Navigating the Roads: A Comprehensive Look at the Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) Region Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Roads: A Comprehensive Look at the Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) Region Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Roads: A Comprehensive Look at the Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) Region Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Roads: A Comprehensive Look at the Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) Region Map
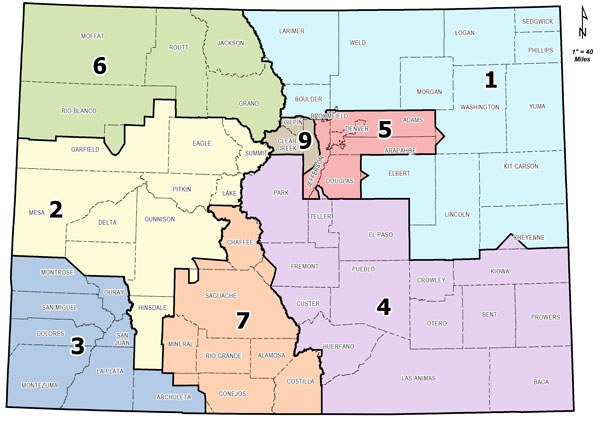
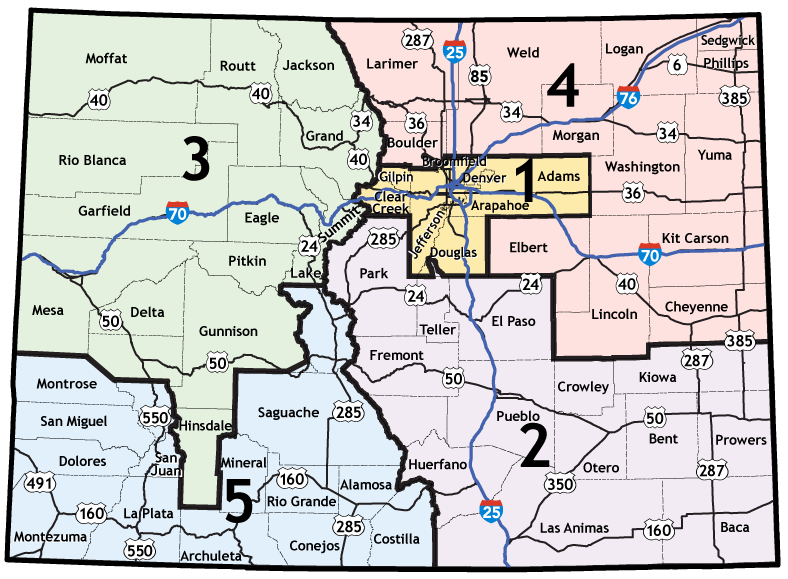
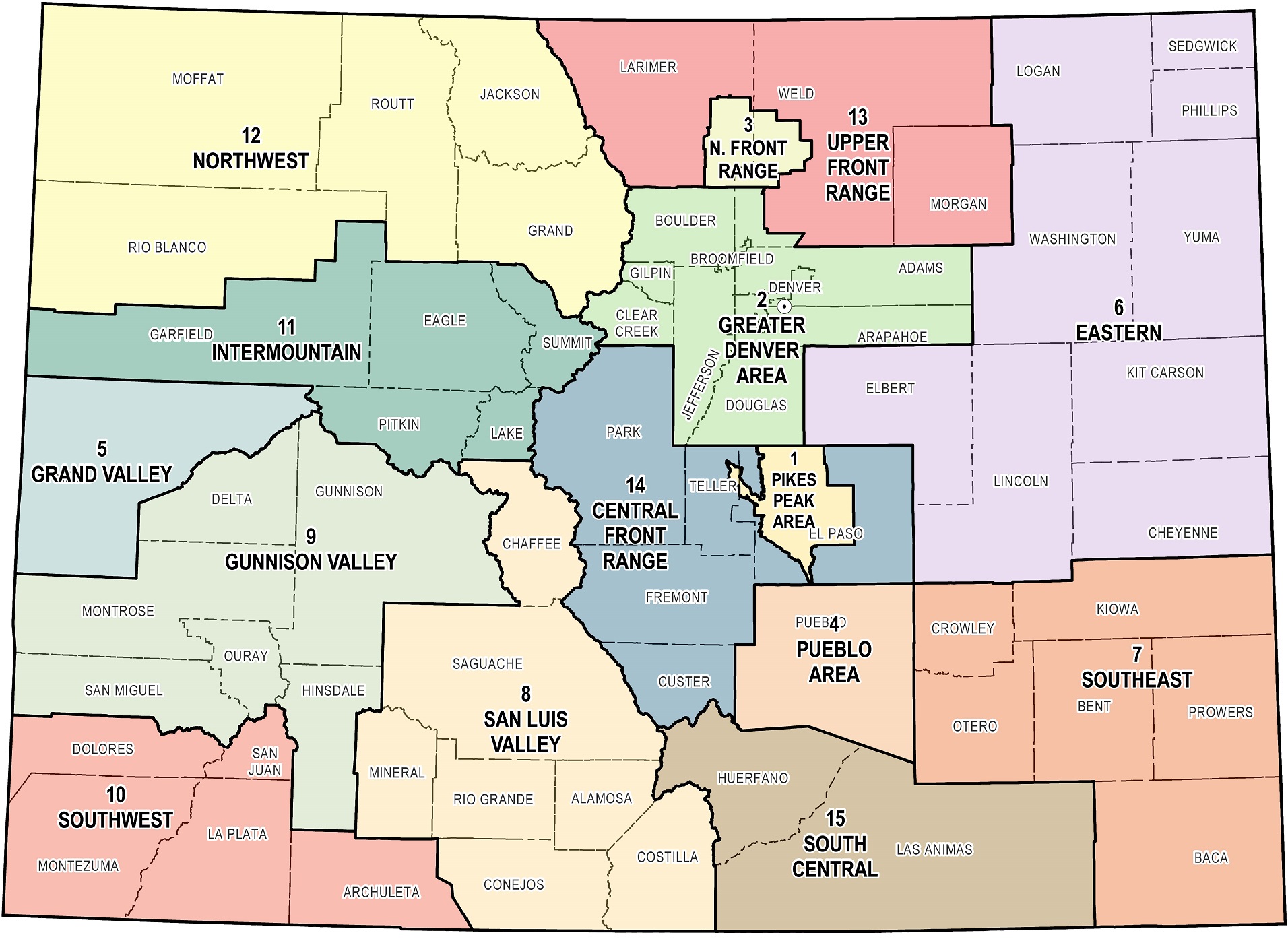
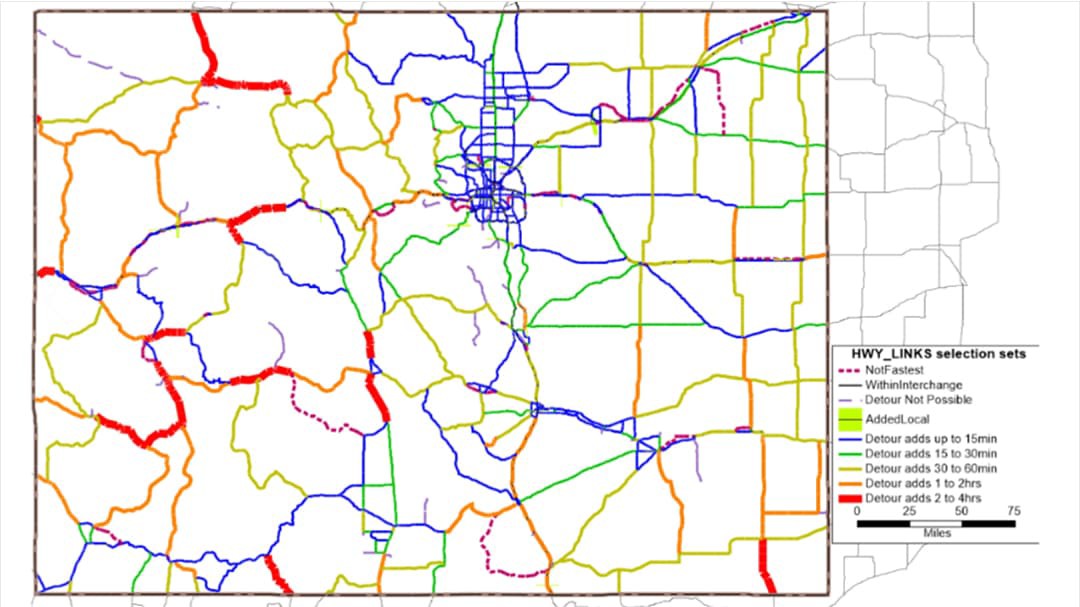
The Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) is responsible for the planning, construction, maintenance, and operation of the state’s vast transportation network. This network encompasses over 40,000 miles of roads, including interstate highways, state highways, and county roads. To effectively manage this intricate system, CDOT has divided the state into eight distinct regions, each with its own unique geographic and transportation characteristics.
Understanding the CDOT Region Map
The CDOT region map serves as a crucial tool for understanding the organization and management of Colorado’s transportation infrastructure. It provides a clear visual representation of the state’s division into eight regions, each with its own dedicated staff and resources. This regional approach allows CDOT to:
- Tailor services to local needs: Each region faces unique transportation challenges, such as mountainous terrain, urban sprawl, or rural isolation. By dividing the state into regions, CDOT can address these specific needs more effectively.
- Improve efficiency and responsiveness: By decentralizing operations, CDOT can react more swiftly to local emergencies, traffic incidents, and maintenance needs.
- Foster collaboration: Each region works closely with local communities, government agencies, and stakeholders to ensure that transportation projects and initiatives align with local priorities.
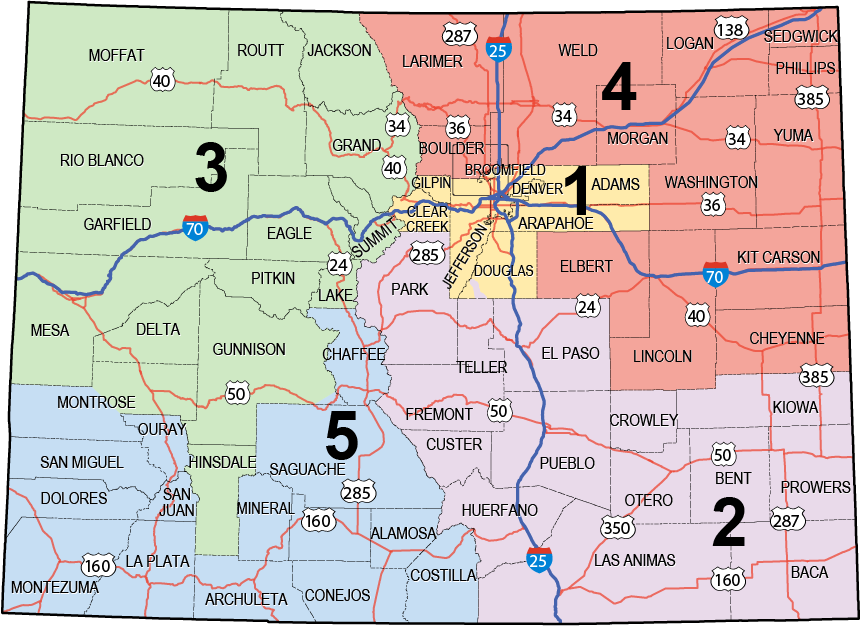
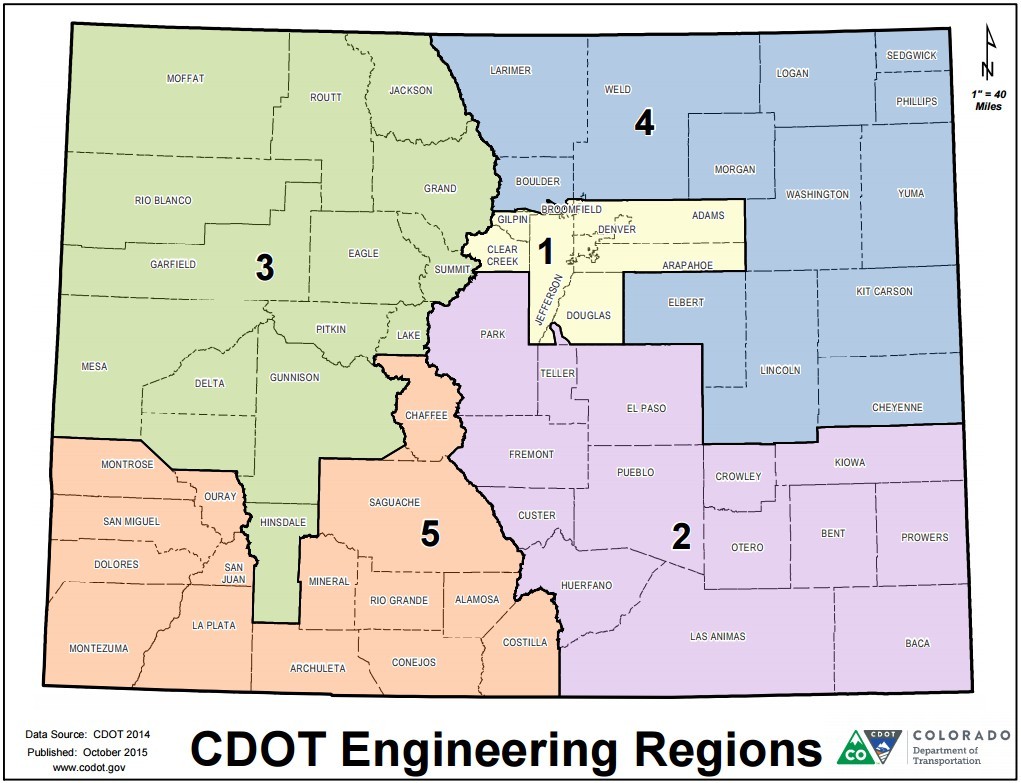
A Closer Look at the Regions
Each of the eight CDOT regions is named after its primary geographic location and encompasses a distinct portion of the state.
- Region 1 (Northwest): This region covers the northwestern corner of Colorado, including the cities of Grand Junction, Montrose, and Durango. It is characterized by its mountainous terrain, vast wilderness areas, and scenic highways.
- Region 2 (North Central): This region encompasses the northern and central parts of the state, including the cities of Fort Collins, Greeley, and Denver. It is home to a diverse range of urban and rural areas, with significant population density and heavy traffic volumes.
- Region 3 (Northeast): This region covers the northeastern portion of the state, including the cities of Sterling, Fort Morgan, and Brighton. It is characterized by its flat, agricultural landscape and its proximity to the state’s eastern border.
- Region 4 (South Central): This region encompasses the southern and central parts of the state, including the cities of Colorado Springs, Pueblo, and Cañon City. It is home to a diverse range of landscapes, including the Front Range, the Arkansas River Valley, and the Sangre de Cristo Mountains.
- Region 5 (Southwest): This region covers the southwestern corner of the state, including the cities of Cortez, Pagosa Springs, and Alamosa. It is characterized by its rugged mountains, high desert, and unique cultural heritage.
- Region 6 (Southeast): This region encompasses the southeastern portion of the state, including the cities of Trinidad, Lamar, and La Junta. It is characterized by its flat, semi-arid landscape and its proximity to the state’s eastern border.
- Region 7 (Metro): This region focuses on the Denver Metropolitan Area, encompassing the cities of Denver, Aurora, Lakewood, and surrounding communities. It is the most densely populated region in the state and faces unique transportation challenges related to urban sprawl, traffic congestion, and public transit.
- Region 8 (Mountain): This region encompasses the mountainous areas of the state, including the cities of Aspen, Vail, Breckenridge, and Telluride. It is characterized by its stunning scenery, challenging terrain, and seasonal weather patterns.
Benefits of the Regional Structure
The regional structure of CDOT provides numerous benefits for the state’s transportation system:
- Improved decision-making: By decentralizing decision-making, CDOT can better address local needs and priorities.
- Increased efficiency: Regionalization allows CDOT to allocate resources more effectively and respond to local transportation issues more quickly.
- Enhanced accountability: Each region is accountable for the performance of its transportation system, fostering a culture of responsibility and continuous improvement.
- Stronger community engagement: By working closely with local communities, CDOT can ensure that transportation projects and initiatives align with local priorities and needs.
FAQs
Q: How can I find information about a specific CDOT region?
A: You can find information about each CDOT region on the agency’s website. The website provides details on the region’s geographic boundaries, staff, projects, and contact information.
Q: What types of transportation projects are managed by CDOT regions?
A: CDOT regions manage a wide range of transportation projects, including highway construction and maintenance, bridge rehabilitation, traffic signal installation, and public transit improvements.
Q: How can I contact a specific CDOT region?
A: You can find contact information for each CDOT region on the agency’s website. This information includes phone numbers, email addresses, and physical addresses.
Q: What are the key challenges facing CDOT regions?
A: CDOT regions face numerous challenges, including limited funding, aging infrastructure, increasing traffic congestion, and the need to adapt to changing transportation needs.
Tips
- Stay informed about CDOT projects in your region: CDOT provides regular updates on its website and social media channels about current and upcoming transportation projects.
- Attend public meetings and workshops: CDOT regularly hosts public meetings and workshops to gather input on transportation projects and initiatives.
- Contact your local CDOT representative: You can find contact information for your local CDOT representative on the agency’s website.
Conclusion
The CDOT region map provides a valuable framework for understanding the organization and management of Colorado’s transportation system. By dividing the state into eight distinct regions, CDOT can tailor its services to local needs, improve efficiency and responsiveness, and foster collaboration with local communities. This regional structure is essential for ensuring that Colorado’s transportation system remains safe, efficient, and sustainable for the future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Roads: A Comprehensive Look at the Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) Region Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!