Navigating the Depths: Understanding Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
Related Articles: Navigating the Depths: Understanding Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Depths: Understanding Lake Erie’s Bathymetry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Depths: Understanding Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
.jpg)
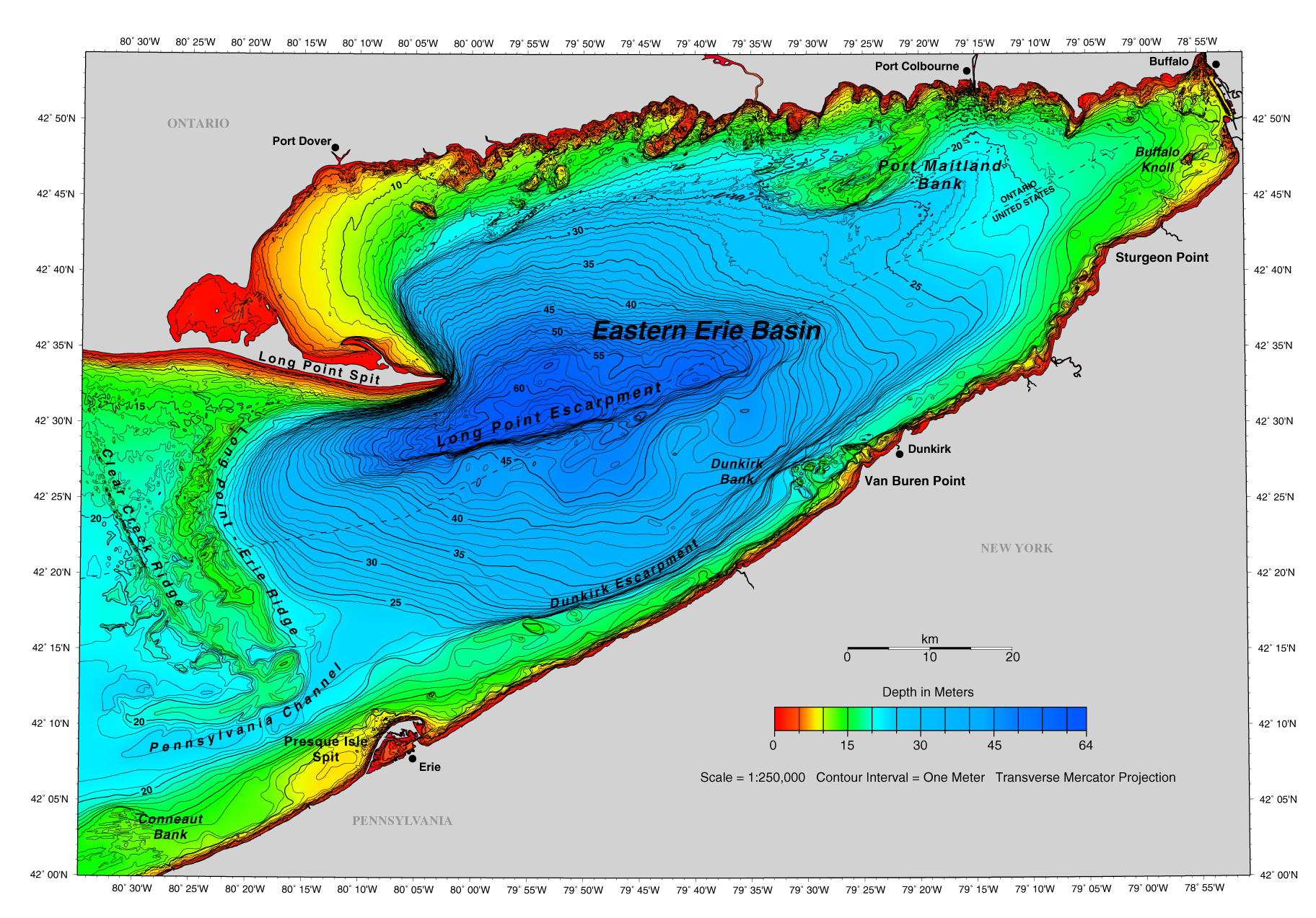
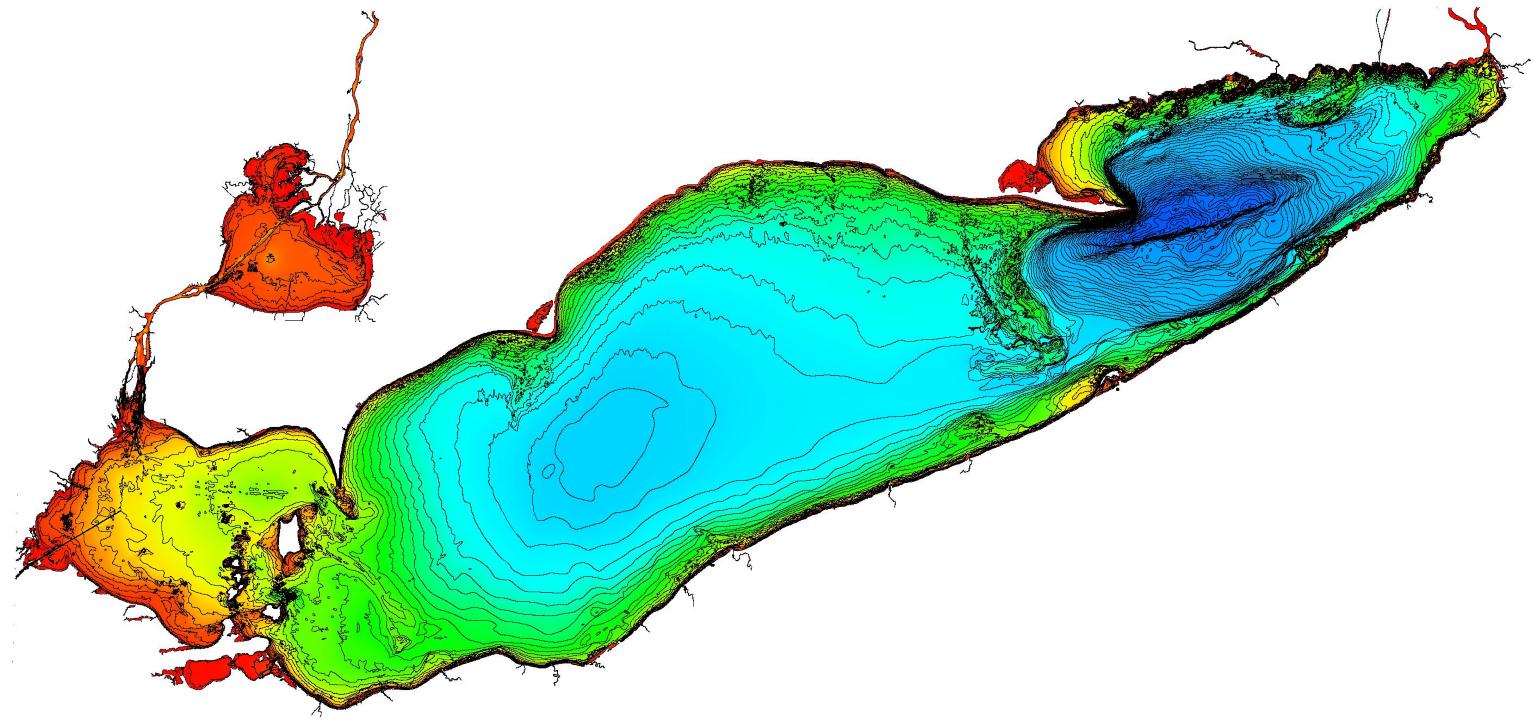
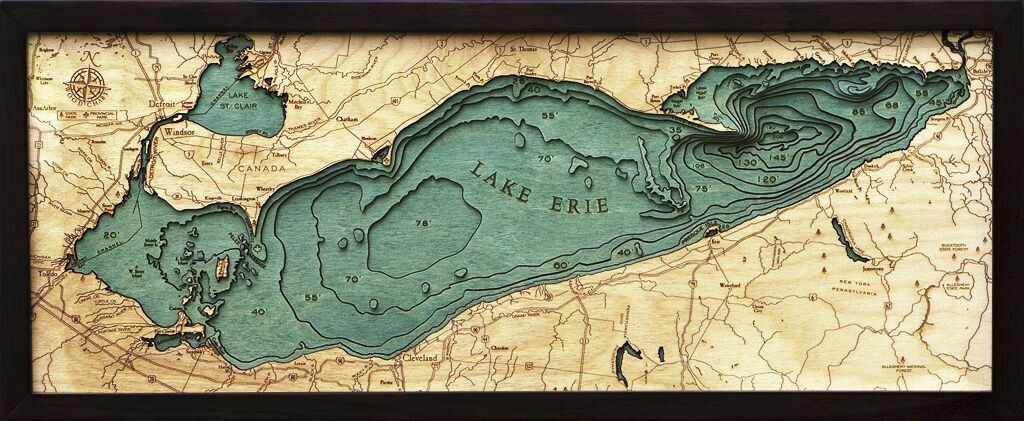
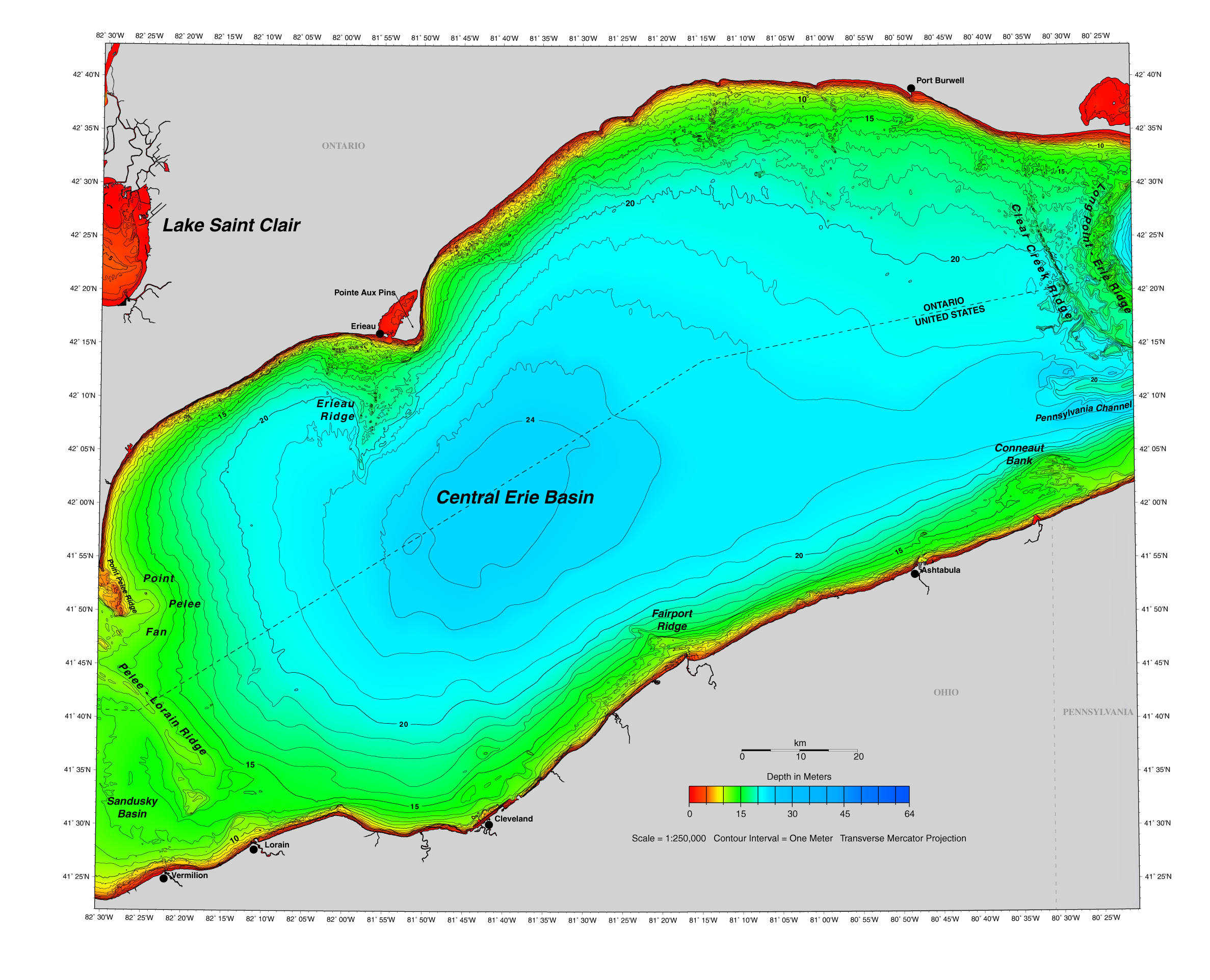
Lake Erie, the shallowest of the Great Lakes, holds a unique position in the North American landscape. Its relatively shallow depths, ranging from a few feet in some areas to over 200 feet in the deepest parts, contribute significantly to its diverse ecosystem and the challenges it faces. Understanding Lake Erie’s bathymetry, the study of underwater topography, is crucial for navigating its waters, managing its resources, and protecting its delicate balance.
A Shallow Giant: Exploring the Depths of Lake Erie
Lake Erie’s shallow depths have a profound impact on its physical characteristics and ecological dynamics. The average depth of the lake is only 62 feet, with the deepest point reaching 210 feet in the central basin. This shallowness contributes to:
-
Rapid Water Warming: Lake Erie’s shallow waters warm up quickly in the summer, creating ideal conditions for the growth of algae and other aquatic plants. This rapid warming also affects water circulation and oxygen levels.
-
Strong Wind Influence: The shallowness of the lake allows winds to exert a significant influence on water movement, leading to frequent mixing and wave action. This dynamic environment can impact water quality, sediment transport, and shoreline erosion.
-
Limited Water Volume: The relatively small volume of water in Lake Erie makes it more susceptible to pollution and other disturbances. Pollutants can accumulate more quickly in the shallow waters, potentially impacting water quality and aquatic life.
-
Diverse Habitats: The varying depths of Lake Erie create a mosaic of habitats, supporting a rich biodiversity. From shallow, sunlit waters to deep, cold basins, each area harbors distinct communities of fish, invertebrates, and plants.
Mapping the Depths: Unveiling Lake Erie’s Underwater Topography
Bathymetric maps are essential tools for understanding and managing Lake Erie’s resources. These maps depict the underwater topography, highlighting the different depths, contours, and features of the lake bottom. They are crucial for:
-
Navigation: Bathymetric maps provide crucial information for boaters, allowing them to navigate safely and avoid hazards such as shallow areas, reefs, and shipwrecks.
-
Fisheries Management: Understanding the distribution of habitats based on depth is vital for managing fisheries. By mapping the locations of spawning grounds, nursery areas, and preferred habitats, fisheries managers can develop sustainable fishing practices.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Bathymetric maps are essential for monitoring changes in the lake bottom, including erosion, sedimentation, and the impact of human activities. These changes can have significant consequences for water quality, habitat availability, and overall ecosystem health.
-
Water Resource Management: Bathymetric data helps water resource managers understand water flow patterns, identify potential areas for water storage, and assess the impact of water withdrawals on lake levels.
The Importance of Bathymetric Data: A Vital Tool for Lake Erie’s Future
Lake Erie’s bathymetry plays a crucial role in its health and management. Understanding the underwater topography allows us to:
-
Protect Habitats: Bathymetric data helps identify sensitive areas, such as spawning grounds, nursery areas, and reefs, which can be targeted for protection from human activities.
-
Manage Pollution: Mapping the lake bottom helps understand how pollutants move and accumulate, informing the development of strategies to reduce pollution and protect water quality.
-
Plan for Climate Change: Bathymetric data is essential for understanding how climate change may impact Lake Erie’s water levels, circulation patterns, and overall ecosystem.
-
Promote Sustainable Use: By understanding the lake’s depths and habitats, we can develop sustainable practices for fishing, recreation, and other human activities, ensuring the long-term health of Lake Erie.
FAQs about Lake Erie’s Bathymetry
Q: How is bathymetric data collected?
A: Bathymetric data is collected using various methods, including sonar, multibeam sonar, and lidar. These technologies emit sound waves or laser pulses that travel through the water and reflect off the lake bottom, providing information about depth and topography.
Q: How often is Lake Erie’s bathymetry updated?
A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific area and the purpose of the data. Some areas may be mapped more frequently than others, depending on factors such as human activities, environmental changes, and research needs.
Q: What are some challenges in mapping Lake Erie’s bathymetry?
A: Challenges include the presence of vegetation, sediment, and other obstacles that can interfere with sonar signals. Weather conditions can also impact data collection, and the vast size of the lake requires significant time and resources for complete mapping.
Q: How can I access bathymetric data for Lake Erie?
A: Bathymetric data for Lake Erie is available from various sources, including government agencies like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), universities, and research institutions.
Tips for Using Lake Erie’s Bathymetric Data
-
Consult with Experts: If you need to use bathymetric data for a specific project, consult with experts who can provide guidance on data interpretation and application.
-
Consider Data Accuracy: Bathymetric data has varying levels of accuracy, so it is important to understand the limitations of the data before using it for decision-making.
-
Utilize Visualization Tools: Bathymetric data can be visualized using various software programs, allowing for a better understanding of the underwater topography.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding for a Healthier Lake
Lake Erie’s bathymetry is not merely a collection of numbers and lines on a map. It represents a crucial aspect of the lake’s ecological functioning, influencing its physical characteristics, biological diversity, and overall health. By understanding and utilizing bathymetric data, we can navigate the depths of Lake Erie responsibly, manage its resources sustainably, and protect its delicate balance for future generations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Depths: Understanding Lake Erie’s Bathymetry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!