Navigating the Blueprint of Life: A Comprehensive Guide to Genome Concept Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Blueprint of Life: A Comprehensive Guide to Genome Concept Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Blueprint of Life: A Comprehensive Guide to Genome Concept Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Blueprint of Life: A Comprehensive Guide to Genome Concept Maps

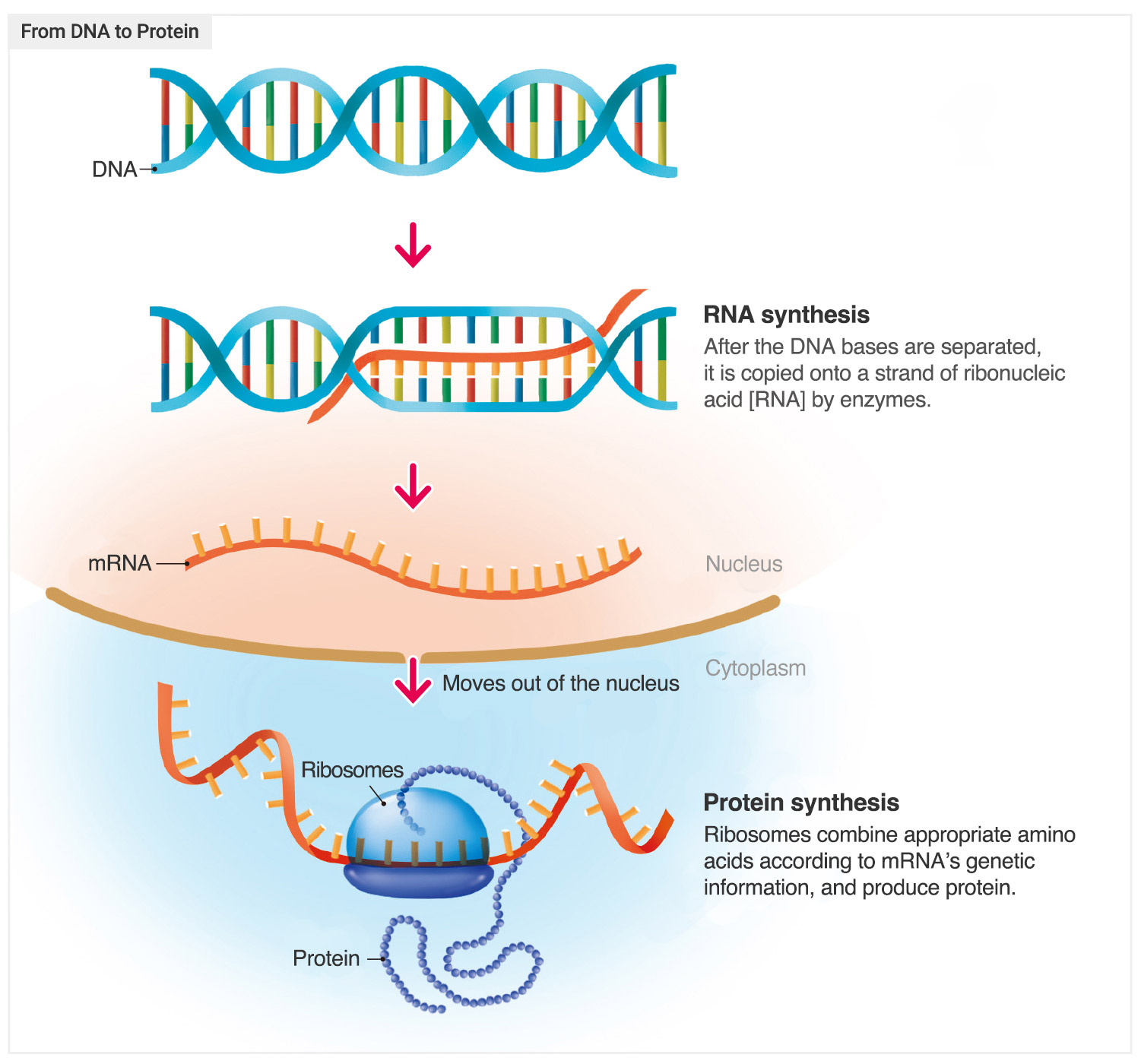
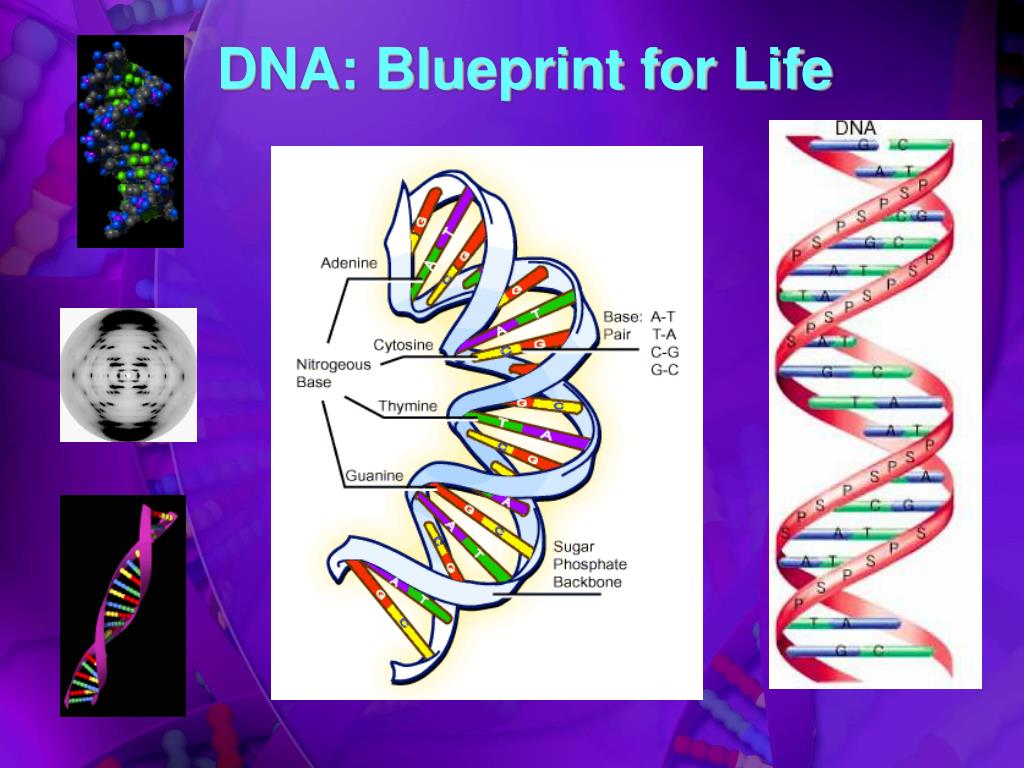
The human genome, a vast and intricate blueprint containing the instructions for building and maintaining an individual, is a testament to the complexity of life. Understanding this intricate code requires a systematic approach, and genome concept maps offer a powerful tool for visualizing and navigating the vast landscape of genomic information.
Understanding the Concept:
A genome concept map is a visual representation of the relationships between different elements within a genome. It serves as a roadmap, connecting genes, proteins, pathways, and other biological entities in a clear and intuitive manner. These maps utilize a hierarchical structure, with nodes representing individual components and links depicting relationships between them.
The Benefits of Visualizing Genomic Information:
The benefits of using genome concept maps extend beyond simple visualization. They offer a powerful framework for:
- Identifying key genes and pathways: By visually connecting different elements, researchers can quickly identify genes and pathways involved in specific biological processes or diseases. This allows for a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms and potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
- Exploring complex interactions: Genome concept maps can reveal intricate relationships between genes, proteins, and other biological entities. This allows for the identification of potential regulatory networks and the exploration of complex biological phenomena.
- Facilitating communication and collaboration: Visual representations are inherently more accessible than textual descriptions. Genome concept maps enable researchers from diverse backgrounds to readily grasp complex genomic information, facilitating communication and fostering collaboration.
- Developing hypotheses and predictions: By observing patterns and connections within the map, researchers can generate hypotheses about gene function and disease mechanisms. This allows for the formulation of testable predictions and the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Types of Genome Concept Maps:
There are various types of genome concept maps, each tailored to specific research needs. Some common examples include:
- Gene Ontology (GO) maps: These maps depict the functional relationships between genes, organizing them into hierarchical categories based on their biological roles.
- Pathway maps: These maps illustrate the interconnectedness of genes and proteins within metabolic and signaling pathways, providing a comprehensive view of cellular processes.
- Disease-specific maps: These maps focus on genes and pathways associated with particular diseases, highlighting potential targets for drug development.
- Comparative genomics maps: These maps compare the genomes of different species, revealing evolutionary relationships and identifying conserved genes and pathways.
Construction and Interpretation:
The creation of a genome concept map requires careful consideration of the research question and the relevant genomic data. The process typically involves:
- Data gathering: Identifying relevant genes, proteins, pathways, and other biological entities from databases and literature.
- Relationship identification: Determining the relationships between these elements based on experimental evidence and existing knowledge.
- Map construction: Using specialized software tools to create a visual representation of the identified relationships, incorporating nodes, links, and hierarchical structures.
- Map interpretation: Analyzing the map to identify patterns, connections, and potential insights, leading to the formulation of hypotheses and predictions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the limitations of genome concept maps?
A: While powerful, genome concept maps have limitations. They rely on existing knowledge and may not capture all complex interactions within a genome. Additionally, the interpretation of these maps can be subjective and require expertise in the relevant biological domain.
Q: What are some popular software tools for constructing genome concept maps?
A: Several software tools are available for constructing genome concept maps, including Cytoscape, Gephi, and PathVisio. These tools offer various functionalities for data visualization, analysis, and interpretation.
Q: How can genome concept maps be used in different research areas?
A: Genome concept maps find applications in various research areas, including:
- Disease research: Identifying potential drug targets and understanding disease mechanisms.
- Evolutionary biology: Comparing genomes of different species and uncovering evolutionary relationships.
- Personalized medicine: Developing tailored treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup.
- Agriculture: Improving crop yields and disease resistance through genetic modification.
Tips for Creating Effective Genome Concept Maps:
- Define a clear research question: Determine the specific goal of the map to ensure focus and clarity.
- Use a consistent and informative labeling system: Clearly label nodes and links with relevant information to enhance understanding.
- Employ visual cues effectively: Utilize colors, shapes, and sizes to highlight key elements and relationships.
- Consider the target audience: Adjust the complexity and level of detail based on the intended audience.
- Continuously update and refine the map: As new knowledge emerges, update the map to reflect the latest findings and maintain its accuracy.
Conclusion:
Genome concept maps provide a valuable tool for navigating the complex landscape of genomic information. By visualizing relationships between genes, proteins, and other biological entities, these maps facilitate understanding, communication, and hypothesis generation. As our knowledge of the genome continues to expand, genome concept maps will remain essential for unraveling the mysteries of life and driving scientific advancements.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Blueprint of Life: A Comprehensive Guide to Genome Concept Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!