the Middle East, including Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Palestine. The Ottoman Empire’s collapse had a profound impact on the region, shaping its political landscape and leaving a lasting legacy of ethnic and religious tensions.
The Ottoman Empire’s Legacy:
The Ottoman Empire’s involvement in World War I had a profound impact on the course of history. The empire’s defeat led to the redrawing of the map of the Middle East and the emergence of new nation-states. The war also contributed to the rise of nationalism and the decline of empires in the region. The Ottoman Empire’s legacy continues to shape the Middle East today, with its diverse population, complex history, and lingering ethnic and religious tensions.
FAQs about the Ottoman Empire’s Map during World War I:
Q: What were the main reasons for the Ottoman Empire’s entry into World War I?
A: The Ottoman Empire’s entry into World War I was driven by a combination of factors, including the growing influence of Germany, the desire for territorial expansion, and the fear of Russia’s ambitions.
Q: What were the key theaters of war for the Ottoman Empire?
A: The Ottoman Empire’s war front encompassed the Dardanelles Campaign, the Caucasus Campaign, and the Middle Eastern Front.
Q: What were the main internal challenges faced by the Ottoman Empire during the war?
A: The Ottoman Empire faced significant internal challenges, including ethnic tensions, economic strain, and political instability.
Q: What were the consequences of the Ottoman Empire’s defeat in World War I?
A: The Ottoman Empire’s defeat led to the empire’s collapse, the redrawing of the map of the Middle East, and the emergence of new nation-states.
Q: What is the significance of the Ottoman Empire’s map during World War I?
A: The map provides a crucial visual representation of the Ottoman Empire’s vast territory, its strategic location, and the impact of the war on its borders and internal divisions.
Tips for Understanding the Ottoman Empire’s Map during World War I:
- Focus on the key geographical features: Pay attention to the strategic locations of the Dardanelles Strait, the Caucasus region, and the Middle Eastern territories.
- Consider the ethnic and religious diversity of the empire: The map highlights the empire’s multi-ethnic and multi-religious population, which played a significant role in the war.
- Analyze the boundaries of the empire before and after the war: The map reveals the empire’s territorial losses and the emergence of new nation-states.
- Research the major battles and campaigns: Understanding the key battles and campaigns will provide context for the map and its strategic significance.
Conclusion:
The Ottoman Empire’s map during World War I serves as a vital tool for understanding the empire’s role in the global conflict and its eventual demise. It highlights the empire’s strategic location, its internal divisions, and the impact of the war on its borders and population. By studying this map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex history of the Ottoman Empire and its enduring legacy in the Middle East.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ottoman Empire in World War I: A Map Unveils a Complex Story. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!