Syria: A Crossroads of History and Geography
Related Articles: Syria: A Crossroads of History and Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Syria: A Crossroads of History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Syria: A Crossroads of History and Geography

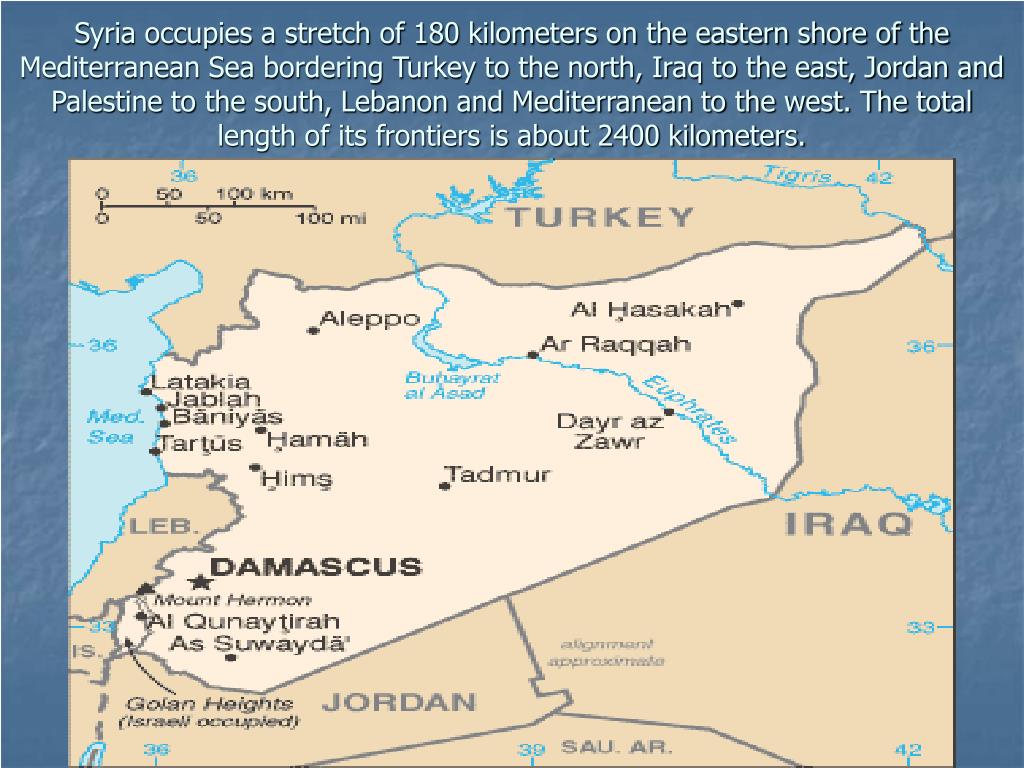
Syria, nestled in the heart of the Middle East, occupies a strategically important position, making it a crossroads of history, culture, and trade for millennia. Its geographical location, nestled between the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Desert, has shaped its destiny, influencing its political, social, and economic landscape.
A Land of Diverse Landscapes:
Syria’s geographical diversity is striking, encompassing a range of landscapes that contribute to its unique character.
-
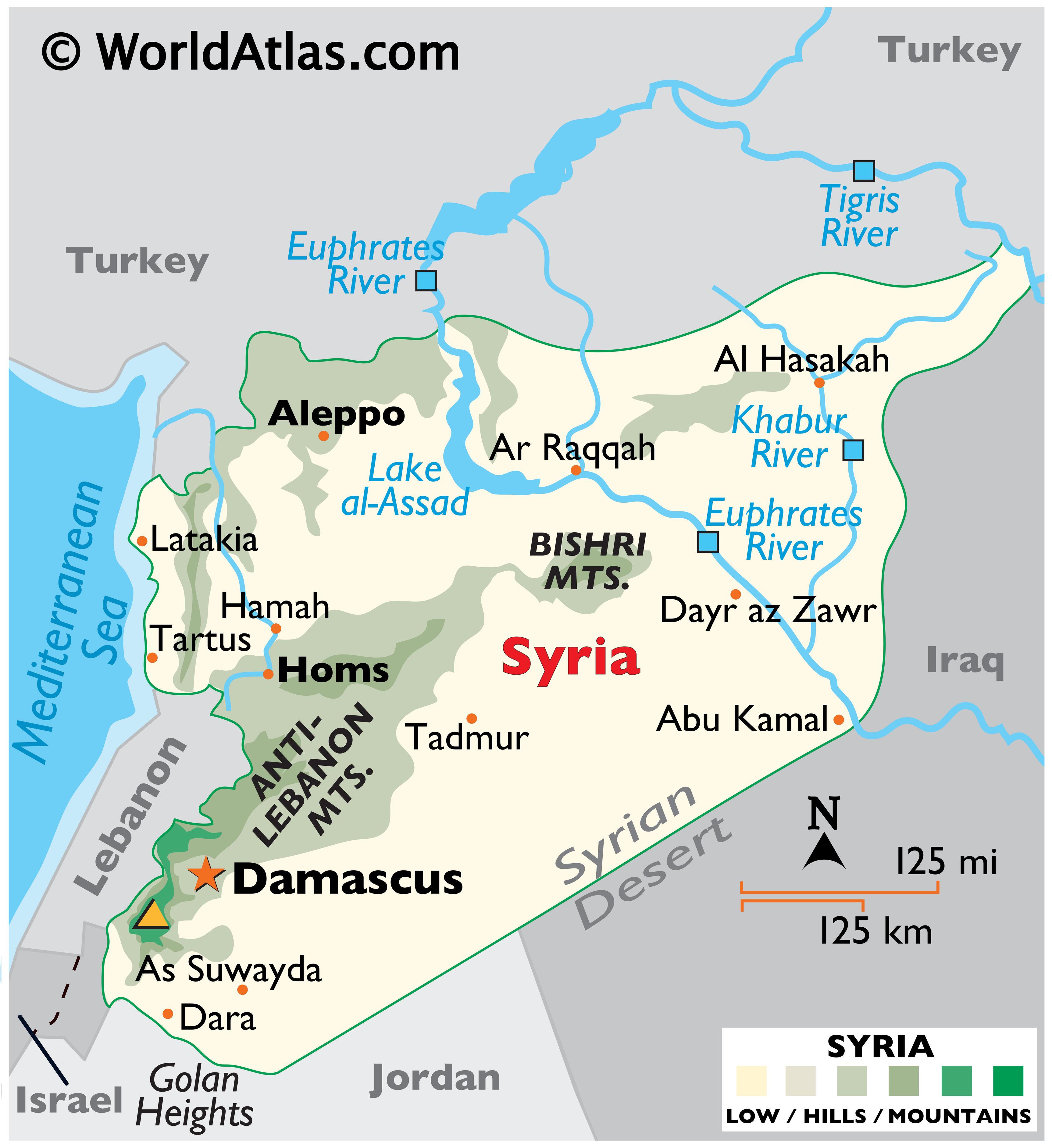
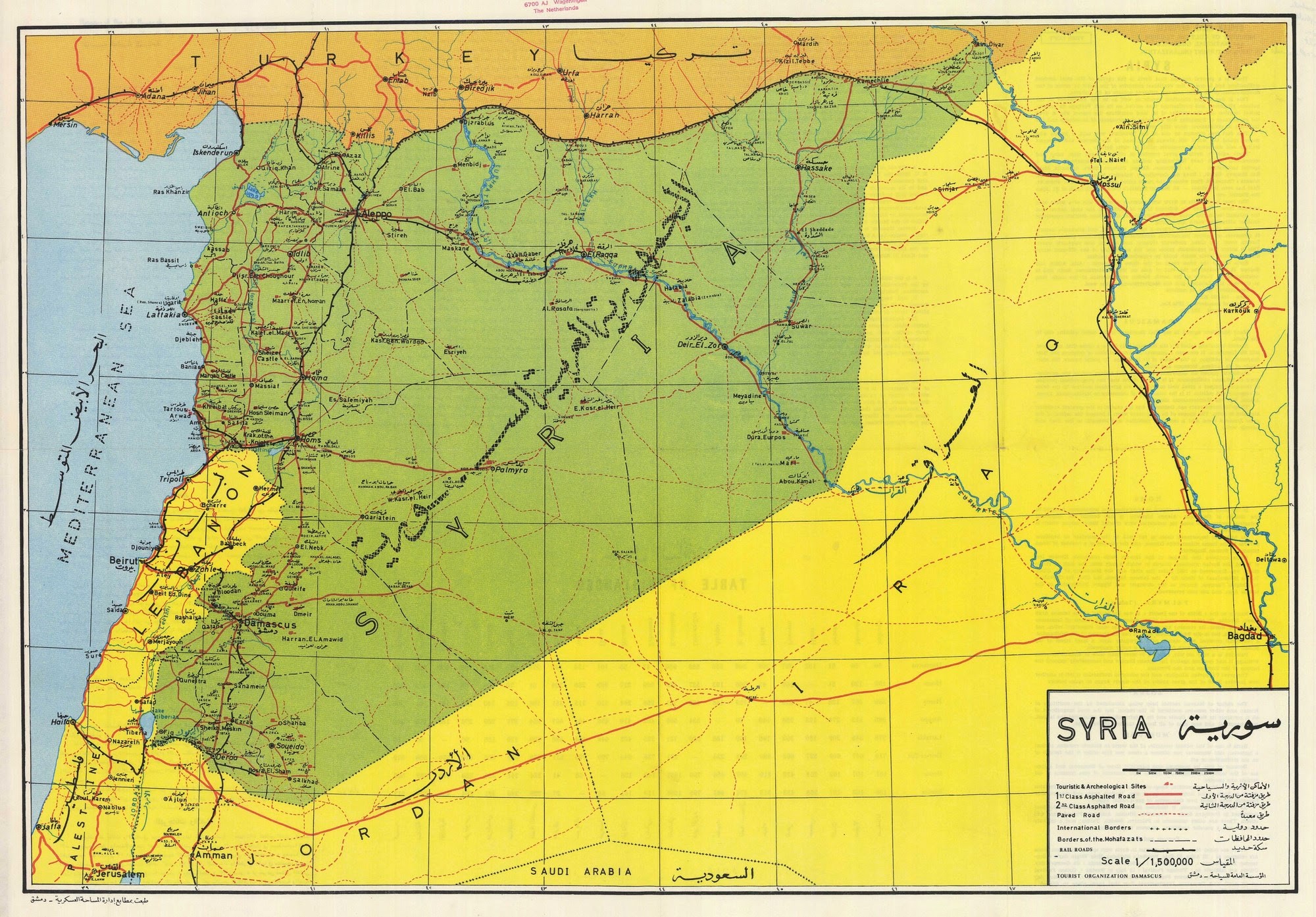
The Mediterranean Coast: A narrow strip along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea, this region enjoys a temperate climate with fertile soils, ideal for agriculture. Cities like Latakia and Tartus, situated on this coast, have historically been important ports, facilitating trade and cultural exchange.
-
The Coastal Mountain Range: Rising from the Mediterranean coast, the Anti-Lebanon and Jabal al-Akhdar mountains offer stunning vistas and provide a cooler climate compared to the lowlands. These mountains are home to diverse flora and fauna, including ancient forests and a rich tapestry of ecosystems.
-
The Syrian Desert: Covering the eastern and southeastern parts of the country, the Syrian Desert is a vast expanse of arid land, characterized by extreme temperatures and sparse vegetation. Despite its harsh conditions, the desert holds historical significance, serving as a route for ancient trade caravans and a refuge for nomadic tribes.
-
The Euphrates River Valley: A fertile strip of land running through the eastern part of the country, the Euphrates River Valley has been a vital source of water and agriculture for centuries. This region is home to ancient cities like Aleppo and Deir ez-Zor, which have flourished thanks to the river’s life-giving properties.
A Bridge Between Continents:
Syria’s geographic location has made it a natural bridge between continents, connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe. This strategic position has played a significant role in shaping its history, making it a crossroads of civilizations and a melting pot of cultures.
-
Ancient Trade Routes: Syria’s location has made it a vital hub for trade since antiquity. The Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting the East and West, traversed Syria, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences.
-
Cultural Exchange: The flow of people and goods through Syria has led to a rich cultural tapestry. Over the centuries, various civilizations, including the Romans, Byzantines, Arabs, and Ottomans, have left their mark on the country, enriching its art, architecture, and traditions.
-
Strategic Importance: Syria’s strategic location has made it a target of geopolitical interests for centuries. Its proximity to major waterways, including the Mediterranean Sea and the Euphrates River, has made it a coveted territory for empires seeking to control trade routes and access to resources.
The Importance of Syria’s Location:
-
Resource Management: Syria’s diverse landscapes hold valuable resources, including fertile agricultural land, rich mineral deposits, and access to fresh water. Effective management of these resources is crucial for the country’s economic development and sustainability.
-
Regional Stability: Syria’s location makes it a key player in regional stability. Its borders with Turkey, Iraq, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, and the Mediterranean Sea create a complex geopolitical landscape where tensions and conflicts can easily escalate.
-
International Relations: Syria’s location has significant implications for its international relations. Its proximity to both Western and Eastern powers, as well as its historical connections to various civilizations, makes it a focal point for diplomacy and global engagement.
FAQs about Syria’s Location:
- Q: How does Syria’s location affect its climate?
A: Syria’s climate is influenced by its proximity to the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Desert. The Mediterranean coast enjoys a temperate climate, while the interior regions experience hot, arid conditions. The mountainous regions receive more rainfall and have a cooler climate.
- Q: What are the main natural resources found in Syria?
A: Syria possesses a variety of natural resources, including fertile agricultural land, mineral deposits (such as phosphates, iron ore, and petroleum), and access to fresh water through the Euphrates River.
- Q: What are the main cities in Syria?
A: Some of the most significant cities in Syria include Damascus (the capital), Aleppo, Homs, Hama, Latakia, and Tartus. These cities have played crucial roles in Syria’s history and continue to be important centers of commerce, culture, and population.
- Q: What are the main ethnic groups in Syria?
A: Syria is home to a diverse population, with the majority being Arabs. Other significant ethnic groups include Kurds, Armenians, Circassians, and Turkmen.
- Q: What are the main religions practiced in Syria?
A: Islam is the dominant religion in Syria, with a majority of the population being Sunni Muslims. Other significant religious groups include Shia Muslims, Christians, and Druze.
Tips for Understanding Syria’s Location:
-
Use a map: A physical map of Syria can help you visualize its geographic features, including its mountains, rivers, and coastal areas.
-
Study its history: Understanding Syria’s historical development is crucial for comprehending its current geopolitical situation.
-
Learn about its culture: Exploring Syria’s rich cultural heritage, including its art, music, literature, and cuisine, provides insight into its unique identity.
-
Follow current events: Staying updated on current events in Syria is essential for understanding its political and social dynamics.
Conclusion:
Syria’s location at the crossroads of history and geography has shaped its destiny, influencing its culture, politics, and economy. Understanding its diverse landscapes, its strategic position, and its role in regional affairs is crucial for appreciating the complexities of this fascinating country. Syria’s future remains uncertain, but its location will continue to play a vital role in its development and its place in the world.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/syria_map.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Syria: A Crossroads of History and Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!