cantonese vs mandarin map
Related Articles: cantonese vs mandarin map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to cantonese vs mandarin map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual Guide to the Linguistic Landscape of China: Cantonese vs. Mandarin
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-the-difference-between-mandarin-and-cantonese-1535880-f4071c021f994466a2b6212e87acc916.png)
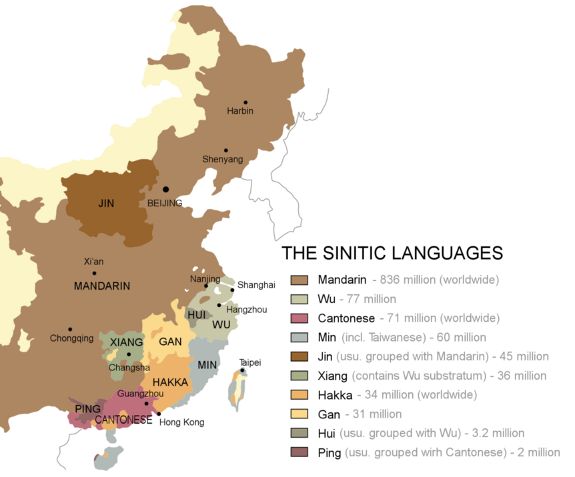
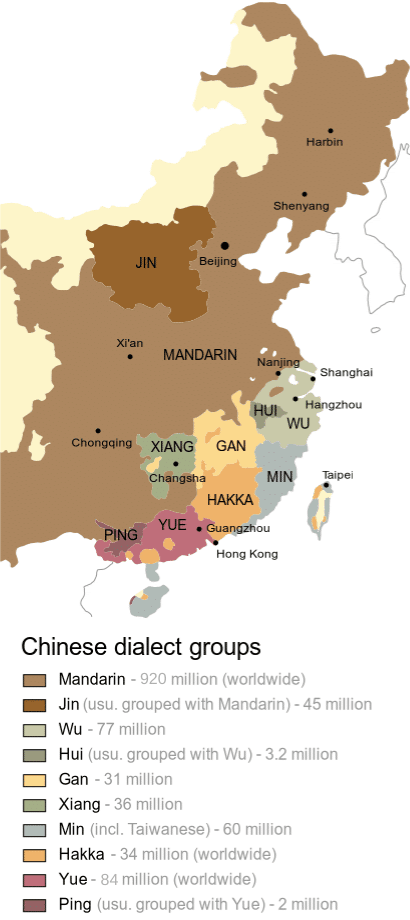
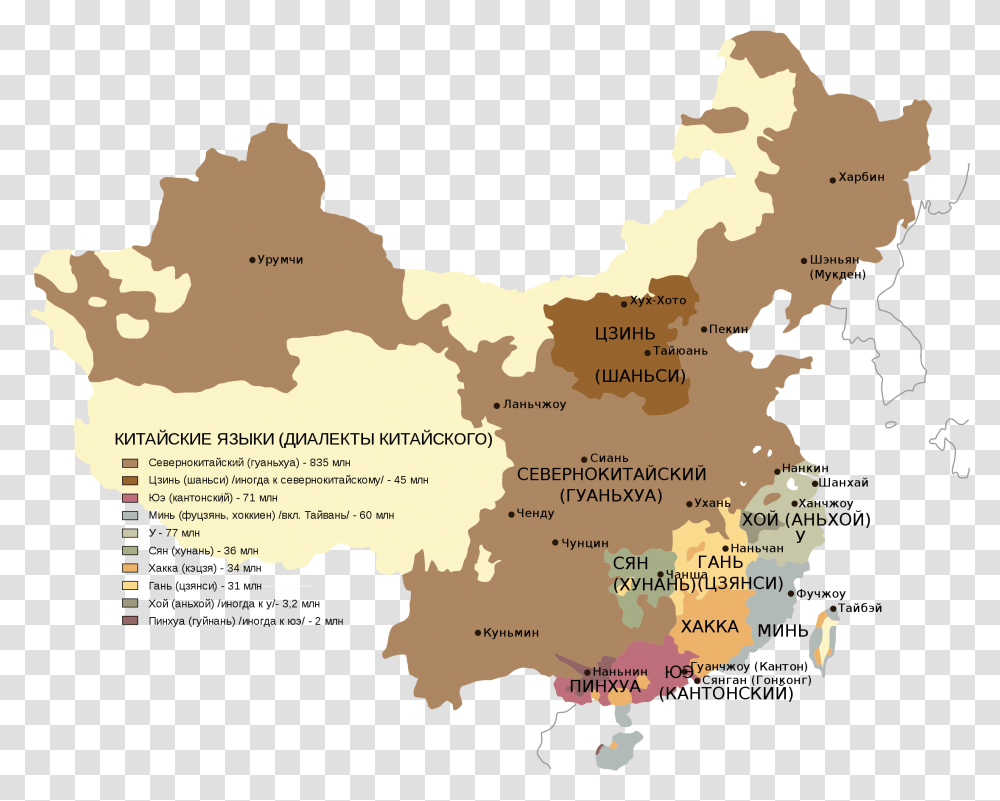
China, a nation of immense cultural and linguistic diversity, boasts a vast array of dialects and languages. Among these, Cantonese and Mandarin stand out as two of the most prominent, each possessing a rich history and a significant number of speakers. While Mandarin has achieved official language status and widespread use, Cantonese continues to thrive in specific regions, particularly in southern China. Understanding the geographical distribution of these two languages is crucial for comprehending the linguistic landscape of China.
Mapping the Linguistic Divide:
A map illustrating the distribution of Cantonese and Mandarin reveals a clear geographical divide. Mandarin, the official language of China, dominates the north and central regions, while Cantonese holds sway in the south, primarily in Guangdong, Guangxi, and Hong Kong. This geographical separation reflects historical and cultural factors that have shaped the linguistic landscape of China.
Historical Influences:
The differences between Cantonese and Mandarin can be traced back to historical events and the evolution of the Chinese language. During the Qin Dynasty (221-206 BC), the unification of China led to the standardization of the written language, but regional variations in spoken language persisted. Over time, these regional variations diverged, resulting in distinct dialects.
Cantonese, originating in the Pearl River Delta region, evolved independently from Mandarin, which developed in the north. This historical separation led to significant differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar between the two languages.
Regional Variations and Dialects:
While Cantonese and Mandarin are the two most prominent languages in China, they are not monolithic entities. Each language encompasses a variety of dialects and sub-dialects, reflecting the diverse linguistic heritage of the country.
Within Cantonese, variations can be observed between the dialects spoken in Guangzhou, Hong Kong, and other Cantonese-speaking regions. Similarly, Mandarin exhibits regional differences, with variations in pronunciation and vocabulary existing between the dialects spoken in Beijing, Shanghai, and other parts of China.
The Rise of Mandarin:
In the 20th century, Mandarin gained prominence as the official language of the People’s Republic of China. This shift was driven by several factors, including the need for a unified language for national communication and the promotion of national unity. The widespread use of Mandarin in education, media, and government has contributed to its dominance in contemporary China.
Cantonese: A Resilient Language:
Despite the dominance of Mandarin, Cantonese remains a vibrant and influential language, particularly in southern China and among overseas Chinese communities. Cantonese enjoys a strong cultural identity and continues to be spoken by millions of people in Hong Kong, Macau, and other regions.
Cultural Significance:
Cantonese and Mandarin are not simply languages; they are integral parts of the cultural identity of their respective regions. Cantonese culture is deeply intertwined with the language, reflected in its music, literature, and cuisine. Similarly, Mandarin plays a significant role in shaping the cultural landscape of northern and central China.
Benefits of Understanding Cantonese and Mandarin:
Understanding the differences between Cantonese and Mandarin offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Cultural Appreciation: Learning about these languages allows for a deeper appreciation of Chinese culture and its diverse regional expressions.
- Improved Communication: Knowing both languages expands communication possibilities within China and with Chinese communities worldwide.
- Business Opportunities: Proficiency in Cantonese and Mandarin can open doors to business opportunities in China and other Cantonese-speaking regions.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main differences between Cantonese and Mandarin?
A: Cantonese and Mandarin differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. Cantonese is known for its tonal complexity and use of unique vocabulary, while Mandarin has a simpler tonal system and a more standardized vocabulary.
Q: Is it difficult to learn both Cantonese and Mandarin?
A: Learning both languages can be challenging, especially due to their distinct tonal systems and vocabulary. However, with dedication and consistent practice, it is achievable.
Q: Which language is more widely spoken?
A: Mandarin is the official language of China and has a significantly larger number of speakers than Cantonese. However, Cantonese remains a prominent language in southern China and overseas Chinese communities.
Q: Can I learn Cantonese without learning Mandarin?
A: Yes, it is possible to learn Cantonese without learning Mandarin. However, understanding Mandarin can provide a broader context for learning Cantonese and facilitate communication with Mandarin speakers.
Tips for Learning Cantonese and Mandarin:
- Immerse yourself in the language: Surround yourself with Cantonese and Mandarin through media, music, and cultural events.
- Practice regularly: Consistent practice is essential for mastering these languages.
- Find a language partner: Engaging in conversation with native speakers can improve fluency and pronunciation.
- Use language learning apps and resources: Utilize online resources and apps to supplement your learning.
Conclusion:
The linguistic landscape of China is rich and diverse, with Cantonese and Mandarin standing as two prominent languages. Understanding the geographical distribution and historical influences behind these languages is crucial for appreciating the cultural and linguistic heritage of China. While Mandarin has achieved official language status and widespread use, Cantonese continues to thrive in specific regions, reflecting the enduring influence of regional dialects and cultural identities. By understanding the nuances of these languages, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and richness of Chinese culture.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into cantonese vs mandarin map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!