Egypt: A Land Bridge Between Continents
Related Articles: Egypt: A Land Bridge Between Continents
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Egypt: A Land Bridge Between Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Egypt: A Land Bridge Between Continents

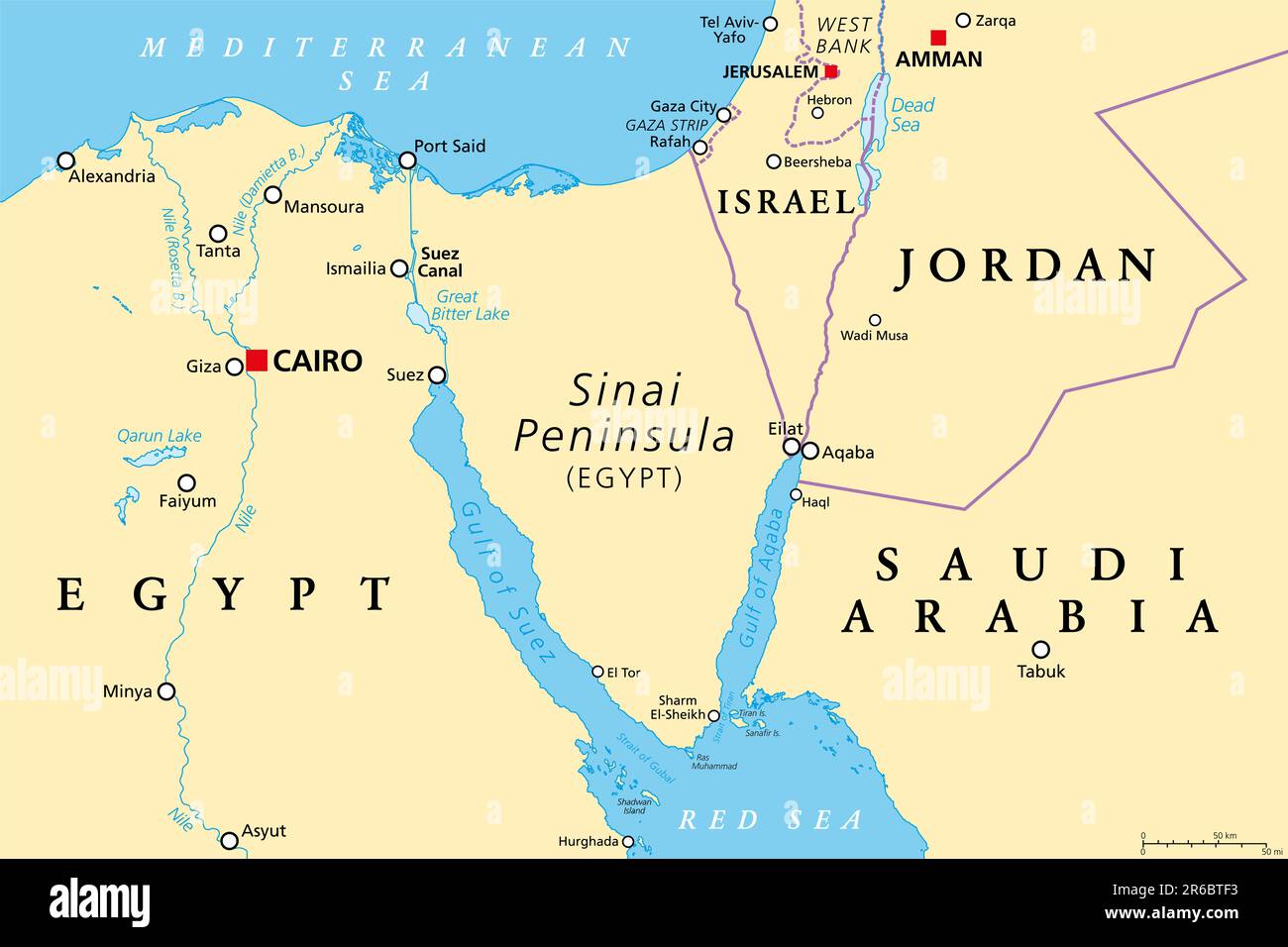
Egypt, a nation steeped in history and culture, occupies a strategically vital location in the northeastern corner of Africa. Its unique geographic position serves as a bridge between the continents of Africa and Asia, making it a crossroads of civilizations for millennia. Understanding Egypt’s location on the map reveals its historical significance, its economic potential, and its enduring impact on the world.
A Land of Contrasts: From Desert to Nile
Egypt’s landscape is a study in contrasts, dominated by the vast Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world. This arid expanse covers the majority of the country, stretching from the Libyan border in the west to the Red Sea in the east. Yet, amidst this sea of sand, the lifeblood of Egypt flows: the Nile River. This mighty waterway cuts through the desert, providing a fertile ribbon of life that has sustained civilization for thousands of years.
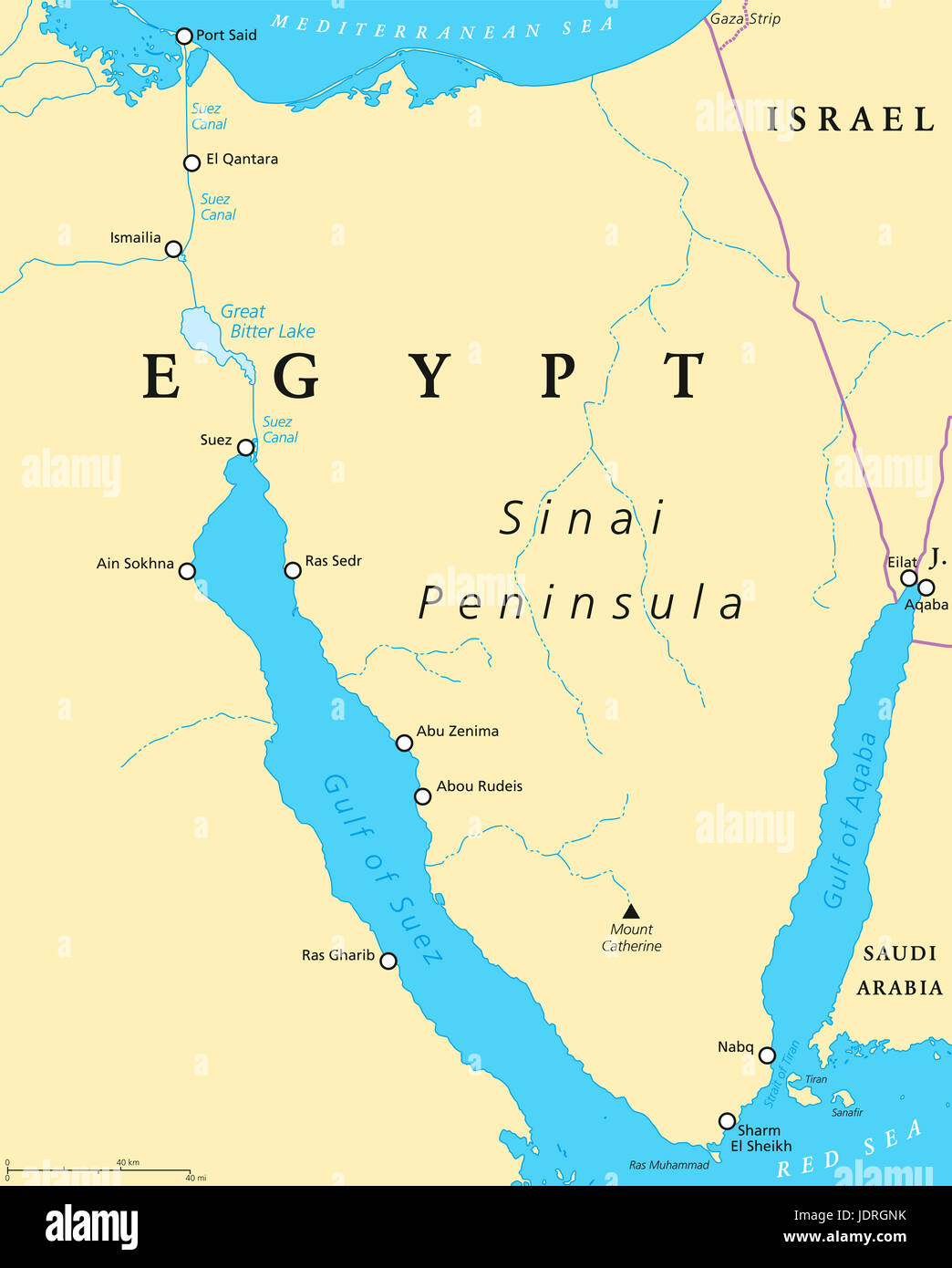
A Gateway to Three Continents:
Egypt’s strategic location at the southern tip of the Sinai Peninsula, a narrow strip of land connecting Africa and Asia, makes it a natural gateway between continents. This unique geographic feature has shaped Egypt’s history, its economy, and its cultural identity.
- Africa: Egypt’s primary geographic affiliation is with Africa. It shares borders with Libya to the west, Sudan to the south, and the Red Sea to the east. Its connection to the African continent is deeply rooted in shared history, culture, and trade routes.
- Asia: The Sinai Peninsula connects Egypt to Asia, specifically the Levant region. This connection has been historically significant for trade, migration, and cultural exchange. Egypt’s proximity to the Middle East and its role in regional politics further underscore its importance in the Asian context.
- Europe: While not directly connected to Europe, Egypt’s proximity to the Mediterranean Sea has facilitated historical and cultural ties with Europe. This connection is evident in the influence of ancient Greek and Roman civilizations on Egyptian culture, as well as in modern-day trade and tourism.
A Crossroads of Civilizations:
Egypt’s strategic location has made it a crossroads of civilizations throughout history. Its position as a bridge between continents has facilitated the exchange of ideas, goods, and people, contributing to the rise and fall of empires and the development of unique cultural identities.
- Ancient Egypt: The ancient Egyptians, renowned for their advanced civilization, thrived along the Nile River, using its fertile banks to develop agriculture and build magnificent monuments. Their influence extended beyond Egypt, reaching into Nubia, the Levant, and even further afield.
- Roman Empire: The Roman Empire conquered Egypt in 30 BC, integrating it into its vast network of provinces. This period saw the spread of Roman culture and influence, shaping Egypt’s architectural landscape and its administrative systems.
- Arab Conquests: The Arab conquest of Egypt in the 7th century AD marked a significant turning point in the country’s history. The introduction of Islam and the Arabic language profoundly shaped Egypt’s cultural and religious identity.
A Land of Economic Potential:
Egypt’s strategic location offers significant economic advantages. Its access to major trade routes, including the Suez Canal, makes it a crucial hub for global commerce.
- Suez Canal: This vital waterway, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, is a critical link in global trade. It allows for the efficient transport of goods between Europe, Asia, and Africa, making Egypt a key player in the global economy.
- Tourism: Egypt’s rich history and culture attract millions of tourists every year. Its ancient pyramids, temples, and archaeological sites are renowned worldwide, making it a major destination for cultural tourism.
- Agriculture: The Nile River continues to be the backbone of Egypt’s agricultural economy, providing fertile land for growing crops like cotton, wheat, and rice. This agricultural potential is further enhanced by the development of modern irrigation systems.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While Egypt’s location offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges. The country’s proximity to conflict zones in the Middle East and its reliance on the Nile River for water resources create potential vulnerabilities. However, Egypt’s strategic location also presents opportunities for economic development and regional cooperation.
- Water Security: The Nile River is a vital resource, but its availability is threatened by climate change and upstream development. This requires proactive measures to ensure water security for Egypt’s growing population.
- Regional Stability: Egypt’s location in a volatile region necessitates diplomatic efforts to promote stability and cooperation. This involves engaging with regional partners to address shared concerns and promote peaceful resolutions.
- Economic Development: Egypt’s strategic location offers potential for economic growth, particularly in sectors like tourism, trade, and logistics. Investing in infrastructure and promoting innovation can unlock this economic potential.
FAQs: Where is Egypt Located on the Map?
- What continent is Egypt located on? Egypt is primarily located in Africa, but its Sinai Peninsula extends into Asia.
- What countries border Egypt? Egypt shares borders with Libya to the west, Sudan to the south, and the Gaza Strip and Israel to the east.
- What major bodies of water surround Egypt? Egypt is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Red Sea to the east, and the Nile River flowing through its center.
- What is the significance of Egypt’s location? Egypt’s location at the crossroads of Africa and Asia has made it a center of trade, cultural exchange, and historical influence for millennia.
- What are the challenges and opportunities presented by Egypt’s location? Egypt faces challenges related to water security, regional stability, and economic development, but its strategic position also offers opportunities for growth and cooperation.
Tips for Understanding Egypt’s Location:
- Use a map: Familiarize yourself with a map of the Middle East and North Africa to visualize Egypt’s location in relation to other countries and geographical features.
- Read about its history: Understanding Egypt’s historical significance and its role in ancient civilizations will provide context for its strategic location.
- Explore its culture: Engage with Egypt’s rich culture, art, and literature to appreciate the influence of its location on its cultural identity.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about current events in the Middle East and North Africa to understand the challenges and opportunities presented by Egypt’s location in the modern world.
Conclusion:
Egypt’s location on the map is more than just a geographical fact; it is a testament to its historical significance, its economic potential, and its enduring impact on the world. As a bridge between continents, Egypt has served as a crossroads of civilizations, a center of trade, and a hub for cultural exchange. Understanding its location unlocks a deeper appreciation for its unique history, its diverse culture, and its ongoing role in shaping the future of the region and the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Egypt: A Land Bridge Between Continents. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!