A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Climate Map: Understanding the Diversity of Weather Patterns
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Climate Map: Understanding the Diversity of Weather Patterns
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Climate Map: Understanding the Diversity of Weather Patterns. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Climate Map: Understanding the Diversity of Weather Patterns

Canada, a vast and geographically diverse nation, experiences a wide range of climatic conditions. From the frigid Arctic to the temperate Pacific coast, the country’s climate map reveals a fascinating tapestry of weather patterns. This article delves into the intricacies of Canada’s climate map, highlighting its importance in understanding the nation’s diverse ecosystems, economic activities, and the challenges posed by climate change.
Understanding the Influence of Latitude and Topography
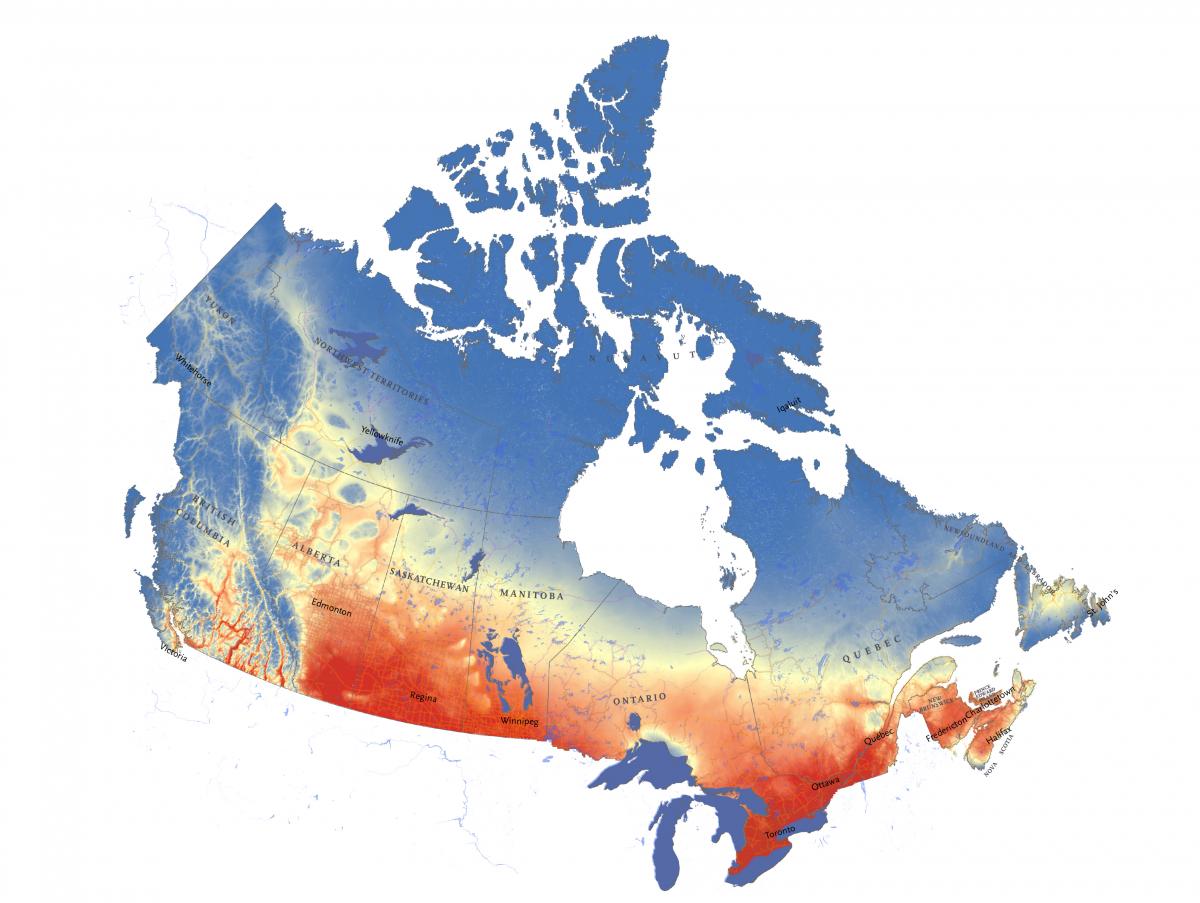
Canada’s climate is primarily shaped by its geographical location and topography. The country stretches over a vast expanse of latitude, from the Arctic Circle in the north to the 49th parallel in the south. This latitudinal gradient significantly influences the amount of solar radiation received, leading to distinct temperature variations across the country.
The Canadian Shield, a vast expanse of ancient rock, covers much of central Canada. This shield, along with the Rocky Mountains in the west, creates a complex topography that influences air circulation and precipitation patterns. The Rocky Mountains act as a barrier, forcing moist Pacific air to rise and cool, resulting in abundant precipitation on the western slopes. Conversely, the eastern slopes experience a rain shadow effect, receiving significantly less precipitation.
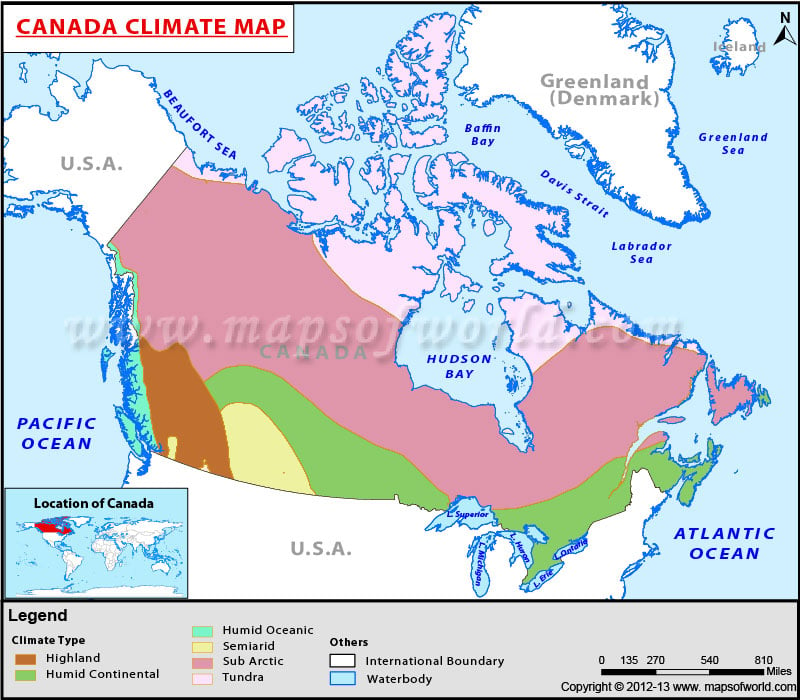
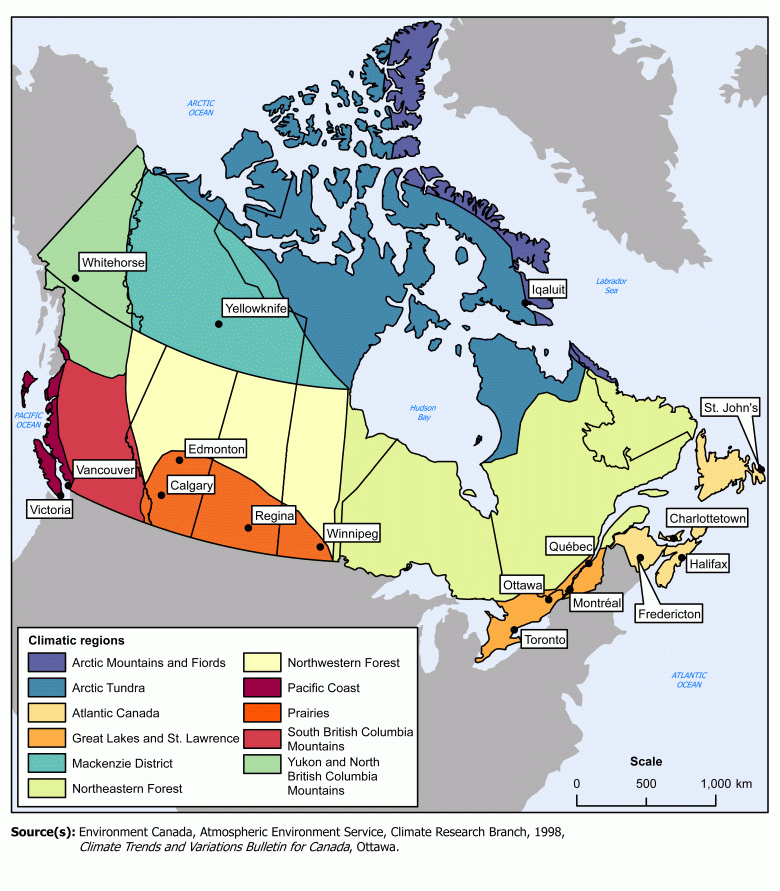
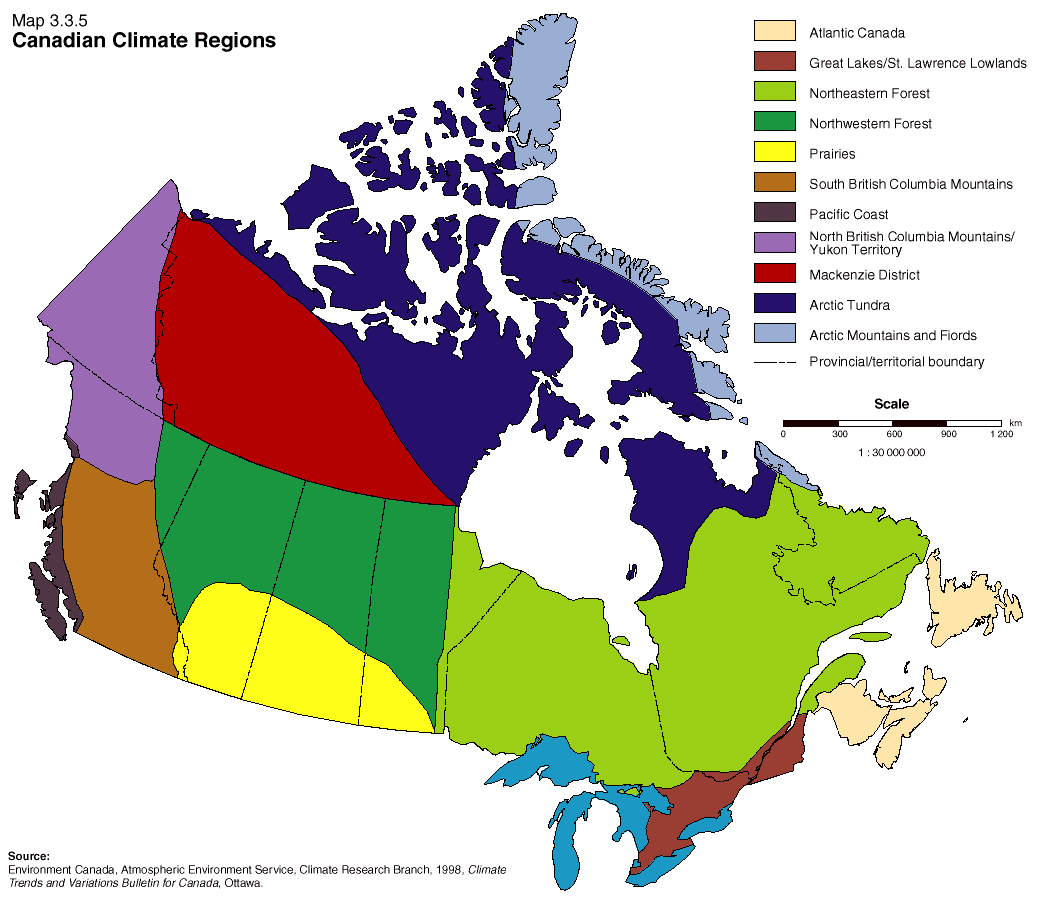
Key Climatic Regions and Their Characteristics
Canada’s climate map can be broadly divided into several distinct regions, each with its unique characteristics:
1. Arctic and Subarctic Regions: Encompassing the northernmost territories, this region is characterized by extremely cold temperatures, permafrost, and low precipitation. The long, dark winters and short, cool summers support a unique ecosystem of tundra and boreal forests.
2. Boreal Forest Region: This vast region stretches across central and eastern Canada, dominated by coniferous forests. The climate is characterized by cold winters, warm but short summers, and moderate precipitation. The boreal forest plays a crucial role in regulating the global carbon cycle and provides valuable timber resources.
3. Prairie Region: Located in the heart of Canada, the prairies experience a semi-arid climate with hot summers and cold winters. The region receives moderate precipitation, mainly in the form of thunderstorms. The prairies are known for their vast grasslands and agricultural potential.
4. Great Lakes Region: The Great Lakes region enjoys a humid continental climate with warm summers and cold, snowy winters. The proximity to the Great Lakes moderates temperatures and increases precipitation, creating a favorable environment for agriculture and forestry.
5. Pacific Maritime Region: This region along the west coast experiences a temperate climate with mild winters and warm, dry summers. The influence of the Pacific Ocean moderates temperatures, resulting in a relatively stable climate with abundant precipitation. The region is known for its lush rainforests and diverse ecosystems.
6. Atlantic Region: The Atlantic region experiences a humid continental climate with warm, humid summers and cold, snowy winters. The influence of the Atlantic Ocean moderates temperatures and brings frequent precipitation. The region is known for its coastal beauty and rich maritime history.
Climate Change and its Impacts
Canada’s climate map is not static; it is undergoing significant changes due to global warming. The country is experiencing a warming trend, with average temperatures increasing at a faster rate than the global average. This warming trend is leading to several impacts, including:
- Rising temperatures: The average temperature across Canada has increased by approximately 1.7 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century. This warming trend is projected to continue, with significant implications for human health, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
- Melting glaciers and permafrost: The warming climate is causing glaciers and permafrost to melt at an accelerated rate. This melting is leading to rising sea levels, changes in water availability, and the release of greenhouse gases trapped in permafrost.
- Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events: Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and wildfires. These events pose significant risks to human life, property, and the environment.
- Changes in vegetation patterns: The warming climate is causing changes in vegetation patterns across Canada. Some plant species are shifting their ranges northward, while others are struggling to adapt to the changing conditions.
The Importance of Understanding Canada’s Climate Map
Understanding Canada’s climate map is crucial for a multitude of reasons:
- Managing natural resources: The climate map provides valuable insights into the distribution of natural resources, such as forests, water, and minerals. This information is essential for sustainable resource management and economic development.
- Planning infrastructure and development: Knowledge of the climate map is crucial for planning infrastructure and development projects. For example, understanding the risk of extreme weather events is essential for designing buildings and transportation systems that can withstand the impacts of climate change.
- Protecting human health: The climate map helps us understand the potential health risks associated with different climatic conditions. This information is vital for developing public health strategies and ensuring the well-being of Canadians.
- Adapting to climate change: The climate map provides a baseline for understanding the impacts of climate change and developing adaptation strategies. This knowledge is essential for mitigating the risks associated with climate change and building a more resilient future.
FAQs about Canada’s Climate Map
Q1: What is the warmest region in Canada?
A: The warmest region in Canada is the Pacific Maritime Region, which enjoys a temperate climate with mild winters and warm, dry summers.
Q2: What is the coldest region in Canada?
A: The coldest region in Canada is the Arctic and Subarctic Region, characterized by extremely cold temperatures, permafrost, and low precipitation.
Q3: What is the wettest region in Canada?
A: The wettest region in Canada is the Pacific Maritime Region, which receives abundant precipitation due to the influence of the Pacific Ocean.
Q4: What is the driest region in Canada?
A: The driest region in Canada is the Prairie Region, which experiences a semi-arid climate with moderate precipitation.
Q5: How is climate change impacting Canada’s climate map?
A: Climate change is causing a warming trend across Canada, with average temperatures increasing at a faster rate than the global average. This warming trend is leading to several impacts, including rising temperatures, melting glaciers and permafrost, increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, and changes in vegetation patterns.
Tips for Understanding Canada’s Climate Map
- Consult reliable sources: Utilize reputable sources like Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) for accurate and up-to-date information on Canada’s climate map.
- Explore interactive maps: Utilize interactive online maps provided by ECCC and other organizations to visualize climate data and understand regional variations.
- Stay informed about climate change: Keep abreast of the latest scientific findings on climate change and its impacts on Canada’s climate.
- Engage in climate action: Support initiatives aimed at mitigating climate change and adapting to its impacts.
Conclusion
Canada’s climate map is a complex and dynamic representation of the nation’s diverse weather patterns. Understanding this map is crucial for managing natural resources, planning infrastructure and development, protecting human health, and adapting to the challenges posed by climate change. By embracing a comprehensive understanding of Canada’s climate, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for all Canadians.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Canada’s Climate Map: Understanding the Diversity of Weather Patterns. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!