Deciphering California’s Temperature Landscape: A Guide to Heat Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering California’s Temperature Landscape: A Guide to Heat Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering California’s Temperature Landscape: A Guide to Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Deciphering California’s Temperature Landscape: A Guide to Heat Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Deciphering California’s Temperature Landscape: A Guide to Heat Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Color Spectrum: A Key to Interpretation
- 3.2 Unveiling the Geographic Patterns: Insights from California’s Heat Maps
- 3.3 Applications of California Heat Maps: From Weather Forecasting to Environmental Monitoring
- 3.4 FAQs about Heat Maps: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Interpreting California Heat Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion: Unveiling California’s Thermal Landscape
- 4 Closure
Deciphering California’s Temperature Landscape: A Guide to Heat Maps
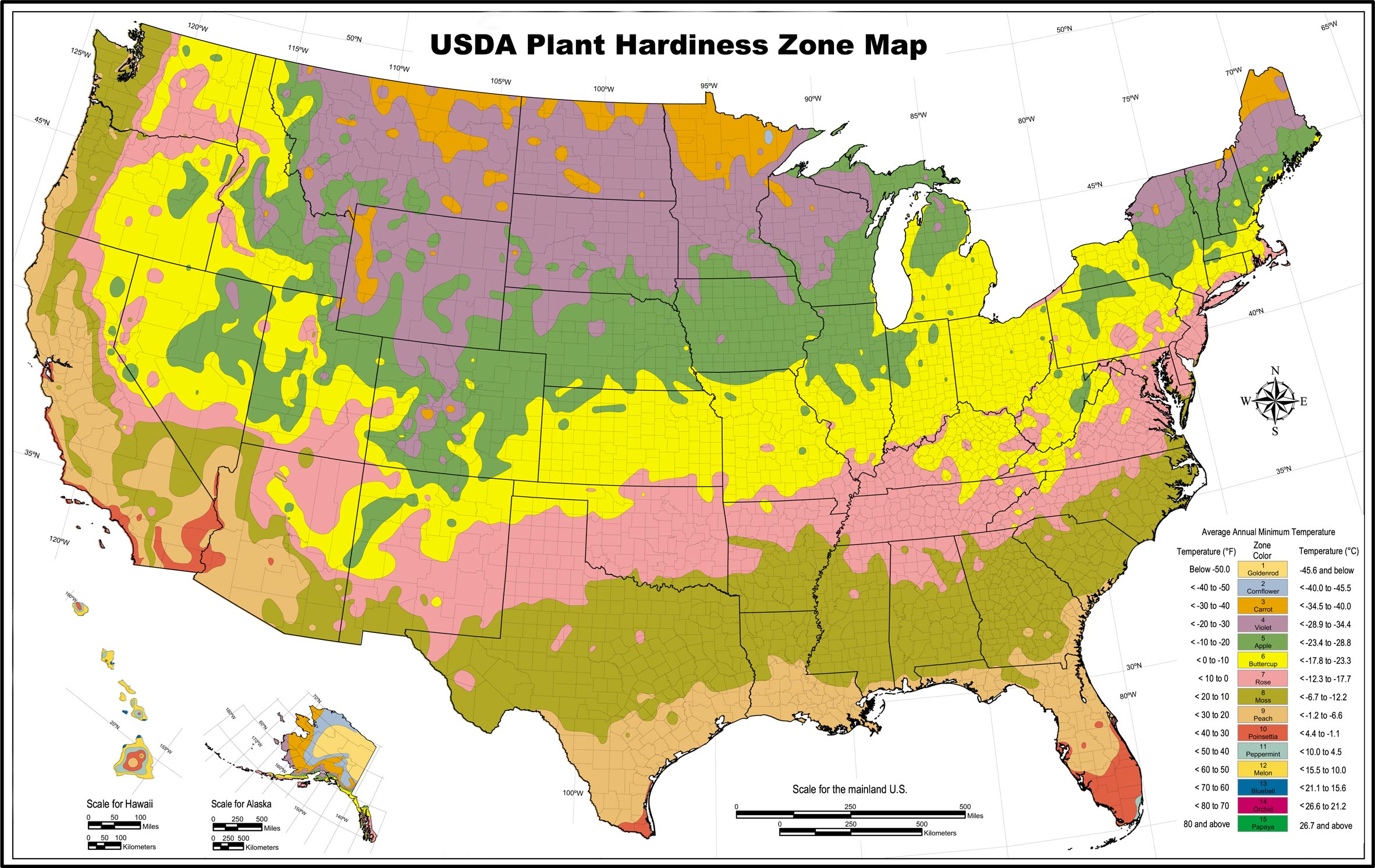
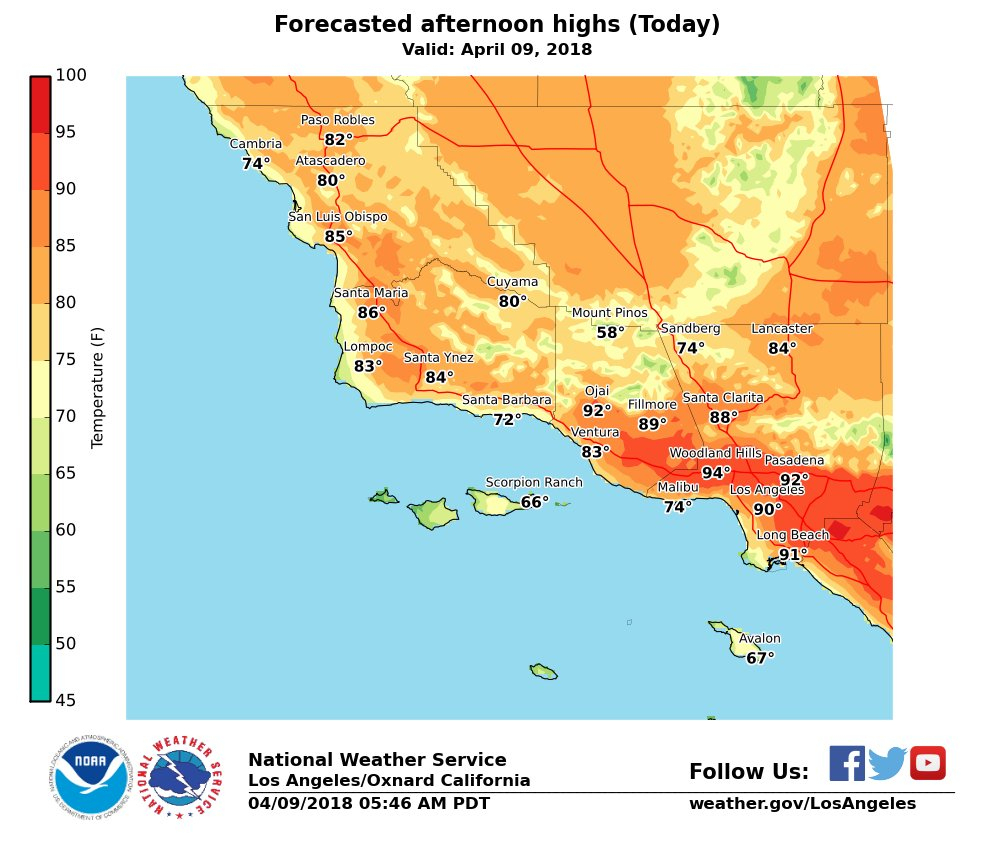
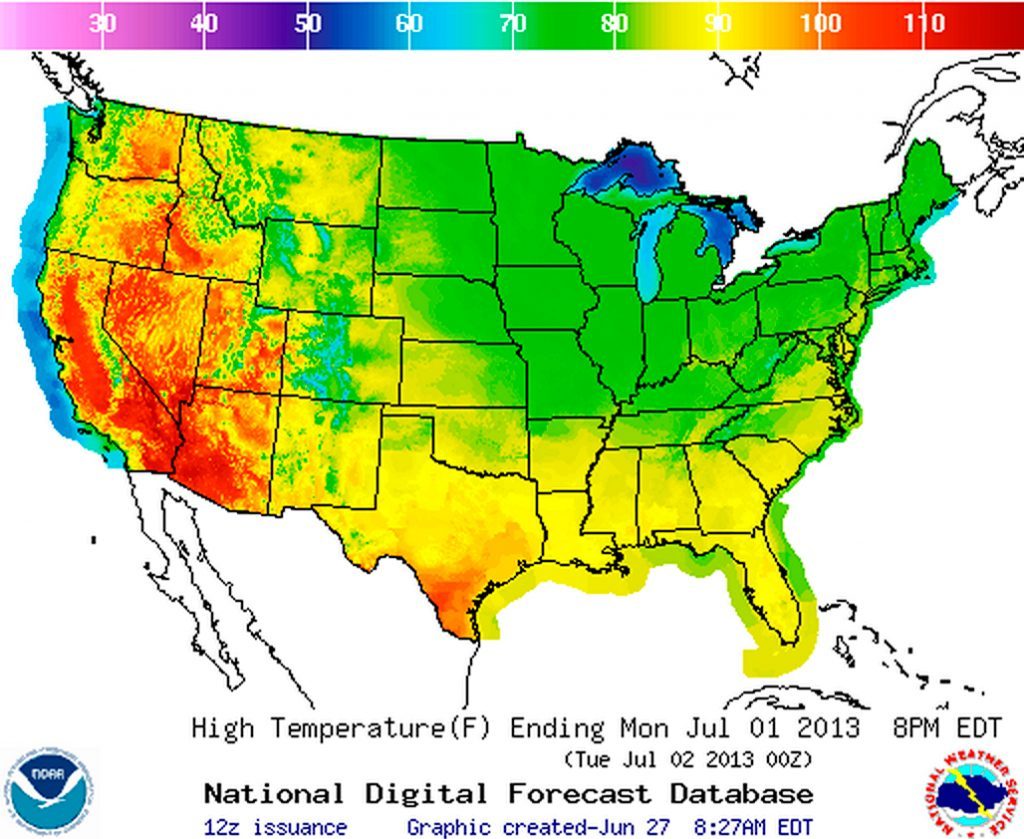
California, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes, experiences a wide range of temperatures across its vast expanse. To effectively visualize and understand this temperature variability, heat maps have become indispensable tools. These maps employ color gradients to represent temperature variations, offering a clear and intuitive representation of the state’s thermal landscape.
Understanding the Color Spectrum: A Key to Interpretation
Heat maps utilize a spectrum of colors, typically ranging from blue to red, to depict temperature variations. Blue hues represent cooler temperatures, while red signifies hotter areas. This color gradient allows for quick identification of the hottest and coldest regions within California.
For instance, a dark blue area on a heat map might indicate the presence of a cool coastal region, while a bright red patch could signify a scorching desert area. Intermediate colors like green or yellow represent temperatures falling between the extremes.
Unveiling the Geographic Patterns: Insights from California’s Heat Maps
California’s heat maps reveal fascinating geographic patterns, highlighting the influence of various factors on temperature distribution. Some key observations include:
- Coastal Influence: The Pacific Ocean’s moderating effect is evident in the cooler temperatures along the coastline. Coastal regions, particularly in Southern California, often exhibit blue hues on heat maps, indicating a milder climate compared to inland areas.
- Mountainous Terrain: California’s mountainous regions, such as the Sierra Nevada and the San Gabriel Mountains, experience significant temperature variations due to elevation. Higher elevations tend to be cooler, reflected in shades of blue on heat maps, while lower elevations can be significantly warmer, often represented by red or orange hues.
- Desert Influence: California’s deserts, like the Mojave and the Sonoran, are notorious for their extreme temperatures. Heat maps depict these regions with intense red and orange colors, signifying scorching temperatures, particularly during the summer months.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Major cities like Los Angeles, San Francisco, and San Diego exhibit a phenomenon known as the urban heat island effect. This effect, caused by the concentration of buildings and infrastructure, leads to higher temperatures in urban areas compared to surrounding rural areas. Heat maps reflect this phenomenon with warmer colors over urban centers.
Applications of California Heat Maps: From Weather Forecasting to Environmental Monitoring
Heat maps serve a multitude of purposes, providing valuable insights for various sectors:
- Weather Forecasting: Heat maps play a crucial role in weather forecasting. By analyzing temperature patterns, meteorologists can predict the likelihood of heat waves, cold snaps, and other weather events. This information allows for timely warnings and preparedness measures.
- Environmental Monitoring: Heat maps assist in monitoring environmental conditions. They help track the spread of wildfires, identify areas vulnerable to drought, and assess the impact of climate change on different regions. This information is crucial for resource management and mitigation efforts.
- Public Health: Heat maps are vital tools in public health. They help identify areas at risk of heat-related illnesses and guide public health initiatives to mitigate these risks.
- Agriculture: Heat maps assist farmers in understanding the thermal conditions of their fields, optimizing crop selection, and planning irrigation schedules.
FAQs about Heat Maps: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the different types of heat maps used in California?
Several types of heat maps are used, including:
- Surface Temperature Maps: These maps depict surface temperatures, typically measured by satellites or ground-based sensors.
- Air Temperature Maps: These maps represent air temperatures at different elevations, often derived from weather stations or models.
- Heat Index Maps: These maps combine air temperature and humidity to calculate the perceived heat experienced by humans.
2. How accurate are California heat maps?
The accuracy of heat maps depends on the data sources used and the spatial resolution of the map. Satellite data provides a broad overview, while ground-based measurements offer more localized information.
3. What are the limitations of heat maps?
Heat maps are valuable tools but have limitations:
- Data Availability: Data availability can influence the accuracy and completeness of heat maps.
- Spatial Resolution: The resolution of heat maps can limit the ability to depict detailed temperature variations.
- Temporal Variations: Heat maps represent temperatures at a specific point in time, and temperature patterns can change rapidly.
Tips for Interpreting California Heat Maps
- Pay attention to the color scale: The color scale indicates the temperature range represented on the map.
- Consider the time of day: Temperatures vary significantly throughout the day, so it’s important to note the time the data was collected.
- Look for spatial patterns: Identify areas with similar temperatures and consider the underlying factors influencing those patterns.
- Compare different maps: Comparing heat maps from different sources or time periods can provide a more comprehensive understanding of temperature trends.
Conclusion: Unveiling California’s Thermal Landscape
Heat maps provide a powerful visualization tool for understanding California’s temperature landscape. By deciphering the color gradients and analyzing the spatial patterns, we gain valuable insights into the influence of geographic features, urban development, and climate change on temperature distribution. These insights are crucial for weather forecasting, environmental monitoring, public health, and agricultural practices, ensuring a more informed and sustainable approach to managing California’s diverse and dynamic thermal environment.


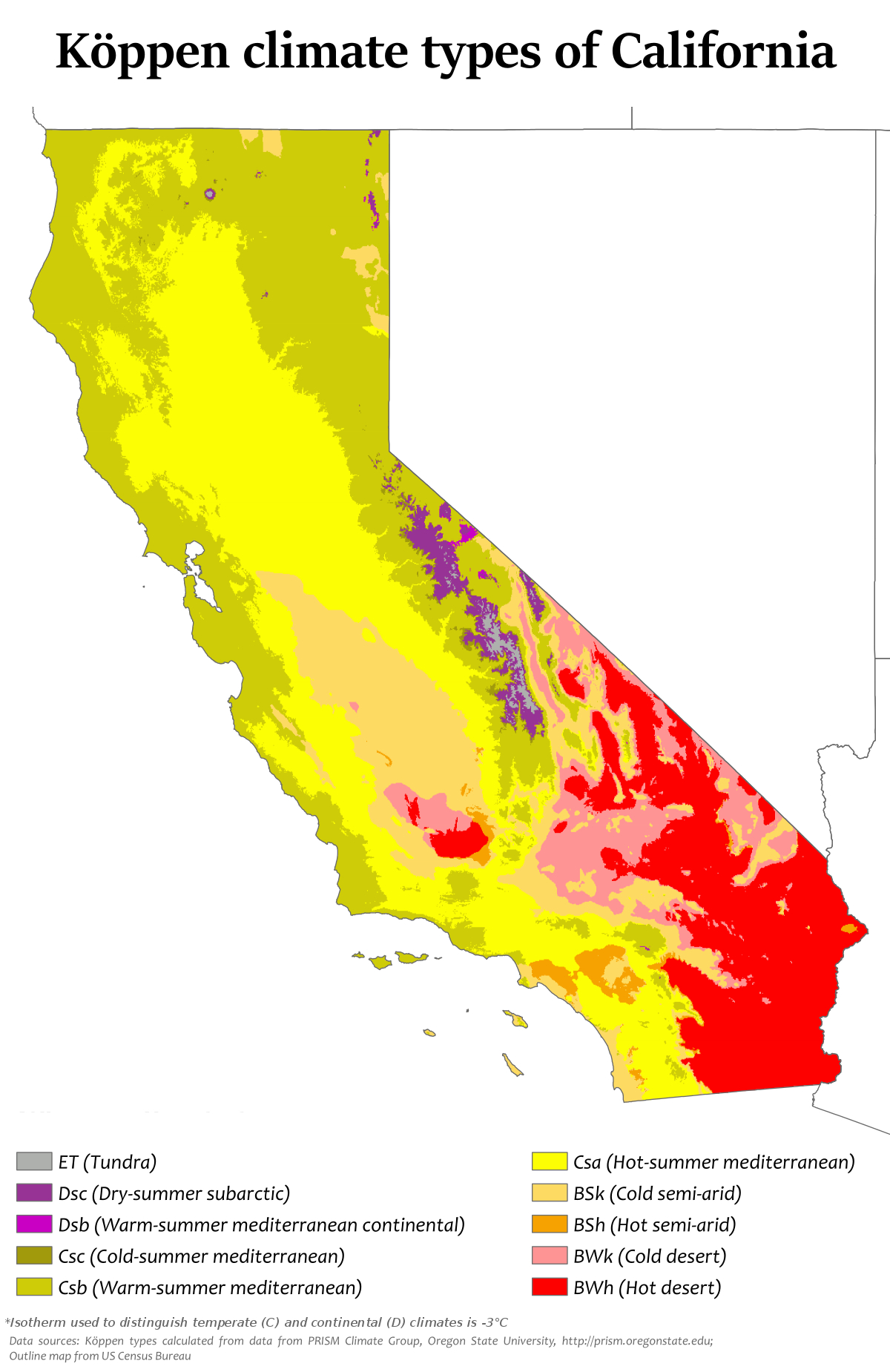

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering California’s Temperature Landscape: A Guide to Heat Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!