Navigating Wisconsin’s Landscape: Understanding Township Maps
Related Articles: Navigating Wisconsin’s Landscape: Understanding Township Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Wisconsin’s Landscape: Understanding Township Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Wisconsin’s Landscape: Understanding Township Maps
Wisconsin, known for its rolling hills, vast lakes, and dense forests, is a state with a unique and fascinating landscape. Understanding the intricate network of townships that define its geography is essential for navigating its diverse terrain, comprehending its history, and appreciating its unique character.
A Historical Perspective: The Foundation of Township Maps
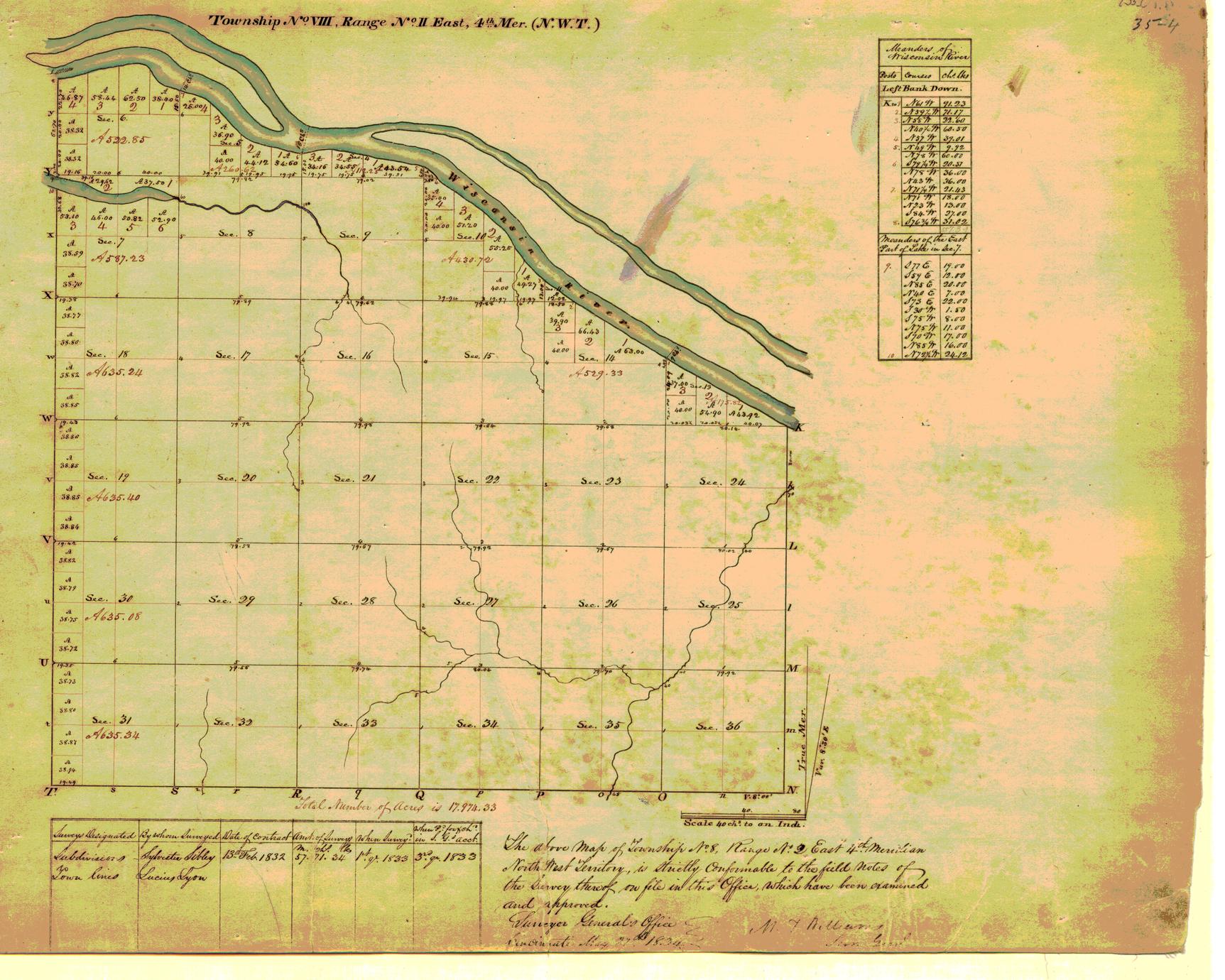
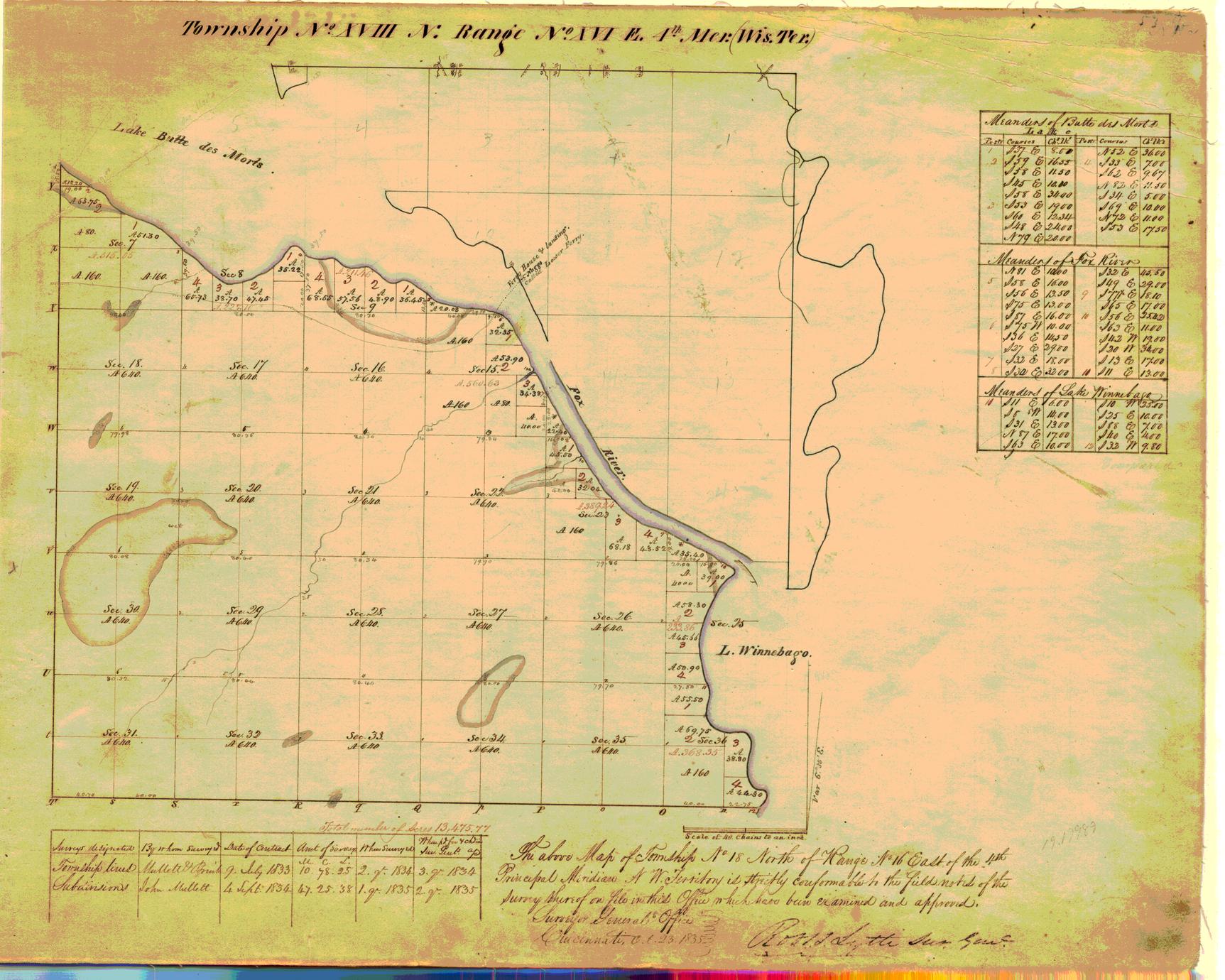
The concept of townships in Wisconsin, as in much of the United States, originates from the Land Ordinance of 1785. This landmark legislation established a systematic grid system for dividing land in the newly acquired territories west of the original thirteen colonies. This grid system, known as the "rectangular survey system," divided land into six-mile square townships, further subdivided into sections, each measuring one square mile.
The implementation of this system in Wisconsin began in the 1830s, as the state transitioned from wilderness to organized territory. Township maps were created to document this division, providing a clear and concise representation of land ownership, boundaries, and resources. These maps served as the foundation for subsequent land management and development, influencing everything from property ownership to the establishment of roads and infrastructure.
Decoding the Township Map: A Guide to Navigating Wisconsin’s Geography
Township maps, often presented as intricate grids, are essential tools for understanding Wisconsin’s geography. They provide a structured overview of the state’s landscape, highlighting key features like:
- Township Boundaries: The map clearly delineates the boundaries of each township, represented by six-mile square grids.
- Section Numbers: Within each township, individual sections are numbered from 1 to 36, following a specific pattern. This numbering system allows for precise land identification and tracking.
- Land Ownership: Township maps often depict land ownership, providing insights into the distribution of property within each township.
- Road Networks: Major roads and highways are frequently indicated on township maps, facilitating navigation and transportation.
- Water Features: Rivers, lakes, and streams are often represented on these maps, providing a visual understanding of the state’s water resources.
- Land Use: Some township maps may also include information about land use, indicating areas dedicated to agriculture, forestry, or urban development.
The Importance of Township Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Township maps serve a multitude of purposes, offering valuable information for diverse stakeholders:
- Landowners: Township maps provide crucial information about property boundaries, allowing landowners to clearly define their land holdings and manage their property effectively.
- Real Estate Professionals: These maps are essential for real estate agents and brokers, enabling them to understand property locations, access, and potential development opportunities.
- Government Agencies: Township maps are vital for planning and managing land use, infrastructure development, and resource management.
- Historians and Researchers: Township maps provide a historical record of land division and development, offering valuable insights into the state’s past.
- Outdoor Enthusiasts: Hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts use township maps to navigate trails, locate campsites, and explore the state’s diverse natural landscapes.
Beyond the Grid: Exploring the Unique Character of Wisconsin Townships
While township maps provide a structured framework for understanding the state’s geography, they are only one piece of the puzzle. Each township in Wisconsin possesses a unique character, shaped by its history, culture, and natural environment.
- Historical Heritage: Townships often bear the names of historical figures or events, reflecting the state’s rich past. Exploring these names can unveil stories of early settlers, Native American tribes, and the development of Wisconsin’s communities.
- Cultural Diversity: Wisconsin’s townships boast a diverse range of cultures, influenced by immigration patterns and the state’s agricultural heritage. Exploring these cultural nuances adds depth and richness to the understanding of Wisconsin’s landscape.
- Natural Beauty: Each township offers a unique natural experience, from rolling farmlands and dense forests to pristine lakes and meandering rivers. Understanding the natural characteristics of each township allows for a deeper appreciation of Wisconsin’s diverse ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can I find a township map for a specific area in Wisconsin?
A: Township maps are available through various sources, including:
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR): The DNR website offers a range of maps, including township maps, for various areas of the state.
- County Government Websites: Many county governments in Wisconsin provide online access to township maps for their respective jurisdictions.
- Online Mapping Services: Websites like Google Maps and ArcGIS offer interactive maps that can be used to locate and visualize township boundaries.
- Local Libraries and Historical Societies: These institutions may have collections of historical maps, including township maps, for specific areas.
Q: What is the difference between a township and a town in Wisconsin?
A: While the terms "township" and "town" are often used interchangeably, they have distinct legal and administrative definitions in Wisconsin:
- Township: A township is a geographic unit of land, typically six miles square, established through the rectangular survey system.
- Town: A town is a unit of local government, encompassing a specific geographic area, which may or may not correspond to a township boundary.
Q: What are some of the benefits of understanding township maps?
A: Understanding township maps provides numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Navigation: Township maps facilitate navigation and exploration within the state.
- Property Management: Landowners can use these maps to define property boundaries and manage their land effectively.
- Historical Research: Township maps provide valuable insights into the history of land division and development in Wisconsin.
- Resource Management: Government agencies utilize these maps for planning and managing land use, infrastructure, and natural resources.
Tips for Using Township Maps
- Refer to a Legend: Township maps often include a legend that explains symbols, colors, and abbreviations used on the map.
- Use a Scale: The map scale indicates the relationship between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground.
- Consider Additional Resources: Township maps can be supplemented with other resources, such as aerial photographs, satellite imagery, and topographic maps.
- Explore Digital Tools: Online mapping services offer interactive features that enhance the utility of township maps.
Conclusion
Township maps are an essential tool for understanding and navigating Wisconsin’s diverse landscape. These maps provide a structured framework for comprehending land division, property ownership, and resource management. By exploring the historical context, cultural nuances, and natural beauty of each township, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the unique character of Wisconsin’s geography.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Wisconsin’s Landscape: Understanding Township Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!