A Tapestry of Provinces: Understanding Afghanistan’s Political Landscape
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Provinces: Understanding Afghanistan’s Political Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Provinces: Understanding Afghanistan’s Political Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Provinces: Understanding Afghanistan’s Political Landscape

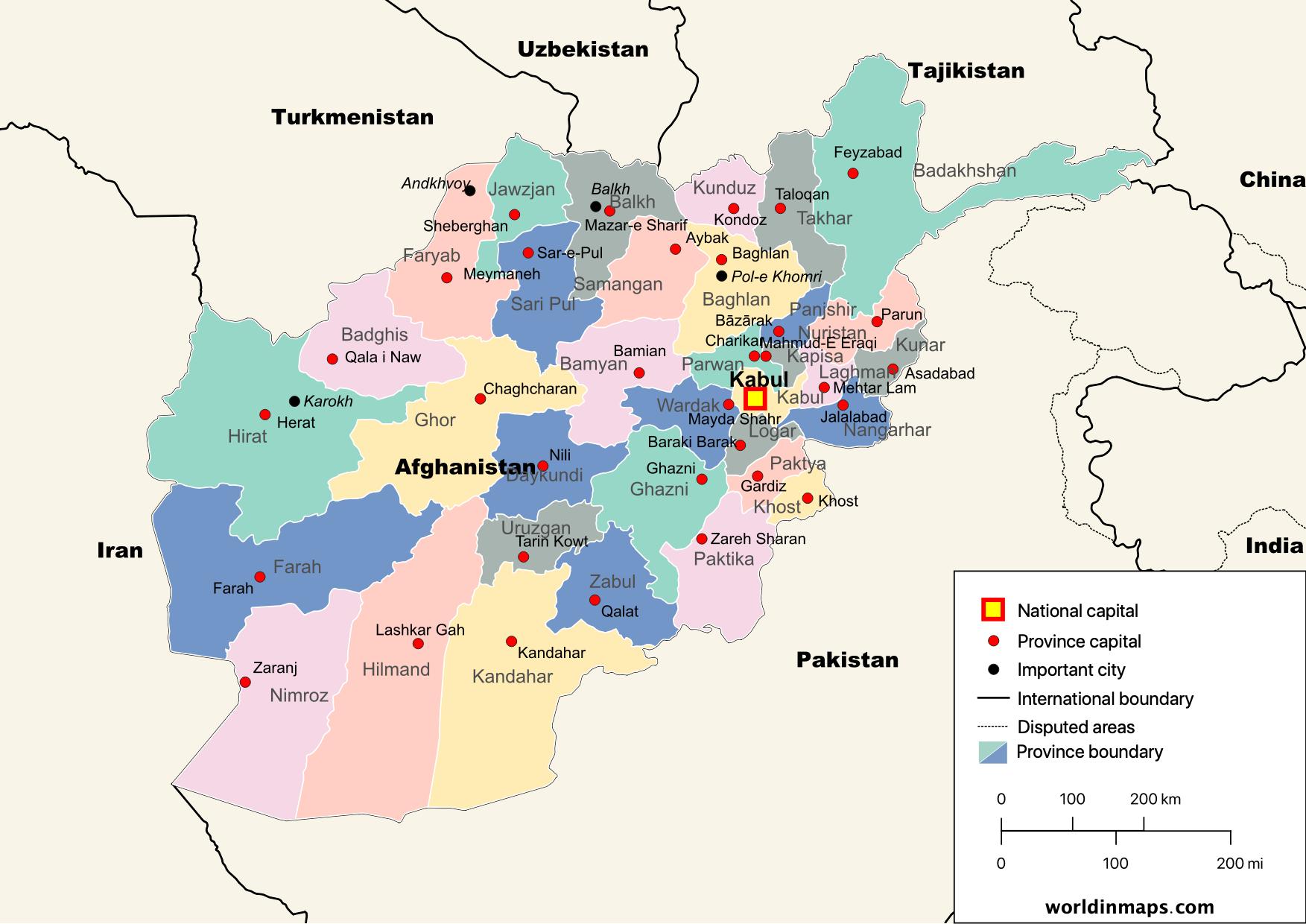
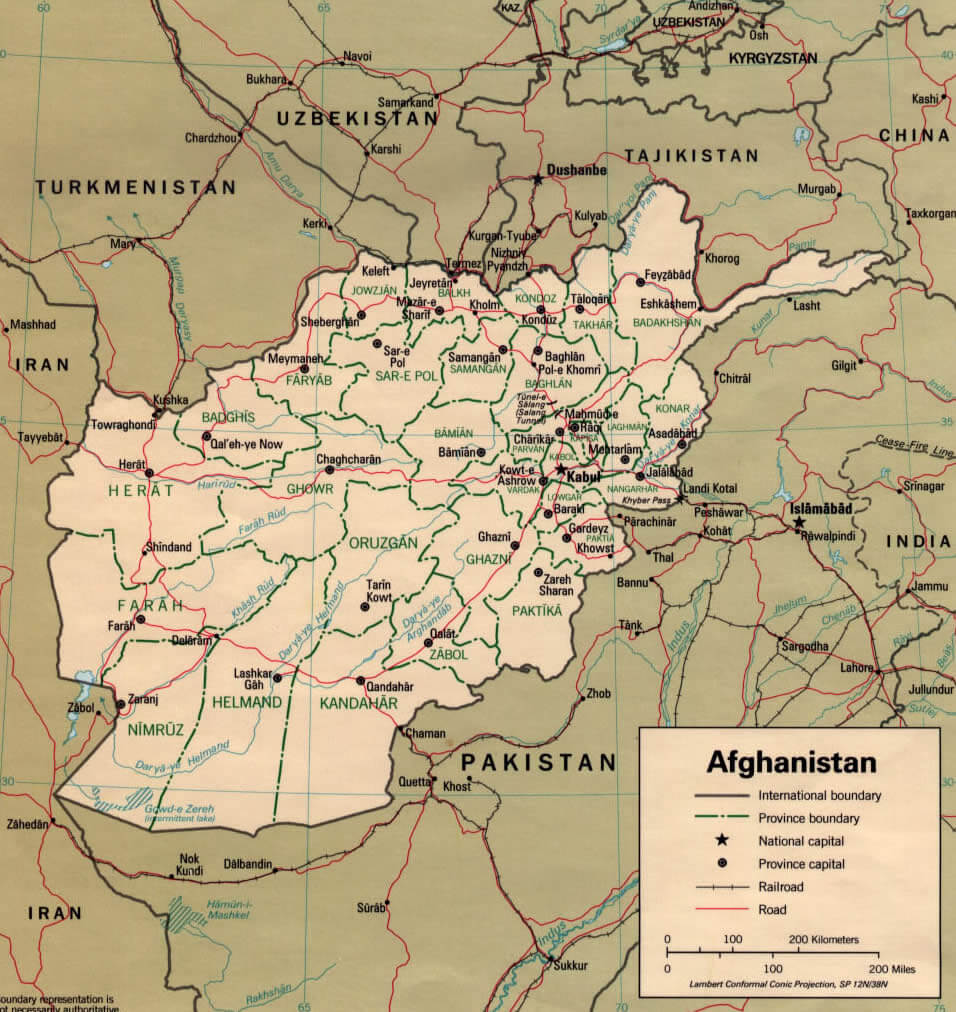
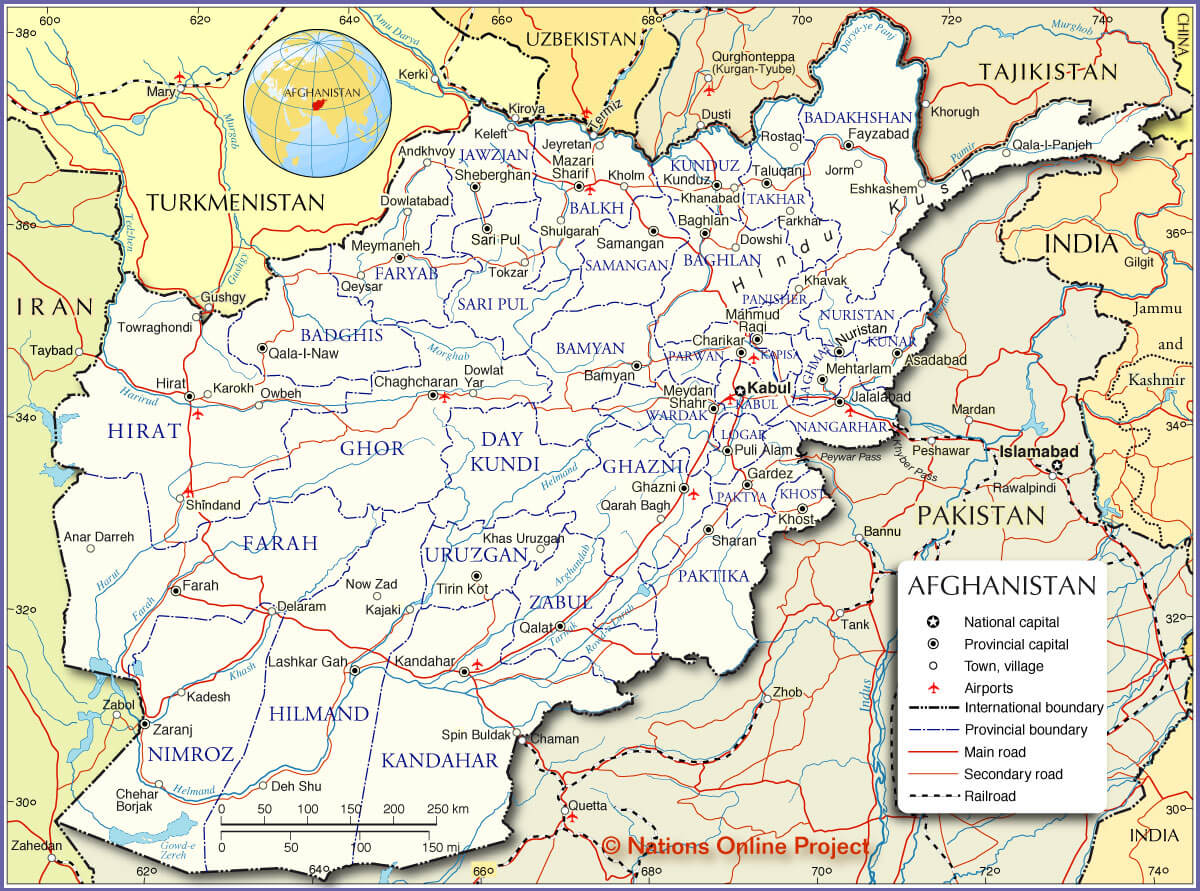
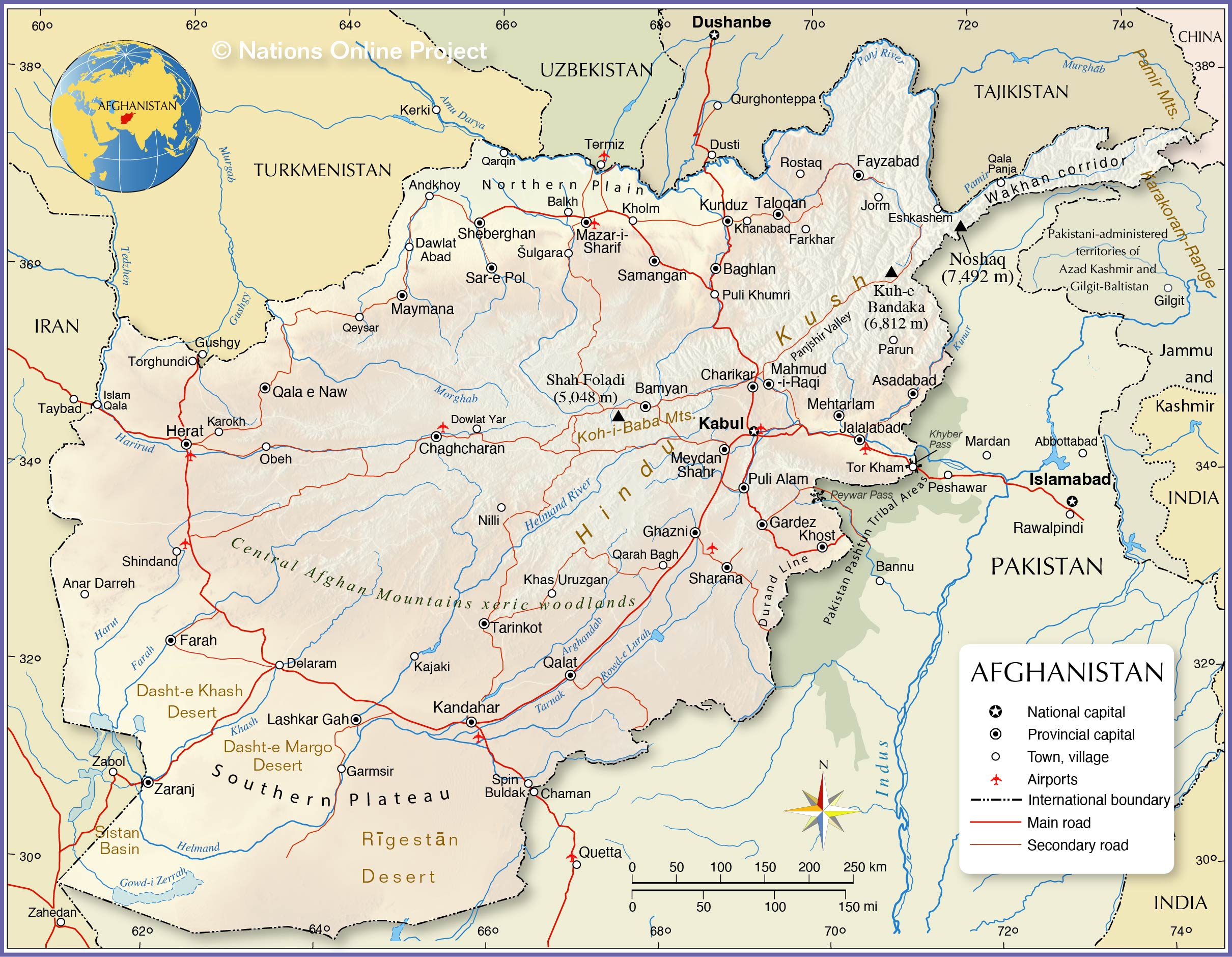
Afghanistan, a landlocked nation nestled in Central Asia, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes and cultures. Its political map, however, reflects a history marked by conflict, change, and the enduring struggle for stability. Understanding this map is crucial for grasping the complexities of Afghanistan’s past, present, and future.
The Foundations of Provincial Division:
Afghanistan’s current political map is divided into 34 provinces, each with its own administrative capital and governor. This division, while seemingly straightforward, is the result of a long and intricate process. The modern provincial structure has its roots in the Durrani Empire (1747-1929), which established a system of centralized governance with provincial units. This system was further refined during the reign of King Amanullah Khan (1919-1929), who aimed to modernize Afghanistan and create a more cohesive national identity.
However, the modern provincial map has been shaped by various factors, including historical boundaries, ethnic distribution, and geopolitical considerations. For example, the Pashtun-dominated provinces in the south and east have historically held greater political influence, while the northern provinces, with their diverse ethnicities, have often sought greater autonomy.
Beyond the Provincial Lines:
The provincial map, however, only tells part of the story. Within each province, there are numerous districts, each with its own administrative structure and local leadership. These districts often reflect the influence of specific tribes, clans, and ethnic groups, adding another layer of complexity to the Afghan political landscape.
Furthermore, the political landscape is further complicated by the existence of various non-state actors, including armed groups, militias, and warlords. These groups, often operating with considerable influence in specific regions, can challenge the authority of the central government and impact the dynamics within provinces.
Understanding the Significance:
The political map of Afghanistan is not merely a geographical representation; it is a reflection of the country’s power dynamics, cultural diversity, and historical complexities. Understanding the provinces, their demographics, and their historical significance is crucial for:
- Effective Governance: Understanding the unique challenges and needs of each province allows for tailored policies and development initiatives, fostering a more equitable and inclusive society.
- Conflict Resolution: Recognizing the power structures and historical grievances within each province can contribute to more effective conflict resolution strategies.
- Peacebuilding and Reconciliation: Understanding the political map can facilitate dialogue and negotiations between different communities, fostering trust and cooperation.
- Economic Development: Understanding the resource distribution and potential economic opportunities within each province can guide development plans and attract investment.
FAQs about Afghanistan’s Political Map:
Q: What are the largest provinces in Afghanistan?
A: The largest provinces by area are Helmand, Kandahar, and Nimroz in the south and east.
Q: What are the most ethnically diverse provinces?
A: Provinces like Balkh, Samangan, and Baghlan in the north are known for their diverse ethnic populations.
Q: How has the political map changed over time?
A: The map has undergone changes throughout history, with provinces being merged, divided, and renamed. Notably, the current map has been in place since the 1970s.
Q: How does the political map influence security and stability?
A: The map reflects the distribution of power and influence, which can influence the presence and activities of various armed groups.
Tips for Understanding Afghanistan’s Political Map:
- Focus on the Historical Context: Delve into the historical development of the provincial boundaries and their influence on current dynamics.
- Explore Ethnic and Tribal Distributions: Understand the diverse ethnic and tribal groups within each province and their significance in the political landscape.
- Consider the Influence of Non-State Actors: Recognize the presence and influence of various armed groups and their impact on provincial governance.
- Analyze the Economic and Resource Landscape: Understand the economic potential of each province and its role in national development.
Conclusion:
Afghanistan’s political map is a complex and dynamic entity, reflecting the country’s rich history, diverse cultures, and enduring challenges. By understanding the map’s historical context, its ethnic and tribal divisions, and the influence of non-state actors, we can gain a more nuanced perspective on the country’s political landscape. This understanding is crucial for promoting effective governance, conflict resolution, peacebuilding, and sustainable development in Afghanistan.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Provinces: Understanding Afghanistan’s Political Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!