Navigating the Invisible: Understanding Air Current Maps and Their Significance
Related Articles: Navigating the Invisible: Understanding Air Current Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Invisible: Understanding Air Current Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Invisible: Understanding Air Current Maps and Their Significance

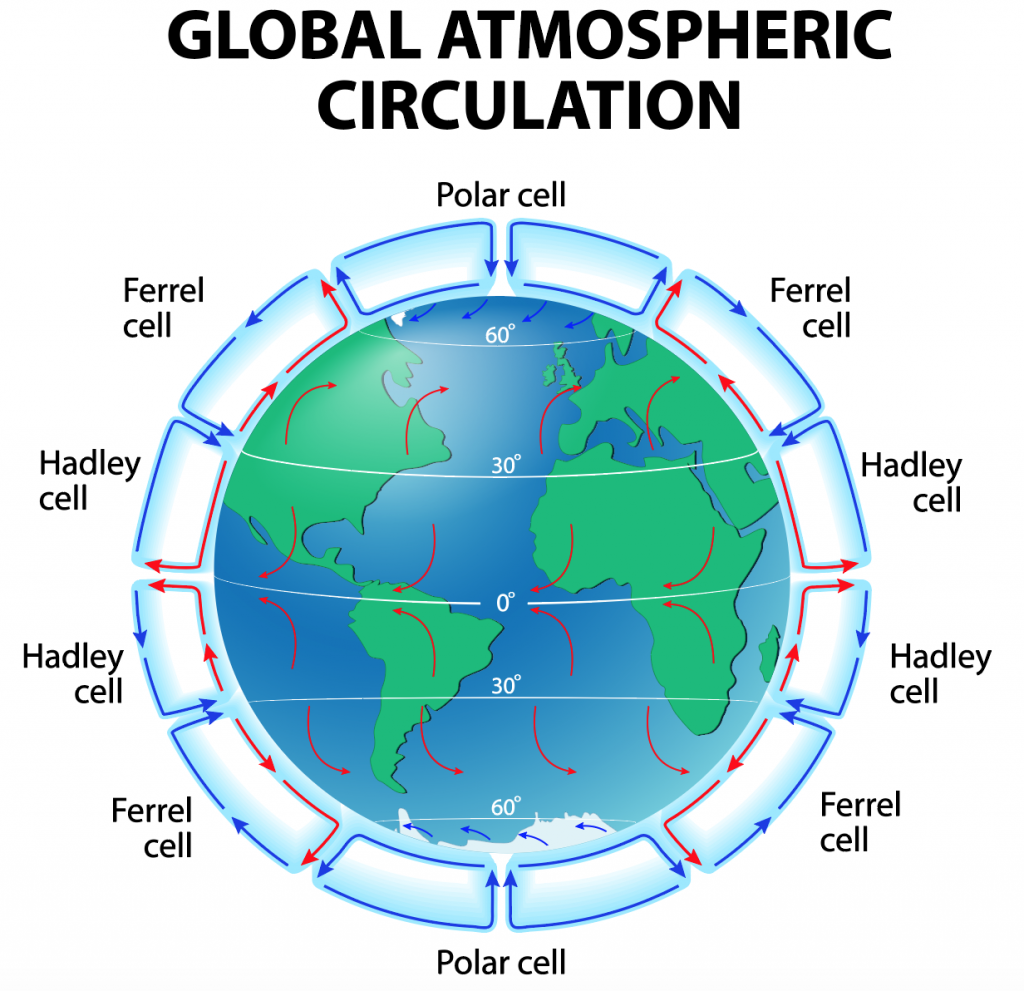
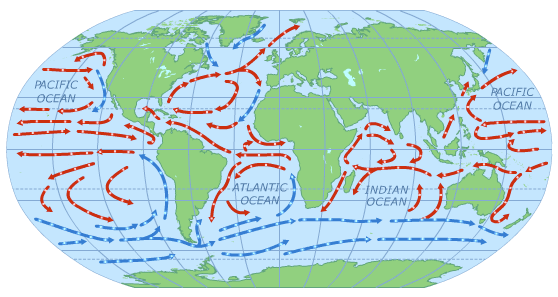
The Earth’s atmosphere is a dynamic and ever-changing entity, driven by a complex interplay of forces. Air currents, the invisible rivers of wind that crisscross the globe, play a pivotal role in shaping weather patterns, influencing climate, and impacting various aspects of human life. Visualizing these currents becomes crucial for comprehending their influence and predicting their impact. This is where air current maps come into play, providing a visual representation of the intricate network of air movement across the planet.
Unveiling the Dynamics of Air Movement
Air current maps, also known as wind maps, are graphical representations of wind speed and direction at different altitudes. They depict the flow of air masses, showcasing the intricate dance of high-pressure and low-pressure systems that drive atmospheric circulation. These maps utilize color gradients and arrows to illustrate the strength and direction of wind, offering a comprehensive overview of the atmospheric dynamics at a specific point in time.
Data Sources and Visualization Techniques
Air current maps rely on data collected from various sources, including:
- Weather Balloons: These instruments, launched twice daily across the globe, measure atmospheric conditions at different altitudes, providing crucial data on wind speed, direction, and temperature.
- Satellites: Orbiting satellites equipped with advanced sensors constantly monitor atmospheric conditions, capturing data on wind patterns and other meteorological variables.
- Ground-based Stations: Networks of weather stations located across the globe provide real-time data on wind speed and direction at ground level.
This data is then processed and analyzed to generate air current maps, utilizing various visualization techniques:
- Isobars: Lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, revealing the presence of high and low-pressure systems, which drive air movement.
- Wind Arrows: Arrows indicating the direction and speed of wind at different locations, visually representing the flow of air.
- Color Gradients: Different colors represent varying wind speeds, providing a visual indication of the intensity of air movement.
Applications of Air Current Maps
Air current maps have wide-ranging applications across various fields, including:
- Meteorology: Forecasting weather patterns, predicting storms and extreme weather events, and understanding climate change.
- Aviation: Planning flight routes, optimizing fuel efficiency, and ensuring safe air travel.
- Shipping: Navigating ships, optimizing routes, and minimizing travel time.
- Renewable Energy: Identifying optimal locations for wind power generation and maximizing energy output.
- Agriculture: Understanding wind patterns for crop irrigation and pest control.
- Environmental Studies: Studying air pollution dispersion, tracking pollutants, and understanding atmospheric processes.
Understanding the Importance of Air Current Maps
Air current maps provide invaluable insights into the complex workings of the atmosphere. They enable us to:
- Predict Weather Patterns: By analyzing the movement of air masses, meteorologists can predict the development and trajectory of storms, providing crucial information for public safety and preparedness.
- Optimize Transportation: Air current maps help optimize flight routes and ship navigation, reducing travel time and fuel consumption, contributing to economic efficiency and environmental sustainability.
- Harness Renewable Energy: Wind maps guide the selection of optimal locations for wind turbines, maximizing energy generation and contributing to the transition towards cleaner energy sources.
- Monitor Environmental Conditions: Air current maps aid in understanding the dispersal of air pollution and tracking the movement of pollutants, providing vital information for environmental management and public health.
FAQs on Air Current Maps
Q: What is the difference between wind speed and wind direction?
A: Wind speed refers to the velocity of air movement, measured in units like meters per second or kilometers per hour. Wind direction indicates the direction from which the wind is blowing, typically expressed as a compass bearing.
Q: How often are air current maps updated?
A: Air current maps are typically updated every few hours, reflecting the dynamic nature of atmospheric conditions. Real-time updates are often available through online weather services and meteorological websites.
Q: How accurate are air current maps?
A: The accuracy of air current maps depends on the quality and frequency of data collection, the sophistication of the visualization techniques employed, and the complexity of atmospheric dynamics. However, advancements in weather forecasting and data processing have significantly enhanced the accuracy and reliability of these maps.
Q: Can air current maps predict future weather events?
A: While air current maps provide valuable information on current atmospheric conditions, they are not capable of predicting future weather events with absolute certainty. Weather forecasting involves complex modeling and analysis of various factors, including air currents, temperature, humidity, and other meteorological variables.
Tips for Using Air Current Maps
- Understand the Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the different symbols used on air current maps, including isobars, wind arrows, and color gradients.
- Consider Altitude: Air currents vary significantly at different altitudes, so it is crucial to consider the altitude level depicted on the map.
- Pay Attention to Scale: Air current maps often use different scales to represent wind speeds and directions, so it is important to understand the scale used.
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare data from different sources to get a comprehensive understanding of air current patterns.
- Stay Updated: Air current maps are dynamic and constantly changing, so it is essential to access the most recent data available.
Conclusion
Air current maps are essential tools for understanding and predicting the dynamics of the Earth’s atmosphere. They provide a visual representation of the intricate network of air movement, enabling us to forecast weather patterns, optimize transportation, harness renewable energy, and monitor environmental conditions. As technology advances and data collection methods become more sophisticated, air current maps will continue to play a crucial role in our understanding and management of the complex and ever-changing atmosphere.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Invisible: Understanding Air Current Maps and Their Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!