Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Peoples: Understanding the Importance of Geographical Representation
Related Articles: Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Peoples: Understanding the Importance of Geographical Representation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Peoples: Understanding the Importance of Geographical Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Peoples: Understanding the Importance of Geographical Representation

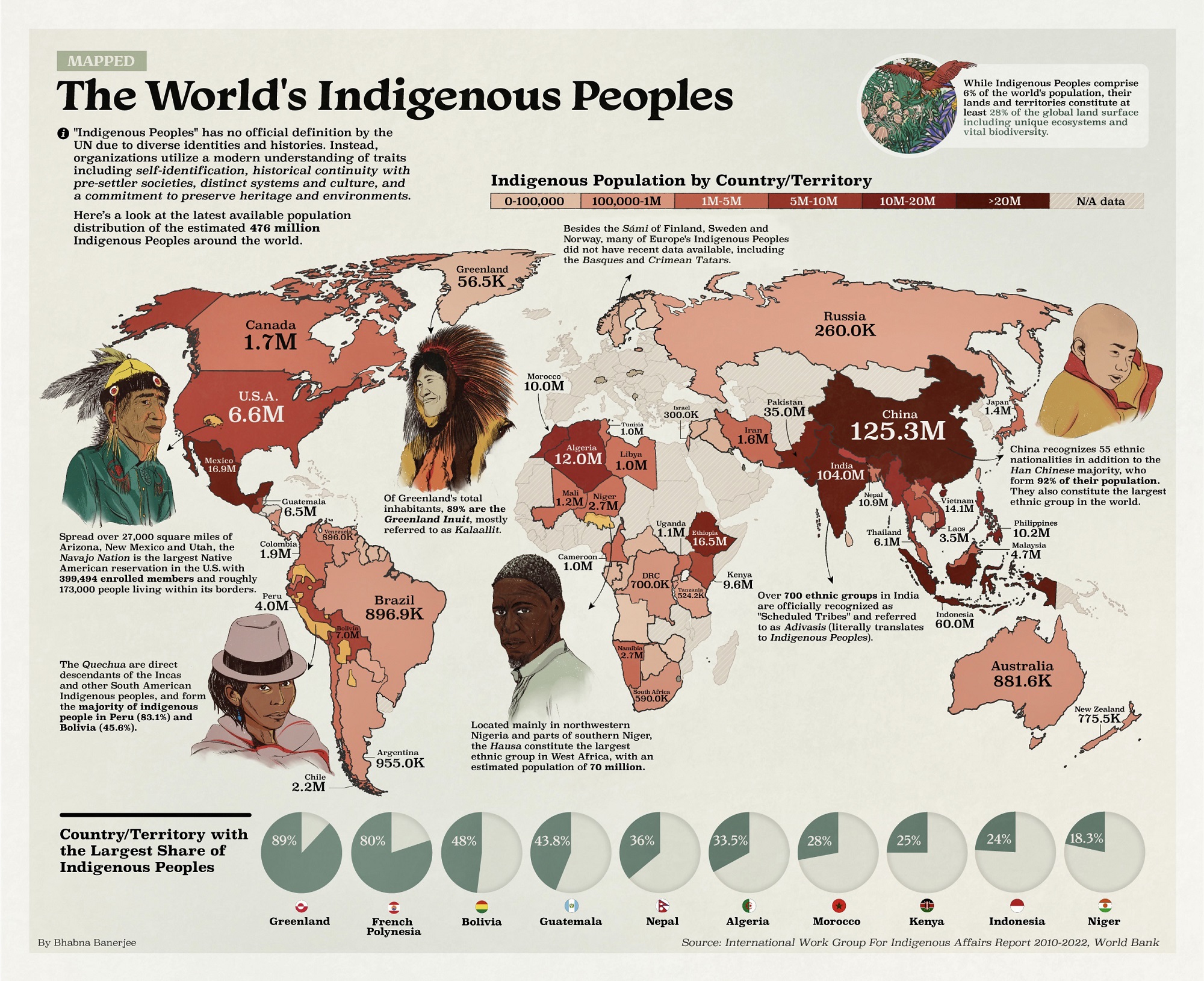
The world’s indigenous populations are a diverse tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions, each with a unique history interwoven with the land they call home. Mapping these diverse communities is not merely a geographical exercise; it is a critical step in understanding their cultural significance, safeguarding their rights, and ensuring their continued existence.
A Visual Representation of Cultural Diversity
Maps of indigenous tribes serve as powerful visual tools for understanding the distribution and diversity of these communities across the globe. They provide a clear and concise representation of the vast array of languages, customs, and traditions that have flourished within specific geographical regions. By visualizing the relationship between indigenous communities and their territories, these maps shed light on the intricate connection between culture and land, highlighting the importance of preserving both.
Understanding Historical and Contemporary Challenges
Maps of indigenous tribes offer crucial insights into the historical and contemporary challenges faced by these communities. They reveal the impact of colonization, displacement, and assimilation policies on indigenous populations, highlighting the ongoing struggle for land rights, self-determination, and cultural preservation. These maps can serve as valuable tools for researchers, policymakers, and advocates working to address these challenges and promote indigenous rights.
Promoting Cultural Awareness and Appreciation
By showcasing the geographic distribution and cultural diversity of indigenous tribes, these maps foster a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of human experience. They challenge Eurocentric perspectives and promote a more inclusive understanding of global history and culture. These maps serve as a reminder of the invaluable contributions of indigenous peoples to art, science, medicine, and environmental stewardship, highlighting the need to recognize and respect their knowledge systems and traditions.
Facilitating Collaboration and Engagement
Maps of indigenous tribes can facilitate collaboration between indigenous communities and external stakeholders, including governments, non-governmental organizations, and researchers. By providing a visual representation of indigenous territories and cultural boundaries, these maps can serve as a foundation for meaningful dialogue, partnership, and resource sharing. They can also assist in the development of culturally appropriate programs and initiatives that address the specific needs and aspirations of indigenous communities.
Navigating the Complexities of Indigenous Identity
It is essential to acknowledge the complexities of indigenous identity and the fluidity of tribal boundaries. Maps should not be interpreted as rigid or definitive representations of indigenous populations. Rather, they should be viewed as dynamic tools that reflect the ongoing evolution and diversity of indigenous cultures and communities. The inclusion of diverse perspectives and voices from indigenous communities is crucial in developing accurate and culturally sensitive maps.
FAQs
1. What are the different types of maps of indigenous tribes?
Maps of indigenous tribes can vary in their scope, focus, and level of detail. Some maps focus on specific regions, while others provide a global overview. They can also differ in their representation of tribal boundaries, language families, or cultural practices.
2. How can I find a map of indigenous tribes?
Various resources are available for accessing maps of indigenous tribes, including online databases, academic journals, and government websites. Specialized organizations focused on indigenous issues often provide detailed maps of specific regions.
3. What are the limitations of maps of indigenous tribes?
Maps of indigenous tribes should be interpreted with caution, recognizing their inherent limitations. They may not capture the full complexity of indigenous identity, cultural diversity, or the dynamic nature of tribal boundaries. It is crucial to consult with indigenous communities and use maps as a starting point for deeper engagement and understanding.
4. How can I contribute to the development of accurate and inclusive maps of indigenous tribes?
Individuals can contribute to the development of accurate and inclusive maps by supporting organizations dedicated to indigenous mapping initiatives, engaging in critical dialogue about the representation of indigenous communities, and advocating for the inclusion of indigenous perspectives in mapping projects.
Tips for Using Maps of Indigenous Tribes
- Consult with indigenous communities: Engage with indigenous communities to ensure that maps accurately reflect their perspectives and priorities.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the historical context of indigenous territories and the impact of colonization on tribal boundaries.
- Acknowledge the fluidity of indigenous identity: Recognize that tribal boundaries are not static and may evolve over time.
- Use maps as a starting point for further research: Maps should serve as a foundation for deeper engagement with indigenous cultures and communities.
Conclusion
Maps of indigenous tribes are valuable tools for understanding the cultural diversity, historical experiences, and ongoing challenges faced by these communities. By visualizing the relationship between indigenous populations and their territories, these maps foster cultural appreciation, promote collaboration, and contribute to the safeguarding of indigenous rights and cultural heritage. It is essential to approach these maps with sensitivity and respect, recognizing the complexities of indigenous identity and the importance of engaging with indigenous communities in the development and interpretation of these visual representations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Tapestry of Indigenous Peoples: Understanding the Importance of Geographical Representation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!