A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Indo-European Language Family
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Indo-European Language Family
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Indo-European Language Family. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Indo-European Language Family
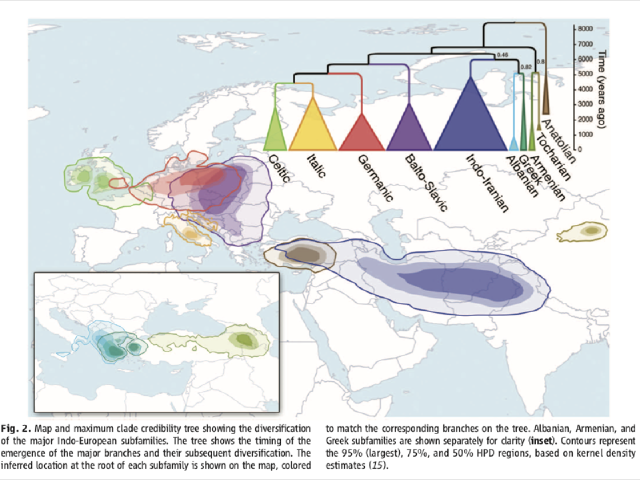
The Indo-European language family is a vast and intricate tapestry, woven together by shared ancestry and a complex history of migration, evolution, and interaction. Understanding this family requires a journey through time, tracing the paths of its branches across continents and millennia. A map of Indo-European languages serves as a powerful visual tool, offering a glimpse into the linguistic landscape of the world and revealing fascinating insights into the interconnectedness of human history and culture.
The Roots of a Linguistic Tree:
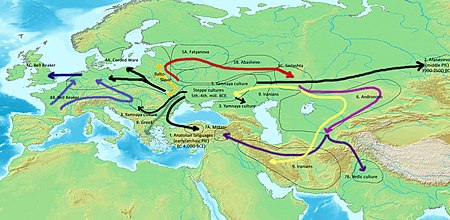
The Indo-European language family is believed to have originated in the Pontic-Caspian steppe, a vast expanse of grassland north of the Black Sea, around 4500 BCE. The Proto-Indo-European language, the ancestor of all Indo-European languages, was spoken by a nomadic people who eventually spread throughout Europe and parts of Asia. This expansion, fueled by factors such as population growth, climate change, and technological advancements, gave rise to the diverse branches of the family we see today.
A Visual Representation of Linguistic Diversity:
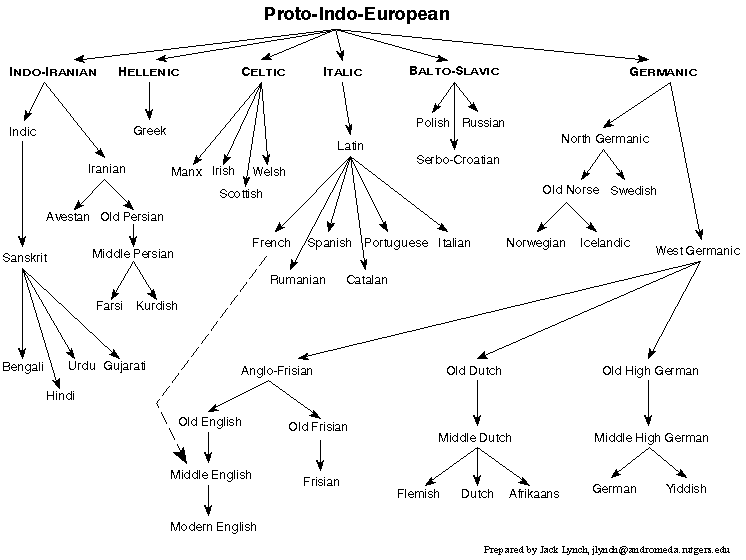
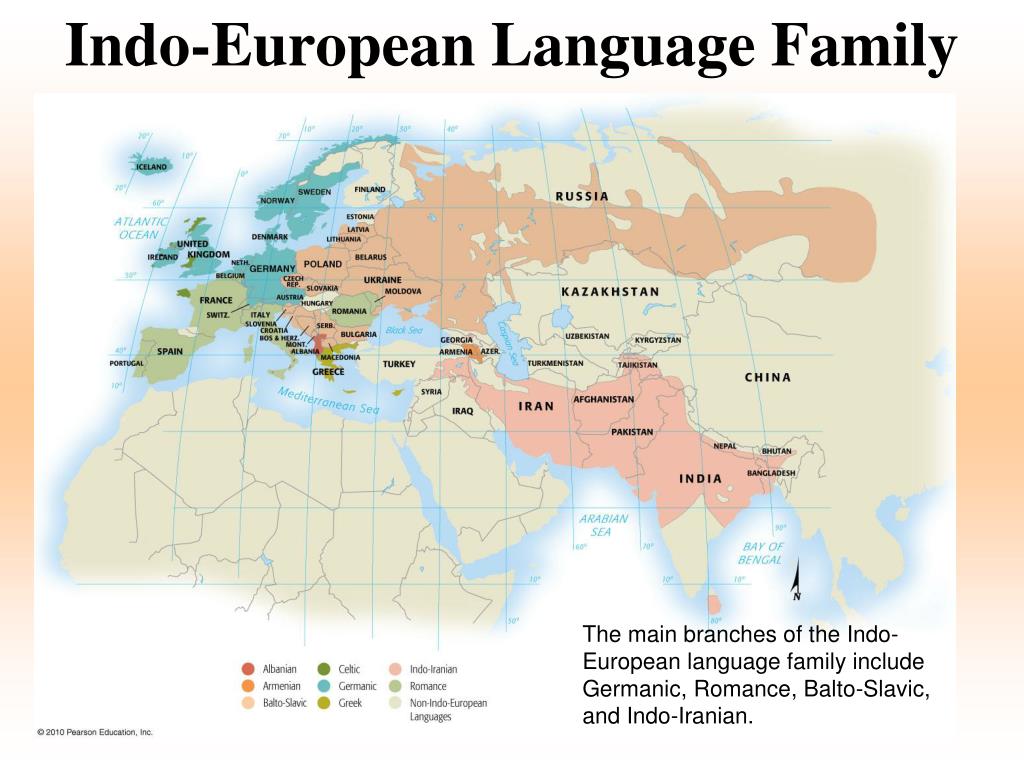
A map of Indo-European languages visually captures the geographical distribution of these branches, revealing the scope and complexity of the family. The map highlights the major branches, including:
- Indo-Iranian: This branch encompasses languages spoken in the Indian subcontinent, Iran, and parts of Central Asia. It includes languages such as Hindi, Urdu, Persian, Bengali, and Punjabi.
- Balto-Slavic: This branch includes languages spoken in Eastern and Central Europe, including Russian, Polish, Ukrainian, Czech, and Lithuanian.
- Germanic: This branch encompasses languages spoken in Northern and Western Europe, including English, German, Dutch, Swedish, and Norwegian.
- Italic: This branch includes languages spoken in the Italian peninsula, including Latin, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, French, and Romanian.
- Celtic: This branch includes languages spoken in parts of Western Europe, including Irish, Welsh, Scottish Gaelic, and Breton.
- Greek: This branch includes the modern Greek language, spoken in Greece and Cyprus.
- Anatolian: This branch, now extinct, included languages spoken in ancient Anatolia (modern Turkey), such as Hittite and Luwian.
The Significance of Linguistic Mapping:
The map of Indo-European languages serves a crucial role in understanding the evolution and spread of these languages. It reveals:
- Migration patterns: The geographical distribution of Indo-European languages offers valuable insights into the migration patterns of the Proto-Indo-European speakers and their descendants. By analyzing the location of related languages, linguists can reconstruct ancient migration routes and identify areas of cultural exchange.
- Language evolution: The map highlights the evolution of Indo-European languages over time. It showcases how languages have diverged and converged, influenced by geographical isolation, cultural contact, and linguistic borrowing.
- Cultural connections: The map underscores the interconnectedness of cultures within the Indo-European language family. It reveals how shared linguistic ancestry has fostered cultural exchange, transmission of knowledge, and the development of common literary traditions.
- Historical insights: The map provides valuable insights into the historical development of Europe and Asia. By analyzing the distribution of Indo-European languages, historians can reconstruct past political boundaries, identify areas of conflict and cooperation, and understand the spread of cultural practices and beliefs.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: How are the relationships between Indo-European languages determined?
A: Linguists use a variety of methods to determine the relationships between Indo-European languages, including:
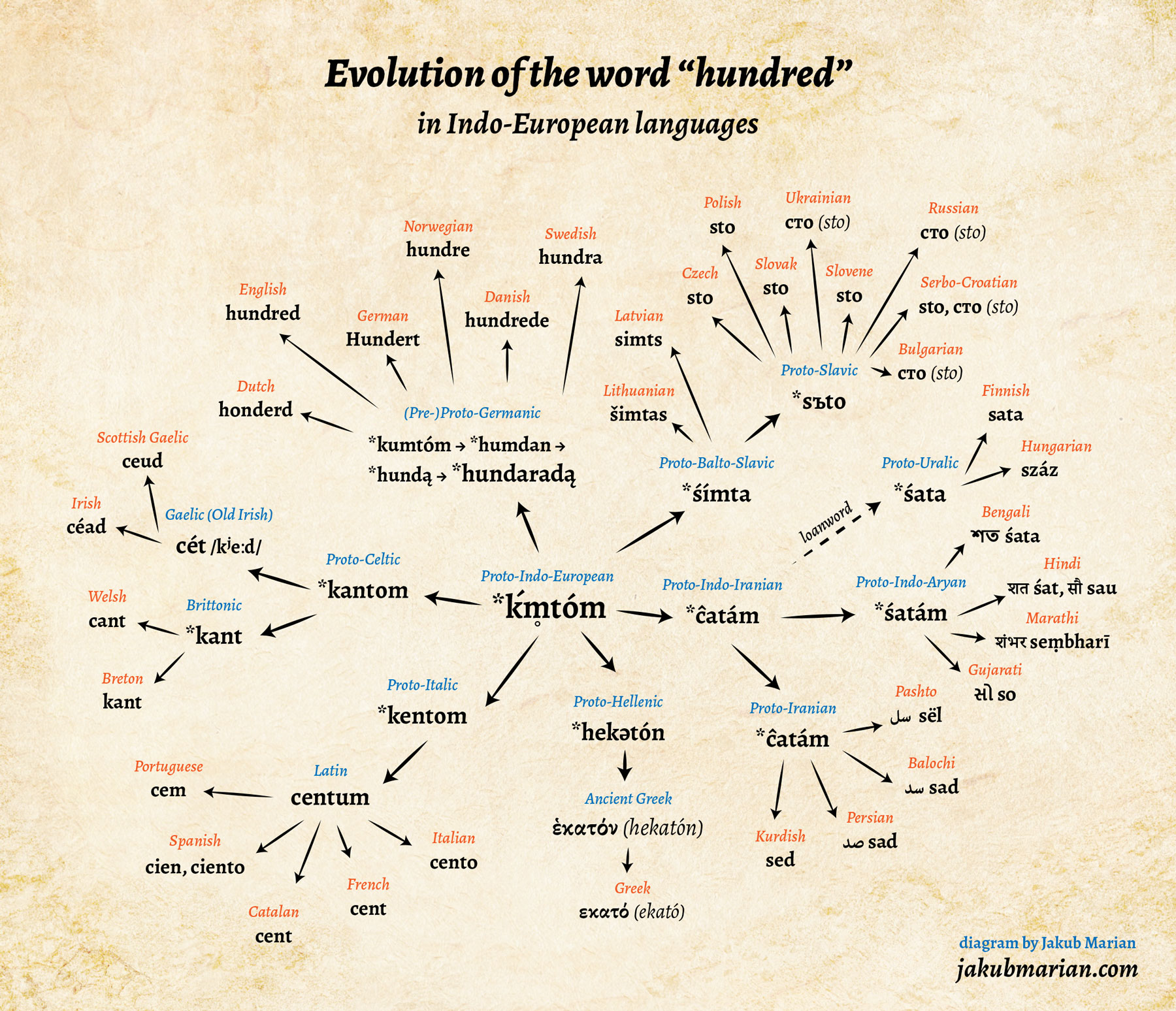
- Comparative linguistics: This method involves comparing the sounds, grammar, and vocabulary of different languages to identify shared features that point to a common ancestor.
- Historical linguistics: This method analyzes the historical development of languages, tracing their evolution over time and identifying points of divergence and convergence.
- Computational linguistics: This method uses computer algorithms to analyze large datasets of linguistic data, identifying patterns and relationships that may not be apparent to the human eye.
Q: What are some of the challenges in mapping Indo-European languages?
A: Mapping Indo-European languages presents several challenges:
- Extinct languages: Many ancient Indo-European languages are extinct, making it difficult to reconstruct their exact relationship to other languages.
- Language contact: Languages have often borrowed features from each other, blurring the lines between related and unrelated languages.
- Dialectal variation: Within a single language, there can be significant variation in dialects, making it difficult to define clear boundaries between languages.
- Political factors: Political boundaries and national identities can sometimes overshadow linguistic relationships, making it challenging to accurately represent the distribution of languages.
Q: What are some tips for understanding the map of Indo-European languages?
A: Here are some tips for navigating the map of Indo-European languages:
- Focus on the major branches: Begin by understanding the major branches of the Indo-European language family and their geographical distribution.
- Look for patterns: Observe how the distribution of languages reflects historical migration patterns, cultural exchange, and linguistic evolution.
- Consider language contact: Remember that languages have often interacted with each other, leading to borrowing and influence.
- Don’t be afraid to ask questions: Don’t hesitate to seek out additional information and resources to deepen your understanding of the map.
Conclusion:
The map of Indo-European languages is a powerful tool for understanding the interconnectedness of human history and culture. It allows us to trace the journey of a vast linguistic family across continents and millennia, revealing the complex interplay of migration, evolution, and cultural exchange. By studying the map, we gain insights into the origins of our languages, the history of our societies, and the shared heritage that unites us all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Indo-European Language Family. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!