Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Guide to Positioning Map Marketing
Related Articles: Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Guide to Positioning Map Marketing
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Guide to Positioning Map Marketing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Guide to Positioning Map Marketing
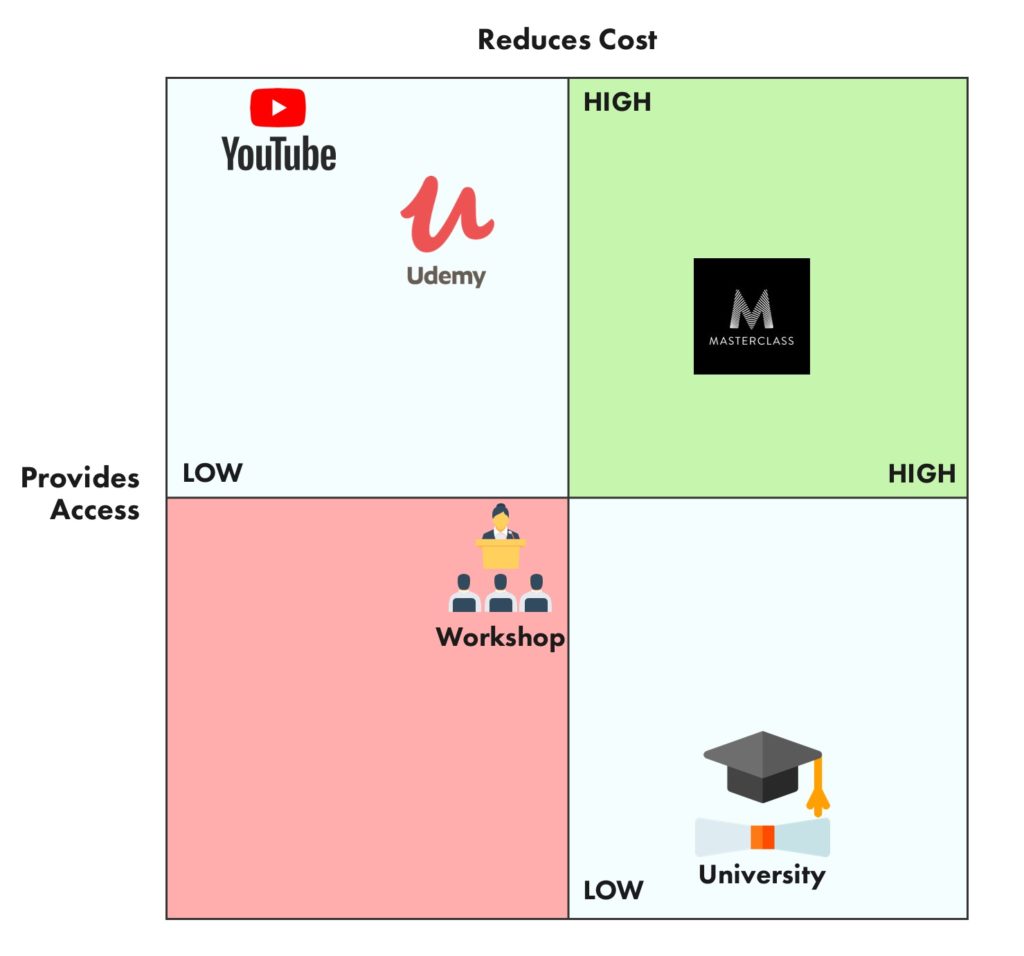
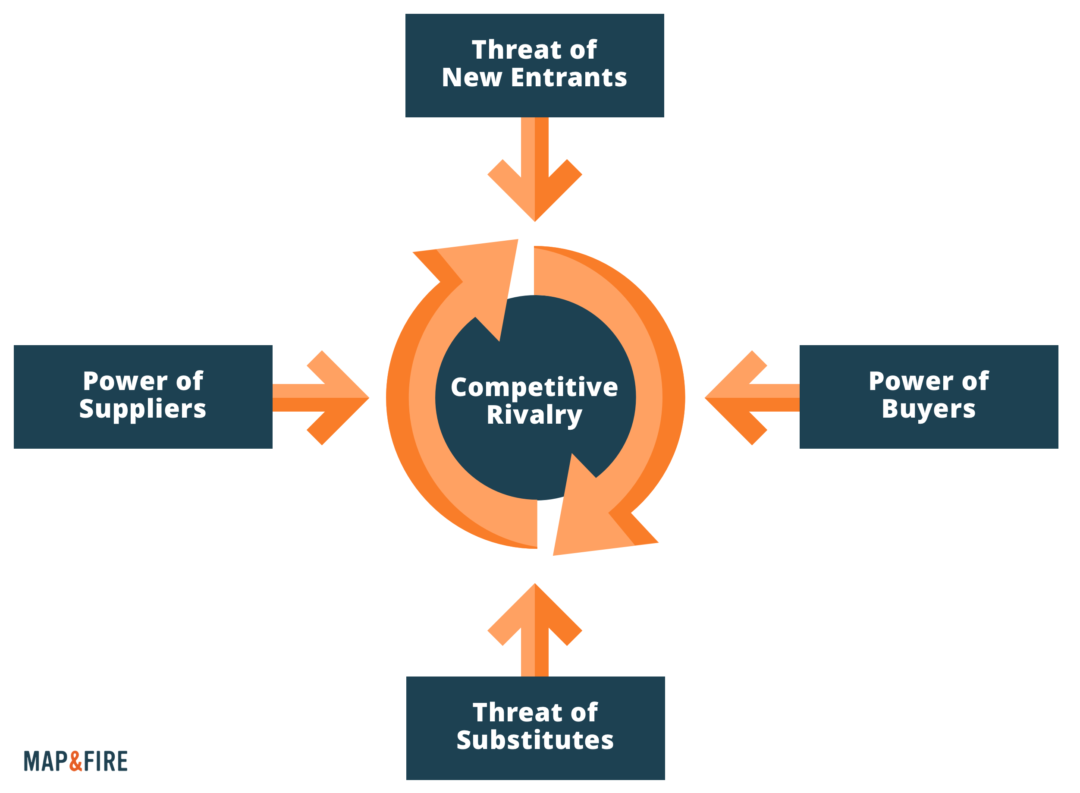
In the saturated marketplace of today, standing out from the crowd is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Companies are constantly vying for consumer attention, and success hinges on effectively communicating their unique value proposition. This is where positioning map marketing comes into play, offering a powerful visual tool to understand and strategically navigate the competitive landscape.
Understanding Positioning Maps
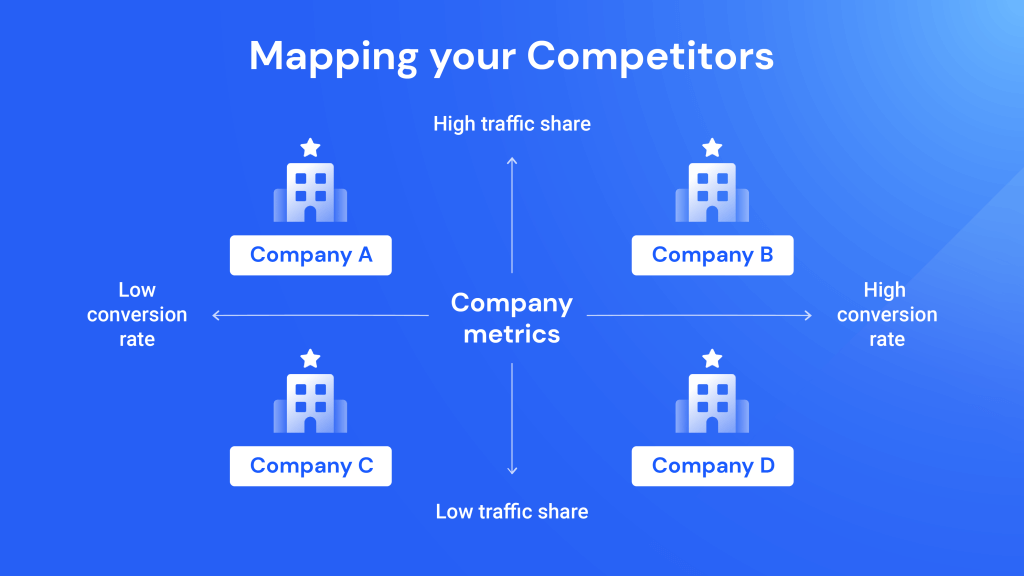
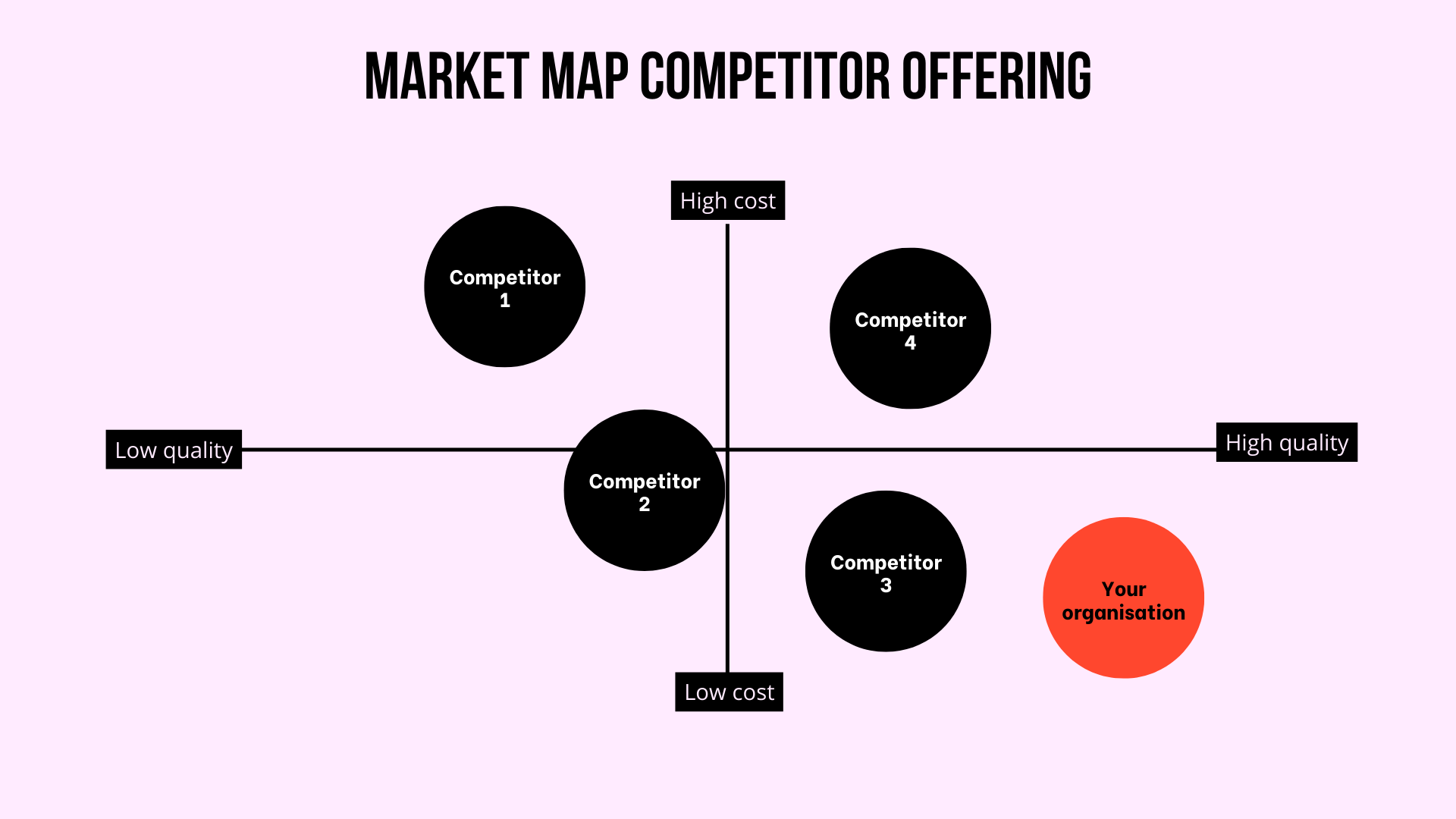
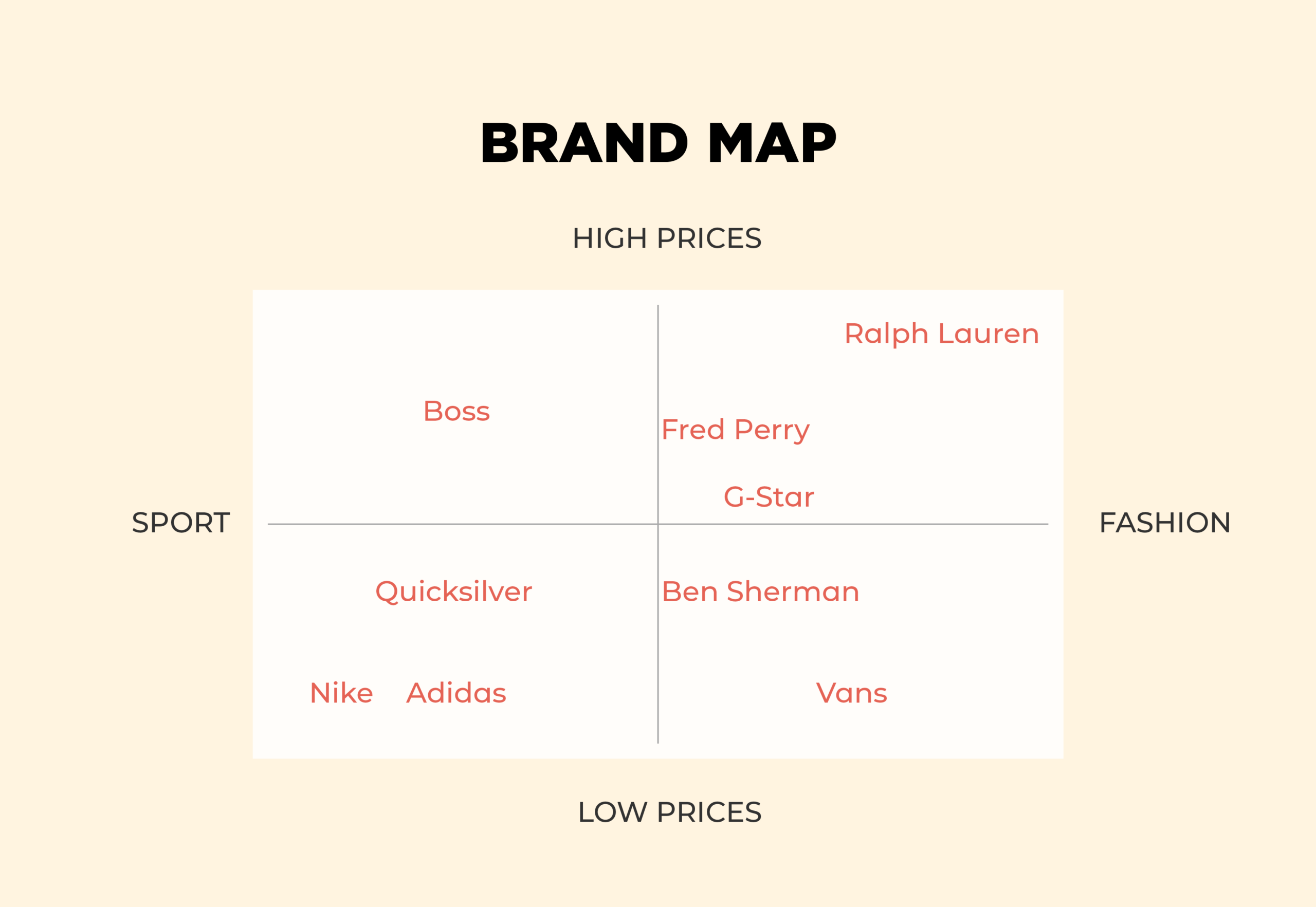
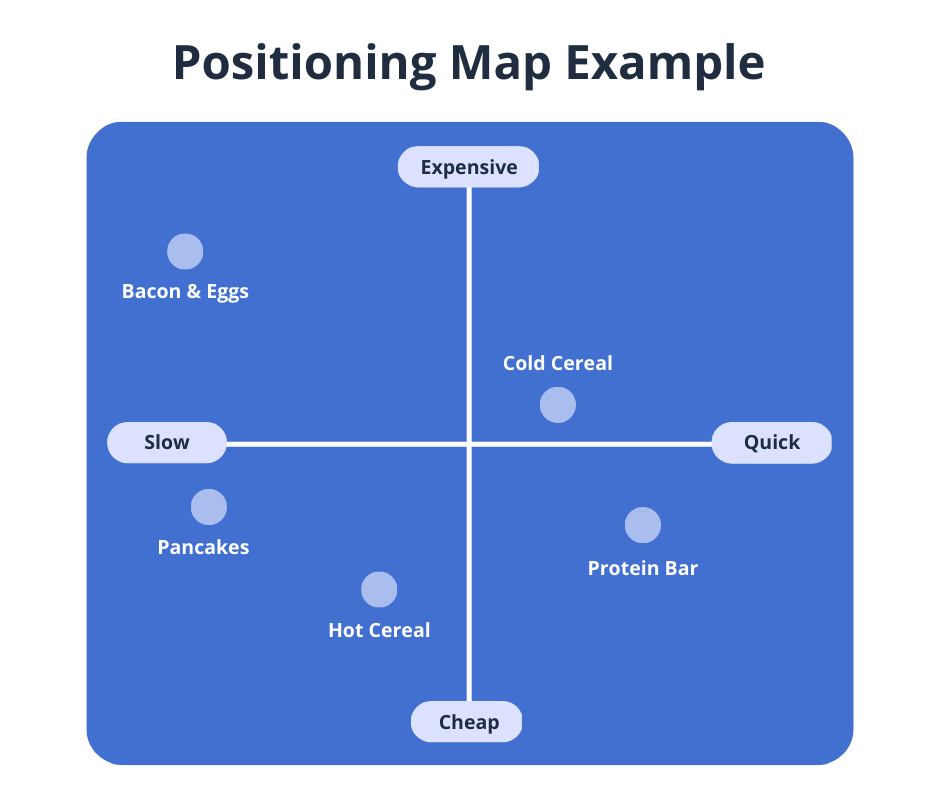
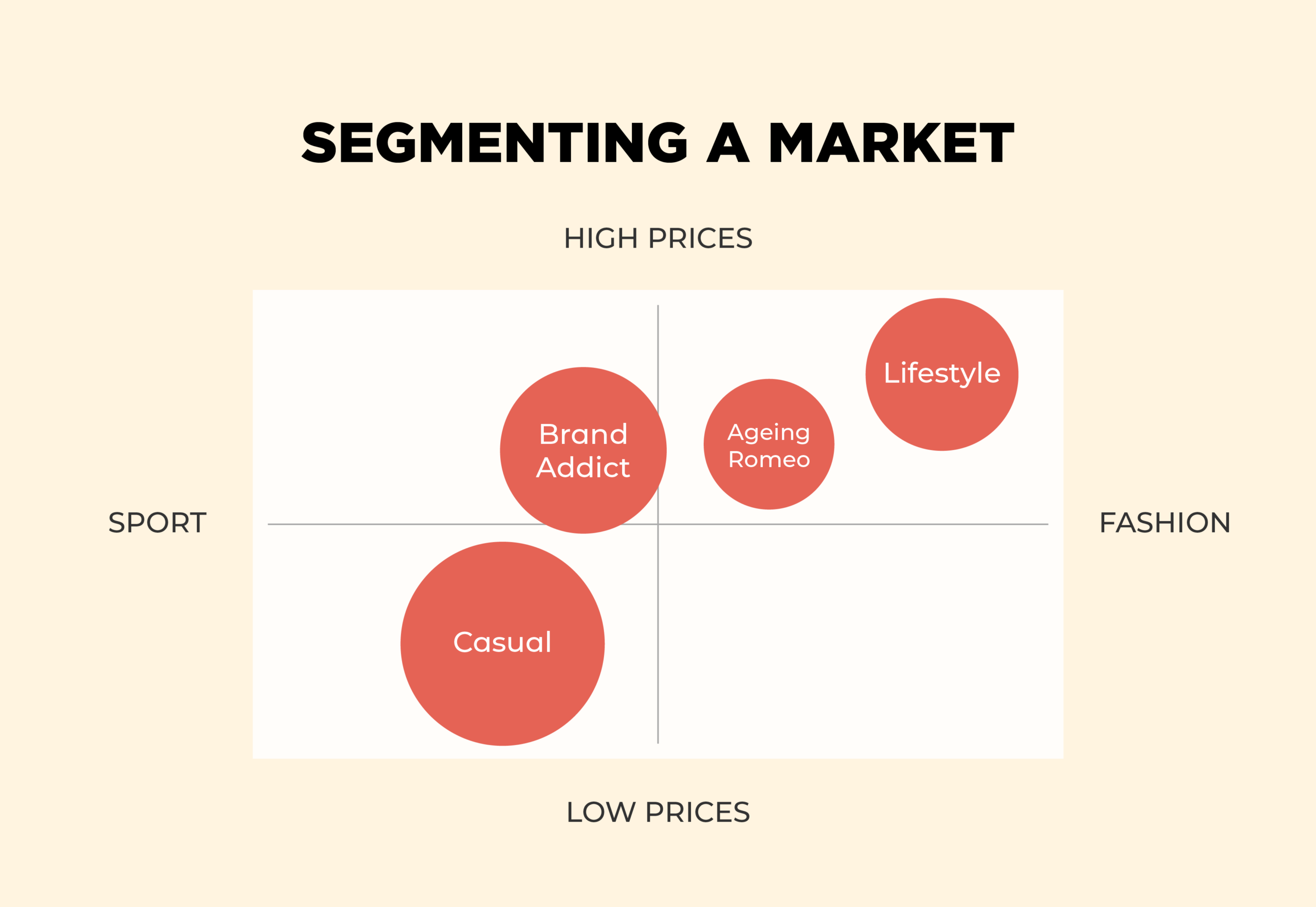
Positioning maps, also known as perceptual maps, are visual representations of how consumers perceive different brands or products within a specific market. They are essentially two-dimensional graphs that plot competing offerings based on key attributes or dimensions deemed important to target customers. These dimensions can include price, quality, features, brand image, or any other factors that influence consumer decision-making.
The Power of Visual Representation
The beauty of positioning maps lies in their ability to translate complex market dynamics into easily digestible visuals. By plotting competing brands on the map, businesses can gain valuable insights into:
- Competitive Landscape: Identifying direct competitors and their positioning within the market.
- Target Audience Preferences: Understanding what attributes are most valued by consumers.
- Positioning Gaps: Identifying untapped areas or niches within the market where there is potential for differentiation.
- Brand Perception: Assessing how consumers perceive the brand relative to competitors.
Building a Positioning Map
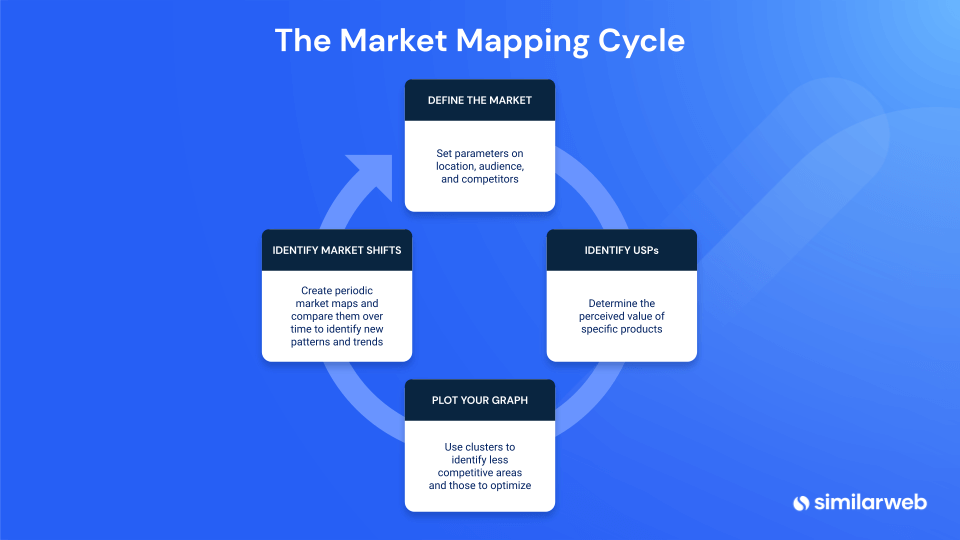
The process of creating a positioning map involves several key steps:
- Defining the Target Market: Clearly identifying the specific customer segment the product or service aims to serve.
- Identifying Key Attributes: Determining the most important factors that influence consumer choices within the target market.
- Data Collection: Gathering data on consumer perceptions of various brands through surveys, interviews, or market research.
- Plotting Brands: Placing competing brands on the map based on their scores on the chosen attributes.
- Analyzing the Results: Interpreting the map to understand the competitive landscape, identify potential gaps, and inform strategic decisions.
Applications of Positioning Map Marketing
Positioning maps are versatile tools with applications across various marketing functions:
- Product Development: Identifying opportunities for new products or services that cater to unmet needs.
- Pricing Strategy: Determining optimal pricing based on the perceived value and competition.
- Marketing Communications: Crafting targeted messaging that resonates with the desired customer segment.
- Brand Positioning: Developing a clear and compelling brand identity that differentiates the offering in the market.
Benefits of Using Positioning Maps
Leveraging positioning maps offers numerous benefits for businesses:
- Enhanced Market Understanding: Gaining a deeper understanding of the competitive landscape and consumer preferences.
- Strategic Differentiation: Identifying opportunities to differentiate the brand and stand out from competitors.
- Targeted Marketing: Developing more effective marketing campaigns that resonate with the desired audience.
- Informed Decision-Making: Making data-driven decisions regarding product development, pricing, and marketing strategies.
FAQs on Positioning Map Marketing
1. What types of data are used to create positioning maps?
Positioning maps rely on data that reflects consumer perceptions. This data can be collected through various methods, including surveys, focus groups, interviews, and market research reports.
2. Can positioning maps be used for all types of products and services?
Yes, positioning maps are applicable to a wide range of products and services, including consumer goods, financial products, healthcare services, and technology solutions.
3. How often should positioning maps be updated?
The frequency of updating positioning maps depends on the dynamism of the market. For rapidly evolving industries, regular updates (e.g., annually) are recommended, while more stable markets may require less frequent updates.
4. What are some limitations of positioning maps?
Positioning maps are based on consumer perceptions, which can be subjective and influenced by factors like personal biases and external influences. Additionally, they are limited to two dimensions, which may not capture all relevant attributes.
Tips for Effective Positioning Map Marketing
- Clearly define the target market and key attributes.
- Use reliable data sources and ensure data accuracy.
- Visualize the map effectively for clarity and impact.
- Consider the map as a dynamic tool, subject to change over time.
- Use the insights gained from the map to inform strategic decisions.
Conclusion
Positioning map marketing provides a powerful visual framework for understanding and navigating the competitive landscape. By leveraging this tool, businesses can gain valuable insights into consumer preferences, identify opportunities for differentiation, and develop more effective marketing strategies. By embracing the power of visual representation, companies can effectively communicate their unique value proposition and secure a competitive advantage in the crowded marketplace.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Guide to Positioning Map Marketing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!